Chapter 11: Behaviorism: After the Founding
... Positive punishment: application of an aversive stimulus that decreases the likelihood that a behavior will reoccur Negative punishment: withdrawal of a pleasurable stimulus that decreases the likelihood that a behavior will reoccur ...
... Positive punishment: application of an aversive stimulus that decreases the likelihood that a behavior will reoccur Negative punishment: withdrawal of a pleasurable stimulus that decreases the likelihood that a behavior will reoccur ...
Animal Behavior Study Guide
... why it is adaptive to the moths. c. Competing Stimuli - examples of how the brain may selectively tune out certain signals or handle competing signals in a hierarchical fashion. d. Central Pattern Generators – such as the one worked out in the sea slug, Tritonia. You don’t need to know ...
... why it is adaptive to the moths. c. Competing Stimuli - examples of how the brain may selectively tune out certain signals or handle competing signals in a hierarchical fashion. d. Central Pattern Generators – such as the one worked out in the sea slug, Tritonia. You don’t need to know ...
File - Justin Daigle, MA, BCBA, LBA
... and decided to take it a step futhur. • Instead of cats and puzzle boxes, Skinner used rats and Skinner boxes. • Coined the terms like reinforcement and punishment • Started thinking about how these prinicples could be applied ...
... and decided to take it a step futhur. • Instead of cats and puzzle boxes, Skinner used rats and Skinner boxes. • Coined the terms like reinforcement and punishment • Started thinking about how these prinicples could be applied ...
Slide 1
... Electrodes are placed on the patient’s head, over the temporal lobes of the brain. Anesthetics and muscle relaxants help minimize discomfort to the patient. Then an electric current is delivered for about one second. The patient has a convulsive seizure and becomes unconscious, awakening after about ...
... Electrodes are placed on the patient’s head, over the temporal lobes of the brain. Anesthetics and muscle relaxants help minimize discomfort to the patient. Then an electric current is delivered for about one second. The patient has a convulsive seizure and becomes unconscious, awakening after about ...
- W.W. Norton
... c. Apply the principles of acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination. Extend these five concepts to the classical conditioning situation you described in Reading Activity 6.2(b). (Complete this activity below.) d. Analyze the acquisition of a phobia and counte ...
... c. Apply the principles of acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination. Extend these five concepts to the classical conditioning situation you described in Reading Activity 6.2(b). (Complete this activity below.) d. Analyze the acquisition of a phobia and counte ...
Sign Tracking (Autoshaping)
... students/assistants noticed a funny thing – Dogs would salivate when he put the food powder in their mouths. – But experienced dogs would salivate when the experimenter walked in the room or at the sight of food – They called this "psychic secretions" which are responses that occur in advance of get ...
... students/assistants noticed a funny thing – Dogs would salivate when he put the food powder in their mouths. – But experienced dogs would salivate when the experimenter walked in the room or at the sight of food – They called this "psychic secretions" which are responses that occur in advance of get ...
Positive Reinforcement - Medford School District
... Positive Reinforcement is a technique used by Parents and Caregivers to modify their children's behavior by reinforcing desired behaviors. This technique has proven effective for parents, teachers, coaches, leaders, and anyone responsible for a child or group of children. The fact that it does not u ...
... Positive Reinforcement is a technique used by Parents and Caregivers to modify their children's behavior by reinforcing desired behaviors. This technique has proven effective for parents, teachers, coaches, leaders, and anyone responsible for a child or group of children. The fact that it does not u ...
The three major parts of a neuron are the ______.
... B) a previously extinguished response C) an extinct instinct D) a forgotten stimulus-response sequence ...
... B) a previously extinguished response C) an extinct instinct D) a forgotten stimulus-response sequence ...
Structuralism and Functionalism
... Sigmund Freud’s philosophy. Man processes early childhood experiences as a reference for behaviors ...
... Sigmund Freud’s philosophy. Man processes early childhood experiences as a reference for behaviors ...
PSYC 100 Chapter 7
... How is operant conditioning different than classical conditioning? Classical conditioning forms association between stimuli. It involves respondent behavior – actions that are automatic responses to stimuli In operant conditioning, organisms associate their own actions with consequences. ...
... How is operant conditioning different than classical conditioning? Classical conditioning forms association between stimuli. It involves respondent behavior – actions that are automatic responses to stimuli In operant conditioning, organisms associate their own actions with consequences. ...
Beyond Freedom and Dignity
... aversions to non-painful events that lead to pain. Reinforcing events modify behavior, if positive by making it more likely, if negative, by making the behavior less likely. This behavior modification is called operant conditioning. Aversive control (spanking, punishments) have been the dominant pat ...
... aversions to non-painful events that lead to pain. Reinforcing events modify behavior, if positive by making it more likely, if negative, by making the behavior less likely. This behavior modification is called operant conditioning. Aversive control (spanking, punishments) have been the dominant pat ...
