day2
... amino acids (single letter amino acid code) and find those of a defined degree of similarity. ...
... amino acids (single letter amino acid code) and find those of a defined degree of similarity. ...
bioinformatics - Campus
... place in a machine called a “thermal cycler” and regulates the succession of amplification cycles during which it ...
... place in a machine called a “thermal cycler” and regulates the succession of amplification cycles during which it ...
Ross - Tree Improvement Program
... Alignment of two human sequences with the same region of the mouse genome shows a SNP between the two human versions of the gene. ...
... Alignment of two human sequences with the same region of the mouse genome shows a SNP between the two human versions of the gene. ...
BICH/GENE 431 KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES Chapter 9 – Mutations
... - transcription and nucleotide excision repair are coupled in order to direct repair to genes that are being expressed – TFIIH in eukaryotes is a general transcription factor and a nucleotide excision repair enzyme ...
... - transcription and nucleotide excision repair are coupled in order to direct repair to genes that are being expressed – TFIIH in eukaryotes is a general transcription factor and a nucleotide excision repair enzyme ...
Finding genes and detecting mutations
... • Small changes such as single base changes or insertions/deletions of < 10bp are harder to detect. Small changes such as single base mutations can be detected in many ways • Purify DNA fragment to be analysed, usually by PCR. A label (radioactive or fluorescent) can be incorporated at this stage. – ...
... • Small changes such as single base changes or insertions/deletions of < 10bp are harder to detect. Small changes such as single base mutations can be detected in many ways • Purify DNA fragment to be analysed, usually by PCR. A label (radioactive or fluorescent) can be incorporated at this stage. – ...
DNA REPLICATION
... The process by which DNA makes copies of itself is called DNA _______________________. The following are the steps for DNA Replication: 1. The double helix _________________________. 2. The hydrogen bonds that hold the base pairs together are broken by _______________________. This separates the two ...
... The process by which DNA makes copies of itself is called DNA _______________________. The following are the steps for DNA Replication: 1. The double helix _________________________. 2. The hydrogen bonds that hold the base pairs together are broken by _______________________. This separates the two ...
For the Tutorial Programme in Proteomics High
... Selection markers are genes that alter the proliferation capabilities of the host cell. The purpose of these markers is to provide growth differences between cells with and without the plasmid, enriching the cell population for the recombinant cells of interest. The selection can be positive or nega ...
... Selection markers are genes that alter the proliferation capabilities of the host cell. The purpose of these markers is to provide growth differences between cells with and without the plasmid, enriching the cell population for the recombinant cells of interest. The selection can be positive or nega ...
Ch 11 homework
... B) fact that individuals of the same species have different phenotypes. C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible as dark stripes on a chromosome. E) flow of information from parent to offspring. 2. Outline the function of the lac op ...
... B) fact that individuals of the same species have different phenotypes. C) process by which genetic information flows from genes to proteins. D) fact that certain genes are visible as dark stripes on a chromosome. E) flow of information from parent to offspring. 2. Outline the function of the lac op ...
Biology CP- Ch. 11 DNA- 11.1
... A=T ( by 2 hydrogen bonds) G=C (by 3 hydrogen bonds) Called Complimentary Base Pairing. Base-pairing rule- each base must pair up with its complementary base. ...
... A=T ( by 2 hydrogen bonds) G=C (by 3 hydrogen bonds) Called Complimentary Base Pairing. Base-pairing rule- each base must pair up with its complementary base. ...
Biology (056) (E) CHAPTER
... 5. What type of gametes will form by genotype RrYy (A)RY, Ry, rY, ry (B) RY, Ry, ry, ry (C) Ry, Ry, Yy, ry (D) Rr, RR, Yy, YY 6. If two opposite alleles come together, one finding morphological expression masking the other, the fact is described as law of (A) Inheritance (B) Dominance (C) Limiting f ...
... 5. What type of gametes will form by genotype RrYy (A)RY, Ry, rY, ry (B) RY, Ry, ry, ry (C) Ry, Ry, Yy, ry (D) Rr, RR, Yy, YY 6. If two opposite alleles come together, one finding morphological expression masking the other, the fact is described as law of (A) Inheritance (B) Dominance (C) Limiting f ...
Advances in Genetics - Madison County Schools
... Used to produce insulin Bacteria has 1 DNA molecule in the cytoplasm Also has small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids Scientists insert a human gene into the plasmid The bacteria and all its offspring will now make the protein that this gene codes for –in this case insulin Since bacte ...
