Okami Study Guide
... though they learn a great many things for which they were not biologically prepared. 3. Habituation and sensitization are the simplest forms of learning. Habituation occurs when a stimulus at first causes a strong response, but due to repeated exposure over time response is lessened. Sensitization o ...
... though they learn a great many things for which they were not biologically prepared. 3. Habituation and sensitization are the simplest forms of learning. Habituation occurs when a stimulus at first causes a strong response, but due to repeated exposure over time response is lessened. Sensitization o ...
Learning Jeopardy
... The tendency for subjects to respond to stimuli similar to the conditioned stimuli. ...
... The tendency for subjects to respond to stimuli similar to the conditioned stimuli. ...
Learning - Forensic Consultation
... map (a mental image of a threedimensional space). They also displayed latent learning (hidden learning that exists without behavioral signs). ...
... map (a mental image of a threedimensional space). They also displayed latent learning (hidden learning that exists without behavioral signs). ...
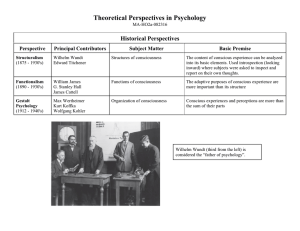
Theoretical Perspectives in Psychology
... Unconscious motives and experiences in early childhood govern personality and mental disorders. ...
... Unconscious motives and experiences in early childhood govern personality and mental disorders. ...
AP Psychology – Leaning Practice Choose the best response to
... A) discrimination B) generalization C) intermittent reinforcement D) shaping E) cognitive processes 11.Paul and Michael sell magazine subscriptions by telephone. Paul is paid $1.00 for every 5 calls he makes, while Michael is paid 1 dollar for every subscription he sells, regardless of the number of ...
... A) discrimination B) generalization C) intermittent reinforcement D) shaping E) cognitive processes 11.Paul and Michael sell magazine subscriptions by telephone. Paul is paid $1.00 for every 5 calls he makes, while Michael is paid 1 dollar for every subscription he sells, regardless of the number of ...
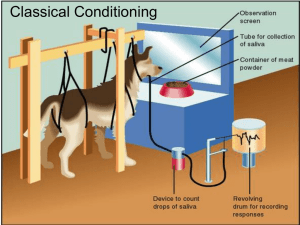
Classical Conditioning
... e. Temporal conditioning – Occurs when the nominal CS is a fixed period of time between presentations of the UCS/US – Combined with trace conditioning based on a period of time • i.e. dog starts to salivate at 7:59am because s/he is fed at 8am everyday ...
... e. Temporal conditioning – Occurs when the nominal CS is a fixed period of time between presentations of the UCS/US – Combined with trace conditioning based on a period of time • i.e. dog starts to salivate at 7:59am because s/he is fed at 8am everyday ...
avoidance behavior
... The Discriminated Avoidance Procedure • A warning stimulus (e.g., a light) signals a forthcoming shock. • If the required response is made during the light (warning stimulus), before the shock occurs, the subject avoids the shock. • If a response is not made during the warning stimulus of the light ...
... The Discriminated Avoidance Procedure • A warning stimulus (e.g., a light) signals a forthcoming shock. • If the required response is made during the light (warning stimulus), before the shock occurs, the subject avoids the shock. • If a response is not made during the warning stimulus of the light ...
psycholanalytic theory
... • Punishment is an unpleasant stimulus that suppresses behavior. • Punishment is often used because it can quickly suppress behavior. However, psychologists suggest utilizing reinforcement due to the inherent weaknesses of punishment. ...
... • Punishment is an unpleasant stimulus that suppresses behavior. • Punishment is often used because it can quickly suppress behavior. However, psychologists suggest utilizing reinforcement due to the inherent weaknesses of punishment. ...
Conditioning and Learning - Kellogg Community College
... made after a certain amount of time has elapsed is reinforced; produces moderate response rates. • Variable Interval Schedule (VI): Reinforcement is given for the first correct response made after a varied amount of time ...
... made after a certain amount of time has elapsed is reinforced; produces moderate response rates. • Variable Interval Schedule (VI): Reinforcement is given for the first correct response made after a varied amount of time ...
نموذج حذف وإضافة
... Operant crying can by controlled: If parents wait until the child’s crying reaches a certain intensity → loud crying is more likely to appear in the future. If parents ignore crying → the absence of reinforcers will extinguish the behavior. Punishment is a wrong way to deal with negative reinforcers ...
... Operant crying can by controlled: If parents wait until the child’s crying reaches a certain intensity → loud crying is more likely to appear in the future. If parents ignore crying → the absence of reinforcers will extinguish the behavior. Punishment is a wrong way to deal with negative reinforcers ...
07Learning
... Dogs given inescapable shock did nothing to escape the shock when later given the opportunity for escape. Dogs given inescapable shock did escape the shock when later given the opportunity for escape. Dogs given inescapable shock later became aggressive when given the opportunity for escape. Dogs gi ...
... Dogs given inescapable shock did nothing to escape the shock when later given the opportunity for escape. Dogs given inescapable shock did escape the shock when later given the opportunity for escape. Dogs given inescapable shock later became aggressive when given the opportunity for escape. Dogs gi ...
