BIOLOGY KEYSTONE!cheat sheet
... *All living things are composed of 4 macromolecules. Macromolecules are large polymers (the prefix “poly” means “many”) that are composed of lots of smaller building blocks called monomers (the prefix “mono” means “one”). * ...
... *All living things are composed of 4 macromolecules. Macromolecules are large polymers (the prefix “poly” means “many”) that are composed of lots of smaller building blocks called monomers (the prefix “mono” means “one”). * ...
Exclusive Highly-Specific Kits and Antibodies for DNA
... pathway to demethylate DNA involving a repair mechanism converting hmC to C and, as such open up entirely new perspectives in epigenetic studies. Since its discovery in neuronal Purkinje, granule and ES cells, studies of this new modified DNA base have been limited by the lack of high quality, valid ...
... pathway to demethylate DNA involving a repair mechanism converting hmC to C and, as such open up entirely new perspectives in epigenetic studies. Since its discovery in neuronal Purkinje, granule and ES cells, studies of this new modified DNA base have been limited by the lack of high quality, valid ...
pGLO2011 Wilkes
... The phenomenon of transformation, which provided a key clue to understanding the molecular basis of the gene, also provided a tool for manipulating the genetic makeup of living organisms. To a large extent, genetic engineering relies on adding relatively short segments of DNA containing a foreign o ...
... The phenomenon of transformation, which provided a key clue to understanding the molecular basis of the gene, also provided a tool for manipulating the genetic makeup of living organisms. To a large extent, genetic engineering relies on adding relatively short segments of DNA containing a foreign o ...
CP Biology Chapter 8 Structure of DNA notes
... DNA double helix, and both involve large enzymes called polymerases. But the end results of the two processes are very different. Replication makes a copy of DNA and transcription makes RNA molecules. Another difference is that replication happens only once during the cell cycle. Transcription can h ...
... DNA double helix, and both involve large enzymes called polymerases. But the end results of the two processes are very different. Replication makes a copy of DNA and transcription makes RNA molecules. Another difference is that replication happens only once during the cell cycle. Transcription can h ...
DNA Scientists Formative Assessment
... 1. Stated the Chromosome Theory of Inheritance by observing how traits were passed to the offspring using grasshopper sperm. 2. Using mutated bread mold they stated that One-Gene codes for One-Enzyme. 3. Hypothesized, in 1952, that protein was the transforming agent in Griffith’s experiment. Used Su ...
... 1. Stated the Chromosome Theory of Inheritance by observing how traits were passed to the offspring using grasshopper sperm. 2. Using mutated bread mold they stated that One-Gene codes for One-Enzyme. 3. Hypothesized, in 1952, that protein was the transforming agent in Griffith’s experiment. Used Su ...
D>3 Round 5 - High School Quizbowl Packet Archive
... 1. A body of land that is surrounded by water on three sides. 2. A low, watery land formed at the mouth of a river. They are often shaped like a triangle. 3. A non-artificial narrow body of water that connects two larger bodies of water. 4. A narrow strip of land connecting two larger landmasses. Th ...
... 1. A body of land that is surrounded by water on three sides. 2. A low, watery land formed at the mouth of a river. They are often shaped like a triangle. 3. A non-artificial narrow body of water that connects two larger bodies of water. 4. A narrow strip of land connecting two larger landmasses. Th ...
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS – CHAPTER 10
... Telomeres are highly repetitive DNA regions that may be many thousands of base pairs in length, located at the ends of linear chromosomes in eukaryotes. They are important in the replication of the 5' end of the DNA strands. (b) How are they maintained? (pp. 226–227) In somatic cells the telomerases ...
... Telomeres are highly repetitive DNA regions that may be many thousands of base pairs in length, located at the ends of linear chromosomes in eukaryotes. They are important in the replication of the 5' end of the DNA strands. (b) How are they maintained? (pp. 226–227) In somatic cells the telomerases ...
Unit 1 Topic 2: Genes and Health
... mammalian lung is adapted for rapid gaseous exchange. 7. Describe the basic structure of an amino acid (structures of specific amino acids are not required) and the formation of polypeptides and proteins (as amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds in condensation reactions) and explain the signi ...
... mammalian lung is adapted for rapid gaseous exchange. 7. Describe the basic structure of an amino acid (structures of specific amino acids are not required) and the formation of polypeptides and proteins (as amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds in condensation reactions) and explain the signi ...
File
... vast amount of information - Encode the specificity and variability of life. 2. Capacity to self-replicate: As cells divide each must get a complete and “exact” copy of the genome - Efficient DNA replication. 3. Expressivity: To carry out metabolism the instructions to synthesize needed enzymes must ...
... vast amount of information - Encode the specificity and variability of life. 2. Capacity to self-replicate: As cells divide each must get a complete and “exact” copy of the genome - Efficient DNA replication. 3. Expressivity: To carry out metabolism the instructions to synthesize needed enzymes must ...
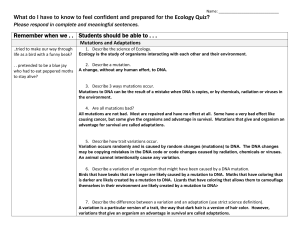
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... 10. Describe an example where the environment affects the benefits of a variation. The most famous example is the peppered moths Before the Industrial Revolution; the trees were light colored so light colored moths have a variation that helped them survive. However, when the trees became dark becaus ...
