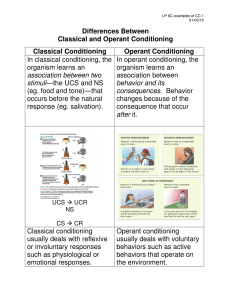
Differences Between Classical and Operant Conditioning Classical
... organism learns an association between two stimuli—the UCS and NS (eg. food and tone)—that occurs before the natural response (eg. salivation). ...
... organism learns an association between two stimuli—the UCS and NS (eg. food and tone)—that occurs before the natural response (eg. salivation). ...
Types of Conditioning
... behavior of small children in response to the sight of certain fast-food restaurants and their signs. In reality, neither the signs themselves nor their actual shape have anything to do with the food they serve, yet to the parent, children seem to become instantly hungry whenever they spot such a si ...
... behavior of small children in response to the sight of certain fast-food restaurants and their signs. In reality, neither the signs themselves nor their actual shape have anything to do with the food they serve, yet to the parent, children seem to become instantly hungry whenever they spot such a si ...
Conditioning: classical and operant
... The principle of classical conditioning is based on the fact that certain stimuli (unconditioned stimuli) automatically elicit certain responses without learning (unconditioned responses). Humans exhibit many reflexes that are not learned behaviors. For example, when exposed to our favorite foods, w ...
... The principle of classical conditioning is based on the fact that certain stimuli (unconditioned stimuli) automatically elicit certain responses without learning (unconditioned responses). Humans exhibit many reflexes that are not learned behaviors. For example, when exposed to our favorite foods, w ...
Observational Learning - Social Studies with Mrs. Gabehart
... 12. In classical conditioning, the stimulus that is originally neutral in regard to the response to be learned is the a) unconditioned stimulus b) unconditioned response c) conditioned stimulus d) conditioned response ...
... 12. In classical conditioning, the stimulus that is originally neutral in regard to the response to be learned is the a) unconditioned stimulus b) unconditioned response c) conditioned stimulus d) conditioned response ...
Classical Conditioning
... o Classical Conditioning: Initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus Neutral stimulus begins triggering conditioned response o Operant Conditioning: The strengthening of a reinforced response o Neutral stimulus should come (.5 seconds) before the uncondition ...
... o Classical Conditioning: Initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus Neutral stimulus begins triggering conditioned response o Operant Conditioning: The strengthening of a reinforced response o Neutral stimulus should come (.5 seconds) before the uncondition ...
Lesson 1: Attributes of Learning and Classical Conditioning
... studying on a VI schedule. c. Responding on a VI schedule tends to be steady and at a moderate rate. 5. Typical response patterns for the intermittent schedules of reinforcement: II. Aversive conditioning is training with stimuli not desired by the organism. A. Punishment (see Lesson 3.II.D.3) 1. T ...
... studying on a VI schedule. c. Responding on a VI schedule tends to be steady and at a moderate rate. 5. Typical response patterns for the intermittent schedules of reinforcement: II. Aversive conditioning is training with stimuli not desired by the organism. A. Punishment (see Lesson 3.II.D.3) 1. T ...
Learned behavior
... of learning. Traditionally learning was defined as any relatively permanent in behavior that results from past experience. However, because learned responses are not always performed, some psychologists prefer to define learning as any relatively permanent change in behavior or mental processes that ...
... of learning. Traditionally learning was defined as any relatively permanent in behavior that results from past experience. However, because learned responses are not always performed, some psychologists prefer to define learning as any relatively permanent change in behavior or mental processes that ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely ...
... Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely ...
Learning ppt
... carcasses laced with nauseainducing poison; developed aversion to sheep meat • wolves penned with sheep later seemed to fear it! ...
... carcasses laced with nauseainducing poison; developed aversion to sheep meat • wolves penned with sheep later seemed to fear it! ...
Operant Conditioning
... “Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire” Tally up the Yes responses of odd and even numbers: ...
... “Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire” Tally up the Yes responses of odd and even numbers: ...
Behavior handout
... Animal Behavior • Action or re-action to stimuli • Happens in the brain (non-motor) and can be manifested through muscular response, but often involves both • There can be a temporal component to the actual behavior (learning) • Short-term trigger for behavior, or effect on the organism • Long-term ...
... Animal Behavior • Action or re-action to stimuli • Happens in the brain (non-motor) and can be manifested through muscular response, but often involves both • There can be a temporal component to the actual behavior (learning) • Short-term trigger for behavior, or effect on the organism • Long-term ...
Powerpoint
... Does misbehavior result from operant food reinforcement or classical conditioning? Timberlake’s appetitive structure view – both kinds of learning contribute to animal misbehavior. ...
