Abstract-Template-2016
... SNPs for evidence of secondary structures that might also be a factor in allelic dropout. The region is GC-rich, and using several prediction algorithms2, 3 it appeared likely that it has a propensity for forming G-quadruplex (G4) structures. These arise from the formation of Gtetrads by hydrogen bo ...
... SNPs for evidence of secondary structures that might also be a factor in allelic dropout. The region is GC-rich, and using several prediction algorithms2, 3 it appeared likely that it has a propensity for forming G-quadruplex (G4) structures. These arise from the formation of Gtetrads by hydrogen bo ...
Abstract-Template-2017 - Queenstown Research Week
... SNPs for evidence of secondary structures that might also be a factor in allelic dropout. The region is GC-rich, and using several prediction algorithms2, 3 it appeared likely that it has a propensity for forming G-quadruplex (G4) structures. These arise from the formation of Gtetrads by hydrogen bo ...
... SNPs for evidence of secondary structures that might also be a factor in allelic dropout. The region is GC-rich, and using several prediction algorithms2, 3 it appeared likely that it has a propensity for forming G-quadruplex (G4) structures. These arise from the formation of Gtetrads by hydrogen bo ...
8.1 study guide KEY
... 7. Avery and his team isolated Griffith's transforming principle and performed ...
... 7. Avery and his team isolated Griffith's transforming principle and performed ...
GENE EXPRESSION - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS A. FROM DNA TO
... enzymes! Remember that the DNA molecule is a code that contains instructions for biological function & structure. Proteins (enzymes) carry out these instructions. The linear sequence of amino acids in a protein determines its 3-D structure & it is this 3-D structure that determines the protein's fun ...
... enzymes! Remember that the DNA molecule is a code that contains instructions for biological function & structure. Proteins (enzymes) carry out these instructions. The linear sequence of amino acids in a protein determines its 3-D structure & it is this 3-D structure that determines the protein's fun ...
Chapter 10 Gene Mutation: Origins and Repair Processes
... The base excision repair pathway. In this example, a uracil that was formed by deamination of cytosin is removed from the sugar-phosphate backbone by DNA glycosylase. These enzymes create apurinic or apyrimidinic (AP) sites. AP endonuclease recognizes these AP sites and cleaves the DNA strand. The ...
... The base excision repair pathway. In this example, a uracil that was formed by deamination of cytosin is removed from the sugar-phosphate backbone by DNA glycosylase. These enzymes create apurinic or apyrimidinic (AP) sites. AP endonuclease recognizes these AP sites and cleaves the DNA strand. The ...
CS262 Discussion Section 4
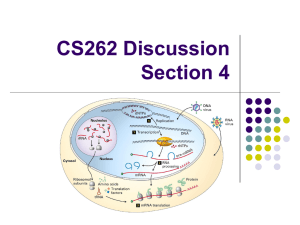
... Deletions and insertions are collectively referred to as indels, because when two sequences are compared, it is impossible to tell whether a deletion has occurred in one, or an insertion has occurred in the other. In a coding region, an indel that is not a multiple of 3 nucleotides causes a frameshi ...
... Deletions and insertions are collectively referred to as indels, because when two sequences are compared, it is impossible to tell whether a deletion has occurred in one, or an insertion has occurred in the other. In a coding region, an indel that is not a multiple of 3 nucleotides causes a frameshi ...
The Origins of Variation
... apparent mutation rate is based only on substitutions that persist in the genome mutations that occur at nucleotide positions that affect phenotype (nonsynonymous) may be eliminated by selection selection, speciation, population size, or other factors may accelerate or retard the molecular clock to ...
... apparent mutation rate is based only on substitutions that persist in the genome mutations that occur at nucleotide positions that affect phenotype (nonsynonymous) may be eliminated by selection selection, speciation, population size, or other factors may accelerate or retard the molecular clock to ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... 4. tRNA: type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis 5. transcription: process in which part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence in RNA 6. RNA polymerase: enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates ...
... 4. tRNA: type of RNA molecule that transfers amino acids to ribosomes during protein synthesis 5. transcription: process in which part of the nucleotide sequence of DNA is copied into a complementary sequence in RNA 6. RNA polymerase: enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA and separates ...
File
... ________________________________________________________________________ o Hershey/Chase wanted to determined which part of the bacteriophage (the protein coat or nucleic acid core) entered the infected cell o They thought this would allow them to learn whether genes are made of protein or DNA o The ...
... ________________________________________________________________________ o Hershey/Chase wanted to determined which part of the bacteriophage (the protein coat or nucleic acid core) entered the infected cell o They thought this would allow them to learn whether genes are made of protein or DNA o The ...
DNA Extraction
... DNA Extraction • DNA extraction is a routine procedure to isolate & collect DNA. • DNA extraction is the first step for subsequent ...
... DNA Extraction • DNA extraction is a routine procedure to isolate & collect DNA. • DNA extraction is the first step for subsequent ...
protein synthesis
... The genetic code must have evolved very early in the history of life • The genetic code is nearly universal, shared by organisms from the simplest bacteria to the most complex plants and animals. • In laboratory experiments, genes can be transcribed and translated after they are transplanted from o ...