Learning Theory and Development of Social
... response will only occur to very specific stimuli. This can be taken a step further: if a CS is presented repeatedly without the UCS then eventually the CR will be "unlearned"... it will become extinct. In the fear of the dentist example, if the child was repeatedly taken to the dentist and there wa ...
... response will only occur to very specific stimuli. This can be taken a step further: if a CS is presented repeatedly without the UCS then eventually the CR will be "unlearned"... it will become extinct. In the fear of the dentist example, if the child was repeatedly taken to the dentist and there wa ...
Chapter 8 pt. 1: Learning and Classical Conditioning
... half was told the reverse….positive instructions assisted conditioning while negative instructions undermined the process Drugs ...
... half was told the reverse….positive instructions assisted conditioning while negative instructions undermined the process Drugs ...
Chapter 6 Learning - Home | W. W. Norton & Company
... state of affairs” likely to be repeated – Any behavior leading to an “annoying state of affairs” less likely to reoccur ...
... state of affairs” likely to be repeated – Any behavior leading to an “annoying state of affairs” less likely to reoccur ...
Ans 336. Livestock Behavior and Well
... something worth pursuing, and they will repeat the behaviors that seem to cause these consequences. • These consequences will increase the behaviors that lead to them, so they are reinforcers. These are consequences the animal will work to attain, so they strengthen the behavior.” ...
... something worth pursuing, and they will repeat the behaviors that seem to cause these consequences. • These consequences will increase the behaviors that lead to them, so they are reinforcers. These are consequences the animal will work to attain, so they strengthen the behavior.” ...
Intro to Learning and Learning Theories
... Developed classical conditioning – learning though association of a stimulus and a response Experimented with dogs Natural response or unconditioned response [UCR] is involuntary Elements that produce UCR are unconditioned stimuli [UCS]. ...
... Developed classical conditioning – learning though association of a stimulus and a response Experimented with dogs Natural response or unconditioned response [UCR] is involuntary Elements that produce UCR are unconditioned stimuli [UCS]. ...
Habitual Behaviour
... can be taught to discriminate between similar stimuli and to only respond to a specific stimulus. For example, imagine that a dog has been trained to run to his owner when he hears a whistle. After the dog has been conditioned, he might respond to a variety sounds that are similar to the whistle. Be ...
... can be taught to discriminate between similar stimuli and to only respond to a specific stimulus. For example, imagine that a dog has been trained to run to his owner when he hears a whistle. After the dog has been conditioned, he might respond to a variety sounds that are similar to the whistle. Be ...
Chapter 8 Learning
... 16. I he procedure in which responses are reinforced onh part of the time is called reinforcement, Under these conditions, learning is generally (faster slower) than it is with continuous reinforcement. Behaxior reinforced in this manner is (very not very) resistant to extinction, 17. When behax ior ...
... 16. I he procedure in which responses are reinforced onh part of the time is called reinforcement, Under these conditions, learning is generally (faster slower) than it is with continuous reinforcement. Behaxior reinforced in this manner is (very not very) resistant to extinction, 17. When behax ior ...
Finish PPT
... Wundt sets up first psychology laboratory. Structuralism – How do people think – introspection…self observation and those of clients. ...
... Wundt sets up first psychology laboratory. Structuralism – How do people think – introspection…self observation and those of clients. ...
Exam 1 - Weber State University
... D. It is more effective than Classical Conditioning in decreasing the probability of behavior than 30. It is easier to train a dog to bark for food than to train it to stand on its hind legs for food. For other species, there is no such difference. This best illustrates the importance of _________ i ...
... D. It is more effective than Classical Conditioning in decreasing the probability of behavior than 30. It is easier to train a dog to bark for food than to train it to stand on its hind legs for food. For other species, there is no such difference. This best illustrates the importance of _________ i ...
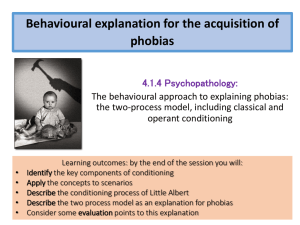
Behavioural explanation
... the behaviour results in a pleasant consequence which means the behaviour is likely to be repeated. • Mowrer (1960) suggested that whenever we avoid a phobic stimulus we successfully escape the fear and anxiety that we would have suffered if we had entered its presence or remained there. • This redu ...
... the behaviour results in a pleasant consequence which means the behaviour is likely to be repeated. • Mowrer (1960) suggested that whenever we avoid a phobic stimulus we successfully escape the fear and anxiety that we would have suffered if we had entered its presence or remained there. • This redu ...
cognition notes learning, memory, problem solving
... – Phobias (a neutral stimulus paired with an anxiety or fear provoking experience resulting in that stimulus evoking fear/anxiety) – Advertisers hope to bank on your arousal by utilizing attractive people and situations to encourage you to purchase their products – Immuno-suppression has been measur ...
... – Phobias (a neutral stimulus paired with an anxiety or fear provoking experience resulting in that stimulus evoking fear/anxiety) – Advertisers hope to bank on your arousal by utilizing attractive people and situations to encourage you to purchase their products – Immuno-suppression has been measur ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.