Whole genome sequencing - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... • Learn how to prepare raw data from the sequencer for further bioinformatic analysis. • Be able to use tools for In silico detection of plasmid, resistance and virulence genes. • Be able to perform global and local WGS analysis to determine clonal relationship of ...
... • Learn how to prepare raw data from the sequencer for further bioinformatic analysis. • Be able to use tools for In silico detection of plasmid, resistance and virulence genes. • Be able to perform global and local WGS analysis to determine clonal relationship of ...
Document
... • Progeny = average of mother & father BVs • Assumed full sibs were identical • Available SNP information can be used to supplement the traditional approach • See difference in full-sibs at birth ...
... • Progeny = average of mother & father BVs • Assumed full sibs were identical • Available SNP information can be used to supplement the traditional approach • See difference in full-sibs at birth ...
1 Lecture 24 – Bacterial genetics I. Prokaryotes – an overview A
... 1. # recombinants increases with time 2. for each, is a time before which no recombinants 3. intercept with x-axis is time of entry 4. # recombinants reaches max, which decreases as TOE increases G. F’ plasmid 1. F may excise from Hfr 2. sometimes excision imprecise, plasmid includes chromosomal seq ...
... 1. # recombinants increases with time 2. for each, is a time before which no recombinants 3. intercept with x-axis is time of entry 4. # recombinants reaches max, which decreases as TOE increases G. F’ plasmid 1. F may excise from Hfr 2. sometimes excision imprecise, plasmid includes chromosomal seq ...
High Frequency of Recombination (Hfr)
... ...bacteria exhibiting a high frequency of recombination, – an alteration DNA sequence such that the genotype of subsequent individuals differs from the parent, ...
... ...bacteria exhibiting a high frequency of recombination, – an alteration DNA sequence such that the genotype of subsequent individuals differs from the parent, ...
Ch. 11 How Genes are Control led
... – Inheritance of traits transmitted by mechanisms that do not alter the sequence of nucleotides in DNA – Chemical modification of DNA bases or histone proteins can result in epigenetic inheritance ...
... – Inheritance of traits transmitted by mechanisms that do not alter the sequence of nucleotides in DNA – Chemical modification of DNA bases or histone proteins can result in epigenetic inheritance ...
This is a test - DNALC::Protocols
... A chromosome is a continuous DNA molecule that can be thousands or millions of base pairs long. The vast length of chromosomes posed a problem for scientists who were trying to isolate and study the stretches of DNA that make up genes. The discovery of restriction enzymes in 1962 gave scientist the ...
... A chromosome is a continuous DNA molecule that can be thousands or millions of base pairs long. The vast length of chromosomes posed a problem for scientists who were trying to isolate and study the stretches of DNA that make up genes. The discovery of restriction enzymes in 1962 gave scientist the ...
DNA sequencing
... DNA As the negative charge increases with size, big DNA molecules would move more quickly But bigger molecules move more slowly through the gel Gives a steady and fine separation of DNA molecules by size Molecules which differ by only one nucleotide in their length can be separated. ...
... DNA As the negative charge increases with size, big DNA molecules would move more quickly But bigger molecules move more slowly through the gel Gives a steady and fine separation of DNA molecules by size Molecules which differ by only one nucleotide in their length can be separated. ...
PEARSON
... • By adding ‘toughness genes’, scientists can make plants more tolerant of frost, drought and salinity (salt level). These genes can be turned ‘off’ and ‘on’ in different parts of the plant. Genetic modification is one tool that farmers can use to maintain or increase crop yields as the climate cha ...
... • By adding ‘toughness genes’, scientists can make plants more tolerant of frost, drought and salinity (salt level). These genes can be turned ‘off’ and ‘on’ in different parts of the plant. Genetic modification is one tool that farmers can use to maintain or increase crop yields as the climate cha ...
Document
... • made up of amino acids • 20 amino acids • Chromosome • self-replicating structure of cells containing the cellular DNA that bears in its nucleotide sequence the linear array of genes ...
... • made up of amino acids • 20 amino acids • Chromosome • self-replicating structure of cells containing the cellular DNA that bears in its nucleotide sequence the linear array of genes ...
Chapter 11 – What is DNA and how does it work?