Option E - OoCities
... Operant conditioning is behavior that develops as a result of the association of reinforcement with a particular response, on a proportion of occasions. ...
... Operant conditioning is behavior that develops as a result of the association of reinforcement with a particular response, on a proportion of occasions. ...
CB4 - FA1 IIPM
... Reinforcement and punishment, the core tools of operant conditioning, are either positive (delivered following a response), or negative (withdrawn following a response). This creates a total of four basic consequences, with the addition of a fifth procedure known as extinction (i.e. no change in con ...
... Reinforcement and punishment, the core tools of operant conditioning, are either positive (delivered following a response), or negative (withdrawn following a response). This creates a total of four basic consequences, with the addition of a fifth procedure known as extinction (i.e. no change in con ...
Behaviorism
... The Law of Effect • referred to his approach to learning as connectionism, hypothesized that an organism learned about connections between situations and types of responses. • one of the first to hypothesize that “if all of these (responses & situational variables) could be analyzed” man could be t ...
... The Law of Effect • referred to his approach to learning as connectionism, hypothesized that an organism learned about connections between situations and types of responses. • one of the first to hypothesize that “if all of these (responses & situational variables) could be analyzed” man could be t ...
Contemporary Perspectives on Abnormal Behavior The Biological
... • Unconditioned stimulus - A stimulus that elicits an unlearned response. • Unconditioned response - An unlearned response. • Conditioned stimulus - A previously neutral stimulus that evokes a conditioned response after repeated pairings with an unconditioned stimulus that had previously evoked t ...
... • Unconditioned stimulus - A stimulus that elicits an unlearned response. • Unconditioned response - An unlearned response. • Conditioned stimulus - A previously neutral stimulus that evokes a conditioned response after repeated pairings with an unconditioned stimulus that had previously evoked t ...
Chapter 4 practice
... 2. The hypnic jerk typically occurs during a. NREM stage 1. b. NREM stage 2. c. REM stage 3. d. REM sleep. 3. Which of the following is not true of hypnosis? a. can be used for pain relief b. can produce increases in strength c. can affect one’s sensory perception d. cannot make a person do somethi ...
... 2. The hypnic jerk typically occurs during a. NREM stage 1. b. NREM stage 2. c. REM stage 3. d. REM sleep. 3. Which of the following is not true of hypnosis? a. can be used for pain relief b. can produce increases in strength c. can affect one’s sensory perception d. cannot make a person do somethi ...
File - AP Psychology
... • Cat’s used ‘trial and error’ to escape box and get food • Voluntary behavior changes because of its consequences: • Pleasant consequences strengthen behavior • Unpleasant consequences weaken behavior • Behaviors followed by positive outcomes are strengthened and behaviors followed by negative outc ...
... • Cat’s used ‘trial and error’ to escape box and get food • Voluntary behavior changes because of its consequences: • Pleasant consequences strengthen behavior • Unpleasant consequences weaken behavior • Behaviors followed by positive outcomes are strengthened and behaviors followed by negative outc ...
Superstition in the Pigeon
... or brushing movements directed toward but not touching the floor. None of these responses appeared in any noticeable strength during adaptation to the cage or until the food hopper was periodically presented. ...
... or brushing movements directed toward but not touching the floor. None of these responses appeared in any noticeable strength during adaptation to the cage or until the food hopper was periodically presented. ...
`Superstition` in the Pigeon
... incomplete pecking or brushing movements directed toward but not touching the floor. None of these responses appeared in any noticeable strength during adaptation to the cage or until the food hopper was periodically presented. In the remaining two cases, conditioned responses were not clearly marke ...
... incomplete pecking or brushing movements directed toward but not touching the floor. None of these responses appeared in any noticeable strength during adaptation to the cage or until the food hopper was periodically presented. In the remaining two cases, conditioned responses were not clearly marke ...
File
... o Neutral stimulus – a stimulus that does not initially elicit any part of an unconditioned response o Unconditioned stimulus (US) – an event that elicits a certain predictable response typically without previous training o Unconditioned response (UR) – an organism’s automatic (or natural) reaction ...
... o Neutral stimulus – a stimulus that does not initially elicit any part of an unconditioned response o Unconditioned stimulus (US) – an event that elicits a certain predictable response typically without previous training o Unconditioned response (UR) – an organism’s automatic (or natural) reaction ...
AP Psychology Crib Notes
... c) Confounding variable – other variables that may influence results d) Experiment group – exposed to manipulation of independent variable e) Control group – an unaffected comparison group f) Subject bias – a subject’s behavior changes due to believed expectations of experiment g) Researcher bias – ...
... c) Confounding variable – other variables that may influence results d) Experiment group – exposed to manipulation of independent variable e) Control group – an unaffected comparison group f) Subject bias – a subject’s behavior changes due to believed expectations of experiment g) Researcher bias – ...
Learning - ISA
... Salivation is an involuntary reflex, while sitting up and rolling over are far more complex responses that we think of as voluntary. ...
... Salivation is an involuntary reflex, while sitting up and rolling over are far more complex responses that we think of as voluntary. ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.