... The genetic code must have evolved very early in the history of life • The genetic code is nearly universal, shared by organisms from the simplest bacteria to the most complex plants and animals. • In laboratory experiments, genes can be transcribed and translated after they are transplanted from o ...
Biology Genetic Engineering Gel Electrophoresis
... their DNA by genetic engineering techniques. These techniques are much more precise, an example is mutagenesis (mutation breeding) where an organism is exposed to radiation or chemicals to create a nonspecific but stable change. Other techniques by which humans modify organisms include: selective br ...
... their DNA by genetic engineering techniques. These techniques are much more precise, an example is mutagenesis (mutation breeding) where an organism is exposed to radiation or chemicals to create a nonspecific but stable change. Other techniques by which humans modify organisms include: selective br ...
Document
... female tissues is random. Its exact position depends on the orientation of the two daughter nuclei after the first cleavage. ...
... female tissues is random. Its exact position depends on the orientation of the two daughter nuclei after the first cleavage. ...
1. How many main types of RNA are there?(B4.2g) a.1 b.3 c
... 26. A DNA molecule containing regions from different sources is called A.DNA ligase. B.recombinant DNA. C.restriction DNA. D.template DNA. ...
... 26. A DNA molecule containing regions from different sources is called A.DNA ligase. B.recombinant DNA. C.restriction DNA. D.template DNA. ...
Document
... If only one band was seen the person would be homozygous –both of the alleles they carry are the same. This method where the probe recognises one locus is called single locus probing. However using a section of the 33 bp repeat as probe Jeffreys obtained a more complex pattern because the repeat was ...
... If only one band was seen the person would be homozygous –both of the alleles they carry are the same. This method where the probe recognises one locus is called single locus probing. However using a section of the 33 bp repeat as probe Jeffreys obtained a more complex pattern because the repeat was ...
MutaGEL® r-Vitamin D3
... The kit MutaGEL r-vitamin D3 contains a set of primer for amplification of the specific DNA sequence within the human vitamin D3 receptor gene VD3R. Amplificates of variing genotypes (start codon polymorphism) are characterized by subsequent specific restriction enzyme digestion. The rare variant (f ...
... The kit MutaGEL r-vitamin D3 contains a set of primer for amplification of the specific DNA sequence within the human vitamin D3 receptor gene VD3R. Amplificates of variing genotypes (start codon polymorphism) are characterized by subsequent specific restriction enzyme digestion. The rare variant (f ...
Retrovirus Protocols
... which cryptic splice sites found in pGen- were removed (1), were originally developed and kindly provided by Dr. Phill Soriano at Fred Huchinson Cancer Center, WA, USA. Gene trap cassettes will be inserted into reverse orientation relative to viral transcription (2). The vectors should be transforme ...
... which cryptic splice sites found in pGen- were removed (1), were originally developed and kindly provided by Dr. Phill Soriano at Fred Huchinson Cancer Center, WA, USA. Gene trap cassettes will be inserted into reverse orientation relative to viral transcription (2). The vectors should be transforme ...
Evolucijska genomika 2
... Gene numbers do not increase as much as expected with complexity: - worm and fly gene numbers (12-14,000) are only about twice those of yeast (6,000) and P. aeruginosa (5,500) - mammalian (human, mouse) gene numbers (~30,000) are only about twice those of invertebrates. Phenotypic variation in m ...
... Gene numbers do not increase as much as expected with complexity: - worm and fly gene numbers (12-14,000) are only about twice those of yeast (6,000) and P. aeruginosa (5,500) - mammalian (human, mouse) gene numbers (~30,000) are only about twice those of invertebrates. Phenotypic variation in m ...
EXAM Banswers2 - HonorsBiologyWiki
... 26. A DNA molecule containing regions from different sources is called A.DNA ligase. B.recombinant DNA. C.restriction DNA. D.template DNA. ...
... 26. A DNA molecule containing regions from different sources is called A.DNA ligase. B.recombinant DNA. C.restriction DNA. D.template DNA. ...
Chapter 12: Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids
... 32. After her adventures in Oz, Dorothy came to BU and became a biochemist. Soon thereafter, she was summoned back to Oz by the wizard to carry out a special project. The wizard, as it happens, had been dabbling in biochemistry himself. He had determined that all the basic rules of protein and nucle ...
... 32. After her adventures in Oz, Dorothy came to BU and became a biochemist. Soon thereafter, she was summoned back to Oz by the wizard to carry out a special project. The wizard, as it happens, had been dabbling in biochemistry himself. He had determined that all the basic rules of protein and nucle ...
Emergent Properties of Reduced-Genome
... of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (VP60) fused to cholera toxin (CTX) was stable in MDS and unstable in WT plasmids. ...
... of rabbit hemorrhagic disease virus (VP60) fused to cholera toxin (CTX) was stable in MDS and unstable in WT plasmids. ...
DNA Methylation studies
... then provides a measure of the extent of methylation. DNA samples from liver cancer were used to estimate their DNA methylation level. These cells were treated with Trichostatin A (TSA) a chemical which affects one of the proteins binding to DNA in the cells. Its effect was observed upon treatment o ...
... then provides a measure of the extent of methylation. DNA samples from liver cancer were used to estimate their DNA methylation level. These cells were treated with Trichostatin A (TSA) a chemical which affects one of the proteins binding to DNA in the cells. Its effect was observed upon treatment o ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.