... Used to produce insulin Bacteria has 1 DNA molecule in the cytoplasm Also has small circular pieces of DNA called plasmids Scientists insert a human gene into the plasmid The bacteria and all its offspring will now make the protein that this gene codes for –in this case insulin Since bacte ...
A Bacterial Plasmid: What can you tell me about the plamid?
... organism’s DNA. Create sticky ends that are complementary to the plasmid’s sticky ends. • Insert the gene using ligase. How does one determine which RE’s to use? ...
... organism’s DNA. Create sticky ends that are complementary to the plasmid’s sticky ends. • Insert the gene using ligase. How does one determine which RE’s to use? ...
DNA Recombination
... In order to remove a gene from one cell and insert it into another cell, the gene must be cut from the original chromosome and implanted into the one in the recipient cell. This is accomplished by using special chemicals called restriction enzymes. These enzymes recognize a specific sequence of nucl ...
... In order to remove a gene from one cell and insert it into another cell, the gene must be cut from the original chromosome and implanted into the one in the recipient cell. This is accomplished by using special chemicals called restriction enzymes. These enzymes recognize a specific sequence of nucl ...
Biotechnology - Genetic Engineering
... Restriction Enzymes: These are enzymes naturally occurring in bacteria. The bacteria use these enzymes to protect themselves from viruses invading them. Restriction enzymes “cut” the DNA the virus injects into them so that the virus cannot be reproduced. Act like “molecular scissors”. Scientist use ...
... Restriction Enzymes: These are enzymes naturally occurring in bacteria. The bacteria use these enzymes to protect themselves from viruses invading them. Restriction enzymes “cut” the DNA the virus injects into them so that the virus cannot be reproduced. Act like “molecular scissors”. Scientist use ...
Kyle Snell
... expression patterns that would not be possible in a diploid. Recently, the significance of endopolyploidy, or “cell polyploidy,” in plants has begun to receive more attention. Endopolyploid cells contain at minimum a doubling of the base nuclear DNA of the plant, and have only been found in select t ...
... expression patterns that would not be possible in a diploid. Recently, the significance of endopolyploidy, or “cell polyploidy,” in plants has begun to receive more attention. Endopolyploid cells contain at minimum a doubling of the base nuclear DNA of the plant, and have only been found in select t ...
Genetic Engineering
... Finding the location of certain genes on chromosomes The arrangement of the nitrogen base pairs (A,T,C and G) determines what an organism looks like Human Genome Project ...
... Finding the location of certain genes on chromosomes The arrangement of the nitrogen base pairs (A,T,C and G) determines what an organism looks like Human Genome Project ...
DNA
... mammals. • This phage can quickly turn an E. coli cell into a T2-producing factory that releases phages when the cell ruptures. ...
... mammals. • This phage can quickly turn an E. coli cell into a T2-producing factory that releases phages when the cell ruptures. ...
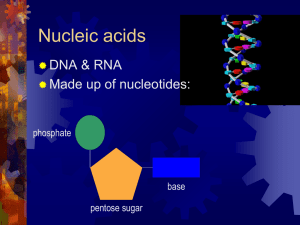
Nucleosides, Nucleotides, and Nucleic Acids
... Three RNAs are involved in gene expression. In the transcription phase, a strand of messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized from a DNA template. The four bases A, G, C, and U, taken three at a time, generate 64 possible combinations called codons. These 64 codons comprise the genetic code and code for t ...
... Three RNAs are involved in gene expression. In the transcription phase, a strand of messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized from a DNA template. The four bases A, G, C, and U, taken three at a time, generate 64 possible combinations called codons. These 64 codons comprise the genetic code and code for t ...
Chapter 9
... cells by first removing their cell walls – Protoplasts in solution will fuse at a low but significant rate (can add polyethylene glycol to increase the frequency of fusion) – Valuable in the genetic manipulation of plant and algal cells ...
... cells by first removing their cell walls – Protoplasts in solution will fuse at a low but significant rate (can add polyethylene glycol to increase the frequency of fusion) – Valuable in the genetic manipulation of plant and algal cells ...
Chapter 13: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... ◉ Naturally occurring DNA molecules are very long, and a single molecule usually carries many genes. ◉ To work directly with specific genes, scientists have developed methods for preparing well-defined segments of DNA in multiple identical copies, a process called DNA cloning. ○ One common approach ...
... ◉ Naturally occurring DNA molecules are very long, and a single molecule usually carries many genes. ◉ To work directly with specific genes, scientists have developed methods for preparing well-defined segments of DNA in multiple identical copies, a process called DNA cloning. ○ One common approach ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.