Resistance * Learning Outcomes
... Wheatstone Bridge – Uses Usually, one resistor is variable and set to monitor something, while the galvanometer is replaced by some circuit. e.g. A thermistor can be used to monitor room / oven temperature and the galvanometer can be replaced by a heater. When the thermistor unbalances the ci ...
... Wheatstone Bridge – Uses Usually, one resistor is variable and set to monitor something, while the galvanometer is replaced by some circuit. e.g. A thermistor can be used to monitor room / oven temperature and the galvanometer can be replaced by a heater. When the thermistor unbalances the ci ...
Section 5. Electricity and Magnetism Course
... The electric field produced by a charge (q1) is defined in terms of a test charge (q2) This test charge will experience a force dependent only on the test charge The test charge must be so small as to not disturb the charge being considered The test charge is positive ...
... The electric field produced by a charge (q1) is defined in terms of a test charge (q2) This test charge will experience a force dependent only on the test charge The test charge must be so small as to not disturb the charge being considered The test charge is positive ...
Development and testing of passive tracking markers for different
... marker. Such a nonlinear magnetic property is partly exhibited by ferro- and ferrimagnetic materials. We therefore selected the ferromagnetic nickel and stainless steel type AISI 410 and the ferrimagnetic copper zinc ferrite as marker candidates. For ferro- and ferrimagnetic materials, in contrast t ...
... marker. Such a nonlinear magnetic property is partly exhibited by ferro- and ferrimagnetic materials. We therefore selected the ferromagnetic nickel and stainless steel type AISI 410 and the ferrimagnetic copper zinc ferrite as marker candidates. For ferro- and ferrimagnetic materials, in contrast t ...
DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATIONS OF A DRUM
... designed. The first feeding hopper, with openness three times as large as the largest size of the feed material, is not equipped with vibrators and a sluice board. The second-stage hopper, suspended from its frame with a spring, is an open-type hopper, which is equipped with a vibration motor. The f ...
... designed. The first feeding hopper, with openness three times as large as the largest size of the feed material, is not equipped with vibrators and a sluice board. The second-stage hopper, suspended from its frame with a spring, is an open-type hopper, which is equipped with a vibration motor. The f ...
Induced EMF - Edvantage Science
... Magnetism, EMF, and Electric Current An Englishman, Michael Faraday (1791-1867) and an American, Joseph Henry (17971878), working independently discovered that magnetism could produce or induce a current in a circuit. Inducing an EMF in a Straight Piece of Wire A current in circuit can be induced if ...
... Magnetism, EMF, and Electric Current An Englishman, Michael Faraday (1791-1867) and an American, Joseph Henry (17971878), working independently discovered that magnetism could produce or induce a current in a circuit. Inducing an EMF in a Straight Piece of Wire A current in circuit can be induced if ...
Braking Index of Isolated Pulsars
... accelerated to relativistic energies and carry away angular momentum. The particle wind is also importantly associated with the magnetic field strength as ~B 2 ...
... accelerated to relativistic energies and carry away angular momentum. The particle wind is also importantly associated with the magnetic field strength as ~B 2 ...
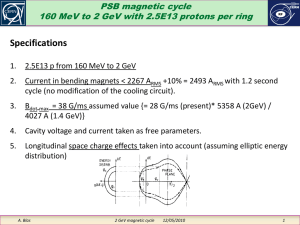
PSB magnetic cycle 2GeV_2
... These simulations concerns h1 uniquely, for a single harmonic acceleration made as fast as possible with a 1.2 eV.s beam emittance and a max 38 G/ms Bdot . The requirement should be lessened (not much) in a dual harmonic context. The h1 cavity voltage should provide more than 11.3 kVP Its current av ...
... These simulations concerns h1 uniquely, for a single harmonic acceleration made as fast as possible with a 1.2 eV.s beam emittance and a max 38 G/ms Bdot . The requirement should be lessened (not much) in a dual harmonic context. The h1 cavity voltage should provide more than 11.3 kVP Its current av ...