... 10. Describe an example where the environment affects the benefits of a variation. The most famous example is the peppered moths Before the Industrial Revolution; the trees were light colored so light colored moths have a variation that helped them survive. However, when the trees became dark becaus ...
1% - Politecnico di Milano
... Nucleotides are linked together though phosphodiester bonds to form long strands of DNA. These bonds are strong covalent bonds between a phosphate group and two 5-carbon ring carbohydrates. They involve the two carbons in position 3 and 5 the DNA polymer is directional. ...
... Nucleotides are linked together though phosphodiester bonds to form long strands of DNA. These bonds are strong covalent bonds between a phosphate group and two 5-carbon ring carbohydrates. They involve the two carbons in position 3 and 5 the DNA polymer is directional. ...
12.11 Restriction fragment analysis is a powerful method that
... gene into plasmid using restriction enzyme and DNA ligase ...
... gene into plasmid using restriction enzyme and DNA ligase ...
Self-Assembly at nano-Scale Binary Nanoparticles Superlattices
... nanogap devices assembled with oligonucleotide-modified Au nanoparticle devices: A) I–V curves of the devices assembled with 30-nmdiameter Au NPs at various temperatures; B,C) I–V curves of the devices assembled with 20-nm (B) and 30-nm (C) diameter Au NPs at T=4.2 K showing the experimental data an ...
... nanogap devices assembled with oligonucleotide-modified Au nanoparticle devices: A) I–V curves of the devices assembled with 30-nmdiameter Au NPs at various temperatures; B,C) I–V curves of the devices assembled with 20-nm (B) and 30-nm (C) diameter Au NPs at T=4.2 K showing the experimental data an ...
Agarose gel electrophoresis
... selectively amplifying defined sequences/regions of DNA/RNA from an initial complex source of nucleic acid - generates sufficient for subsequent analysis and/or manipulation Amplification of a small amount of DNA using specific DNA primers (a common method of creating copies of specific fragments ...
... selectively amplifying defined sequences/regions of DNA/RNA from an initial complex source of nucleic acid - generates sufficient for subsequent analysis and/or manipulation Amplification of a small amount of DNA using specific DNA primers (a common method of creating copies of specific fragments ...
Quizzes
... Name one macroscopic (not molecular/cellualr) feature that the following organisms have in common. You must use a different answer for each question. ...
... Name one macroscopic (not molecular/cellualr) feature that the following organisms have in common. You must use a different answer for each question. ...
File
... prokaryotes have a circular DNA- means no problem with ends eukaryotes have linear DNA - problem with replicating ends (telemers); ends have repeat sequencesenzyme telemerase can extend ends up to an early age; after that every time DNA replicates, it is shortened. prokaryote - one origin of replica ...
... prokaryotes have a circular DNA- means no problem with ends eukaryotes have linear DNA - problem with replicating ends (telemers); ends have repeat sequencesenzyme telemerase can extend ends up to an early age; after that every time DNA replicates, it is shortened. prokaryote - one origin of replica ...
DNA, RNA, Proteins
... USE THE mRNA CODE WHEEL to tell the amino acid sequence coded for by the following message: U C A ...
... USE THE mRNA CODE WHEEL to tell the amino acid sequence coded for by the following message: U C A ...
Proteins
... perform specific functions for the organism; therefore, individual cells differentiate and become specialized in structure and function. Differentiation happens due to selective gene expression – some genes are turned off, some are turned on. Internal and external environments can influence gene ...
... perform specific functions for the organism; therefore, individual cells differentiate and become specialized in structure and function. Differentiation happens due to selective gene expression – some genes are turned off, some are turned on. Internal and external environments can influence gene ...
Genetics Review Sheet
... What is a gene? Where are chromosomes located? 2 main scientists that established the structure of DNA? Female scientist who paved the way for them? Shape of DNA? Sugar of DNA? 4 bases of DNA? What pairs with what? MITOSIS Resources: Mitosis Poster During what stage of mitosis does DNA replicate? Ho ...
... What is a gene? Where are chromosomes located? 2 main scientists that established the structure of DNA? Female scientist who paved the way for them? Shape of DNA? Sugar of DNA? 4 bases of DNA? What pairs with what? MITOSIS Resources: Mitosis Poster During what stage of mitosis does DNA replicate? Ho ...
What is a GENE? - West East University
... The sex cells of any organism--sperm or ova (eggs)--are haploid. Each one contains only half the number of genes of the original diploid germ cell from which it was derived during meiosis. The Vocabulary of Genetics gene: a unit of inheritance; a sequence of DNA that codes for a particular polypept ...
... The sex cells of any organism--sperm or ova (eggs)--are haploid. Each one contains only half the number of genes of the original diploid germ cell from which it was derived during meiosis. The Vocabulary of Genetics gene: a unit of inheritance; a sequence of DNA that codes for a particular polypept ...
Biogenetic Engineering & Manipulating Genes
... • PCR (polymerase chain reaction) • Gel electrophoresis • Restriction fragment analysis (RFLPs) • Southern blotting • DNA sequencing • Human genome project ...
... • PCR (polymerase chain reaction) • Gel electrophoresis • Restriction fragment analysis (RFLPs) • Southern blotting • DNA sequencing • Human genome project ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.