... Does misbehavior result from operant food reinforcement or classical conditioning? Timberlake’s appetitive structure view – both kinds of learning contribute to animal misbehavior. ...
Fall 2015 10-6 Chapter 7 Pt 2
... pigeon to peck to obtain food, but not to flap its wings to obtain food. Or to teach cats tricks that involve leaping high and landing on their feet! ...
... pigeon to peck to obtain food, but not to flap its wings to obtain food. Or to teach cats tricks that involve leaping high and landing on their feet! ...
Notes-Undergrad-Child-Psychopath-Wk1Day2
... and diseases occur in human populations, and with factors that influence these patterns of occurrence. Three interrelated components of epidemiological research involve: 1. Assessing the occurrence of new cases (incidence rate) or existing cases (prevalence rate) of the disorder at a given period of ...
... and diseases occur in human populations, and with factors that influence these patterns of occurrence. Three interrelated components of epidemiological research involve: 1. Assessing the occurrence of new cases (incidence rate) or existing cases (prevalence rate) of the disorder at a given period of ...
AP Psychology Learning PPT
... Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely ...
... Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely ...
Classical Conditioning - Anoka
... • Punishment can effectively control certain behaviors. • Especially useful if teaching a child not to do a dangerous behavior • Most still suggest reinforcing an incompatible behavior rather than using punishment ...
... • Punishment can effectively control certain behaviors. • Especially useful if teaching a child not to do a dangerous behavior • Most still suggest reinforcing an incompatible behavior rather than using punishment ...
Learning - McMurray VMC
... the unconditioned stimulus no longer followed the conditioned stimulus? When the US (food) does not follow the CS (tone), CR (salivation) begins to decrease and eventually causes extinction. ...
... the unconditioned stimulus no longer followed the conditioned stimulus? When the US (food) does not follow the CS (tone), CR (salivation) begins to decrease and eventually causes extinction. ...
5 - smw15.org
... Invisible Fencing technique applies WatsonMowrer theory of conditioning Potential to provoke aggression is a concern Treatment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Stimulus extinction and response prevention have been used to treat these individuals Usually combined with other methods ...
... Invisible Fencing technique applies WatsonMowrer theory of conditioning Potential to provoke aggression is a concern Treatment of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Stimulus extinction and response prevention have been used to treat these individuals Usually combined with other methods ...
LEARNING PSY 381, 4 credits, FALL 2015 15:20
... learning and behavior. It will emphasize the theories and learning styles about cognitive behavior analysis, and to teach the different propositions about behavioral and cognitive theories of learning, the objectives and methods of scientific experiments with their results, their contributions to th ...
... learning and behavior. It will emphasize the theories and learning styles about cognitive behavior analysis, and to teach the different propositions about behavioral and cognitive theories of learning, the objectives and methods of scientific experiments with their results, their contributions to th ...
PSYCHOLOGY
... Stage 1 – characterized by avoidance of punishment Stage 2 – characterized by a desire to further one’s own ...
... Stage 1 – characterized by avoidance of punishment Stage 2 – characterized by a desire to further one’s own ...
What are the link`s between Thorndike`s Associationist theories and
... what is being discussed. However, the success of operant and classical conditioning are rampant in the homes of our students, so it is engrained into their minds (or actions) that they are to be rewarded when they do things correctly. For example, parents in some ...
... what is being discussed. However, the success of operant and classical conditioning are rampant in the homes of our students, so it is engrained into their minds (or actions) that they are to be rewarded when they do things correctly. For example, parents in some ...
Chapter 5: Learning - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... Studied animals to see if they utilized reasoning to solve problems He determined that a cats’ learning is based on a trial and error bases Law of Effect—learning principle proposed by Thorndike that proposes that responses followed by a satisfying effect become strengthened and are more likely to r ...
... Studied animals to see if they utilized reasoning to solve problems He determined that a cats’ learning is based on a trial and error bases Law of Effect—learning principle proposed by Thorndike that proposes that responses followed by a satisfying effect become strengthened and are more likely to r ...
Learning - pressthebar
... • Through conditioning Baby Hannah smiles and laughs at the title screen with dark background and white writing that precedes a funny song and cartoon on her “Merrytubbies” video tape. Her parents notice that she also smiles and giggles at the FBI Warning screen appearing on movie ...
... • Through conditioning Baby Hannah smiles and laughs at the title screen with dark background and white writing that precedes a funny song and cartoon on her “Merrytubbies” video tape. Her parents notice that she also smiles and giggles at the FBI Warning screen appearing on movie ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.