Electric and Magnetic Fields - Hydro
... hold circuits that power them, and the transmission and distribution lines that bring electricity into our homes. The time we spend close to such equipment considerably influences our exposure to EMFs. We have seen that all electrical equipment produces an electric and a magnetic field when in opera ...
... hold circuits that power them, and the transmission and distribution lines that bring electricity into our homes. The time we spend close to such equipment considerably influences our exposure to EMFs. We have seen that all electrical equipment produces an electric and a magnetic field when in opera ...
25070- H3-ws58 (ans) NAME blame : Resistance 1) Resistance is
... 9) Determine the resistance of a copper coil at a temperature of 65°C if the resistance at 0°C was 150 given that 0 = 0·00427. (Old-p37) ...
... 9) Determine the resistance of a copper coil at a temperature of 65°C if the resistance at 0°C was 150 given that 0 = 0·00427. (Old-p37) ...
Solutions - UCSB C.L.A.S.
... Now we can use Ohm’s law to find the current: I R 6 All of this current must go through R1, since there is no other path parallel to it. We can use the formula for power dissipated by a resistor: P=I2R = IV = V2/R. In this case the first one works fine: P1 2 A2 4 16W ...
... Now we can use Ohm’s law to find the current: I R 6 All of this current must go through R1, since there is no other path parallel to it. We can use the formula for power dissipated by a resistor: P=I2R = IV = V2/R. In this case the first one works fine: P1 2 A2 4 16W ...
Practice Questions
... 2. What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on a proton moving at 2.5105 m/s (a) at right angle; (b) at 30°; (c) parallel to a magnetic field of 0.50 T? Ans: (a) 210-14 N; (b) 110-14 N; (c) 0 N 3. A magnetic field of 0.10 T points in the positive x direction. A charged particle carrying 1.0 μC ...
... 2. What is the magnitude of the magnetic force on a proton moving at 2.5105 m/s (a) at right angle; (b) at 30°; (c) parallel to a magnetic field of 0.50 T? Ans: (a) 210-14 N; (b) 110-14 N; (c) 0 N 3. A magnetic field of 0.10 T points in the positive x direction. A charged particle carrying 1.0 μC ...
QUANTIZED MAGNETIC FLUX IN BOHR
... Instead of interpretating the energy shifts of atomic levels due to the Zeeman effect, Paschen-Back effect and the hyperfine level splitting as the additional energy of a magnetic moment within a magnetic field, these effects are here considered to be the result of the quantization of the magnetic f ...
... Instead of interpretating the energy shifts of atomic levels due to the Zeeman effect, Paschen-Back effect and the hyperfine level splitting as the additional energy of a magnetic moment within a magnetic field, these effects are here considered to be the result of the quantization of the magnetic f ...
Orbital Notation and Electron Configuration
... without drawing the orbitals… Fill electrons into lower energy levels first Follow order of filling Remember how many electrons each level can ...
... without drawing the orbitals… Fill electrons into lower energy levels first Follow order of filling Remember how many electrons each level can ...
magnetic orientation by hatchling loggerhead sea turtles
... lateral displacement resulted in a series of circles around the perimeter of the satellite dish. Circling could be slow or fast, with the course of the turtle changing by 1-8°s~\ Hatchlings occasionally reversed direction; in all cases, however, circling was characterized by continuous movement arou ...
... lateral displacement resulted in a series of circles around the perimeter of the satellite dish. Circling could be slow or fast, with the course of the turtle changing by 1-8°s~\ Hatchlings occasionally reversed direction; in all cases, however, circling was characterized by continuous movement arou ...
Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on the spin orientation.The main application of GMR is magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as cells that store one bit of information.In literature, the term giant magnetoresistance is sometimes confused with colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic semiconductors, which is not related to the multilayer structure.