The Living Cell - Carnegie Institution for Science
... How Does DNA Make Protein? 1. Chromosomes (DNA) carry the genetic message 2. Messenger RNA copies the genetic message 3. Transfer RNA holds an amino acid ...
... How Does DNA Make Protein? 1. Chromosomes (DNA) carry the genetic message 2. Messenger RNA copies the genetic message 3. Transfer RNA holds an amino acid ...
The Nucleus: DNA, Chromatin And Chromosomes
... - Transfers the appropriate amino-acid to a growing protein chain - There is one t-RNA for each amino-acid ...
... - Transfers the appropriate amino-acid to a growing protein chain - There is one t-RNA for each amino-acid ...
Test 3
... 2. You have isolated a fragment of viral DNA that totally encodes at least two proteins, 120 and 80 amino acids long. The DNA fragment is 400 base pairs long. (a) Why might you consider this unusual? (b) You sequence the two proteins and find no sequence homology. Propose a model to account for thes ...
... 2. You have isolated a fragment of viral DNA that totally encodes at least two proteins, 120 and 80 amino acids long. The DNA fragment is 400 base pairs long. (a) Why might you consider this unusual? (b) You sequence the two proteins and find no sequence homology. Propose a model to account for thes ...
Kinetic proofreading - Weizmann Institute of Science
... Fluorescently labeled tRNA molecules. Antibiotic inhibitors of tRNA selection. Nonhydrolizable GTP analogues. Enzymatically and chemically altered ribosome complexes GTPase activity stimulation Codon recognition (different rates, k3, for cognate state and non-cognate) GTP hydrolysis Phosphate releas ...
... Fluorescently labeled tRNA molecules. Antibiotic inhibitors of tRNA selection. Nonhydrolizable GTP analogues. Enzymatically and chemically altered ribosome complexes GTPase activity stimulation Codon recognition (different rates, k3, for cognate state and non-cognate) GTP hydrolysis Phosphate releas ...
Chapter 16 - Human Ancestry
... - Fine hand coordination; use of symbols A preserved man, frozen in ice from about 5,200 years ago, is genetically like us - Ötzi, the Ice Man ...
... - Fine hand coordination; use of symbols A preserved man, frozen in ice from about 5,200 years ago, is genetically like us - Ötzi, the Ice Man ...
chapter 12 - TeacherWeb
... d. has a phenotypic ratio that equals its genotypic ratio e. has 16 different genotypic possibilities 16. The base height of the dingdong plant is 10 cm. Four genes contribute to the height of the plant, and each dominant allele contributes 3 cm to height. If you cross a 10-cm plant (quadruply homoz ...
... d. has a phenotypic ratio that equals its genotypic ratio e. has 16 different genotypic possibilities 16. The base height of the dingdong plant is 10 cm. Four genes contribute to the height of the plant, and each dominant allele contributes 3 cm to height. If you cross a 10-cm plant (quadruply homoz ...
Mitosis and Cell Cycle
... progression of cells through the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) enzymes. • A kinase is a type of enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from high-energy donor molecules, such as ATP, to specific substrates, a process referred to as phosphorylation. ...
... progression of cells through the cell cycle by activating cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) enzymes. • A kinase is a type of enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from high-energy donor molecules, such as ATP, to specific substrates, a process referred to as phosphorylation. ...
Genetic Disorders
... muscles of the body get weaker and weaker and slowly stop working because of a lack of a certain protein (see the relationship to genetics?) Can be passed on by one or both parents, depending on the form of MD (therefore is autosomal dominant and recessive) ...
... muscles of the body get weaker and weaker and slowly stop working because of a lack of a certain protein (see the relationship to genetics?) Can be passed on by one or both parents, depending on the form of MD (therefore is autosomal dominant and recessive) ...
Advanced Environmental Biotechnology II
... systems modeling approaches allows for the analysis of community population structure, functional capabilities and dynamics. The process typically begins with sequencing of DNA extracted from an environmental sample, either after cloning the DNA into a library or by affixing to beads and direct sequ ...
... systems modeling approaches allows for the analysis of community population structure, functional capabilities and dynamics. The process typically begins with sequencing of DNA extracted from an environmental sample, either after cloning the DNA into a library or by affixing to beads and direct sequ ...
Chapter 3
... 14. Identify and describe the steps that result in DNA replication Know why it is called semi-conservative replication Role of DNA polymerase and helicase 15. Describe the events that take place in transcription 16. Describe the events that take place in translation – protein synthesis 17. Know ...
... 14. Identify and describe the steps that result in DNA replication Know why it is called semi-conservative replication Role of DNA polymerase and helicase 15. Describe the events that take place in transcription 16. Describe the events that take place in translation – protein synthesis 17. Know ...
Diversity
... proteins encoded, the researchers identified amino acids that were identical in 2 distantly related species but different in 2 closely related species. This focuses on evolutionary drift. One pattern was seen: amino acids predicted to be among the 1st incorporated into the genetic code are decreasin ...
... proteins encoded, the researchers identified amino acids that were identical in 2 distantly related species but different in 2 closely related species. This focuses on evolutionary drift. One pattern was seen: amino acids predicted to be among the 1st incorporated into the genetic code are decreasin ...
DNA-Based Mutations
... eg. Trisomy 21 (3 copies of chromosome 21 in cells instead of 2) -Down Syndrome. -- caused by errors during Mitosis of somatic cell chromosomes and/or Meiosis of sex cell chromosomes. Gene Mutations -- usually occur during DNA replication which means that the errors would be evident in future cells, ...
... eg. Trisomy 21 (3 copies of chromosome 21 in cells instead of 2) -Down Syndrome. -- caused by errors during Mitosis of somatic cell chromosomes and/or Meiosis of sex cell chromosomes. Gene Mutations -- usually occur during DNA replication which means that the errors would be evident in future cells, ...
RECOMBINANT DNA
... 1. Obtain ONE strip of plasmid DNA and ONE strip of a human gene. 2. Genetic engineers use plasmids to introduce new genes into bacteria. The plasmid DNA is actually circular and the two ends are normally connected. Tape together the two ends of the plasmid DNA molecule to form a ring. 3. Genetic en ...
... 1. Obtain ONE strip of plasmid DNA and ONE strip of a human gene. 2. Genetic engineers use plasmids to introduce new genes into bacteria. The plasmid DNA is actually circular and the two ends are normally connected. Tape together the two ends of the plasmid DNA molecule to form a ring. 3. Genetic en ...
DNA (double helix)
... Different genes are activated in different cells, creating the specific proteins that give a particular cell type its character. http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEPC/NIH/gene03.html ...
... Different genes are activated in different cells, creating the specific proteins that give a particular cell type its character. http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEPC/NIH/gene03.html ...
Photosynthesis - Cathedral High School
... the HEXA gene on chromosome 15 This causes a stop codon in the wrong location Deficient hexosaminidase (hex A). ...
... the HEXA gene on chromosome 15 This causes a stop codon in the wrong location Deficient hexosaminidase (hex A). ...
Cell Cycle PowerPoint
... • Cell division is the process by smaller which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells (IDENTICAL CELLS!). ...
... • Cell division is the process by smaller which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells (IDENTICAL CELLS!). ...
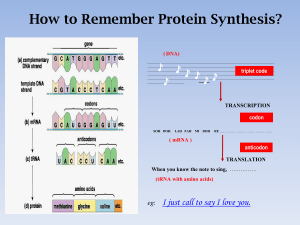
How to remember Protein Synthesis
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
... • DNA in the nucleus contains a triplet code; each group of three bases stands for one amino acid. • During transcription, an mRNA copy of the DNA template is made. • The mRNA is processed before leaving the nucleus. • The mRNA joins with a ribosome, where tRNA carries the amino acids into position ...
MB207Jan2010
... chromosomes during meiosis • Chromosome must synapse (pair) in order for chiasmata to form where crossing-over occurs – DNA synapsis: base pairing between complementary strands from 2 DNA molecules – Chiasmata: regions where paired homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis, a c ...
... chromosomes during meiosis • Chromosome must synapse (pair) in order for chiasmata to form where crossing-over occurs – DNA synapsis: base pairing between complementary strands from 2 DNA molecules – Chiasmata: regions where paired homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis, a c ...
Cells are exposed to DNA damaging agents that can affect their
... where a collection of proteins interact to work in such various processes as DNA repair or RNA splicing. Also, some important molecules in the size range of 100 kDa are multi-domain proteins which are difficult to express and crystallize, so that most structural information is restricted to single d ...
... where a collection of proteins interact to work in such various processes as DNA repair or RNA splicing. Also, some important molecules in the size range of 100 kDa are multi-domain proteins which are difficult to express and crystallize, so that most structural information is restricted to single d ...
AP Biology Double helix structure of DNA
... “It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic AP Biology material.” Watson & Crick ...
... “It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic AP Biology material.” Watson & Crick ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.