... 20.) Put the steps of DNA replication in order: A.) New complementary nucleotides move in to match both halves of the DNA ladder. B.) Two identical DNA molecules are formed! C.) They form hydrogen bonds with the old nucleotides. D.) DNA unzips at the hydrogen bonds. ...
... 20.) Put the steps of DNA replication in order: A.) New complementary nucleotides move in to match both halves of the DNA ladder. B.) Two identical DNA molecules are formed! C.) They form hydrogen bonds with the old nucleotides. D.) DNA unzips at the hydrogen bonds. ...
BI0 10-3 P0WERPOINT
... • Genes that are close to each other on the same chromosome are said to be “linked.” • Genes that are linked on the same chromosome usually do not independently assort • Fruit fly was used to study linkage • When crossing over occurs, genes that are close together in location on a homologous pair ma ...
... • Genes that are close to each other on the same chromosome are said to be “linked.” • Genes that are linked on the same chromosome usually do not independently assort • Fruit fly was used to study linkage • When crossing over occurs, genes that are close together in location on a homologous pair ma ...
Exercise - GEP Community Server
... and the stop codon is on the left. Click on the Augustus004 and a box appears that allows you to Show Details; click here and a view of the gene sequence can be seen. Be sure to scroll down until you can see the color-coded sequence. This provides an exact view of 5’-UTR (brown), exons (green), intr ...
... and the stop codon is on the left. Click on the Augustus004 and a box appears that allows you to Show Details; click here and a view of the gene sequence can be seen. Be sure to scroll down until you can see the color-coded sequence. This provides an exact view of 5’-UTR (brown), exons (green), intr ...
doc
... 5. Review the process of transcription. Have students write down the RNA sequence that would come from the DNA on the board. 6. Pass out the supplies: base templates, paper, scissors, and glue or tape. Using their templates of the four RNA nitrogen bases, have students cut out the correct number of ...
... 5. Review the process of transcription. Have students write down the RNA sequence that would come from the DNA on the board. 6. Pass out the supplies: base templates, paper, scissors, and glue or tape. Using their templates of the four RNA nitrogen bases, have students cut out the correct number of ...
High Frequency of Recombination (Hfr)
... ...bacteria exhibiting a high frequency of recombination, – an alteration DNA sequence such that the genotype of subsequent individuals differs from the parent, ...
... ...bacteria exhibiting a high frequency of recombination, – an alteration DNA sequence such that the genotype of subsequent individuals differs from the parent, ...
Please read the following information in your groups. Make sure you
... • Only a few mutated cells that do survive lose their ability to maintain normal cell growth. • Potentially cancerous cells are often destroyed by the body’s immune system. • DNA and its associated repair enzymes have a precise self-checking system that cuts and repairs any abnormal DNA segments bef ...
... • Only a few mutated cells that do survive lose their ability to maintain normal cell growth. • Potentially cancerous cells are often destroyed by the body’s immune system. • DNA and its associated repair enzymes have a precise self-checking system that cuts and repairs any abnormal DNA segments bef ...
ch 12 quick check answers
... Target DNA must be denatured before it can be located with a probe. True: Target DNA must be denatured (made single stranded) before it can be located with a probe. The probe is single stranded and it can pair with a complementary base sequence in the single-stranded target DNA. ...
... Target DNA must be denatured before it can be located with a probe. True: Target DNA must be denatured (made single stranded) before it can be located with a probe. The probe is single stranded and it can pair with a complementary base sequence in the single-stranded target DNA. ...
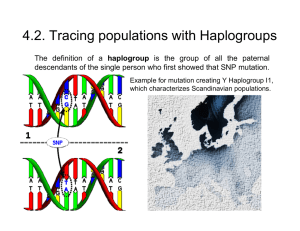
4.2. Tracing populations with Haplogroups
... Is there indication for genetic linkage? Based on lack of identification of any Neanderthal genes in human DNA and on results of theoretical population models the maximum initial input of Neanderthal genes into the Paleolithic European gene pool has been estimated to lie between 0.02% and 0.09%. ...
... Is there indication for genetic linkage? Based on lack of identification of any Neanderthal genes in human DNA and on results of theoretical population models the maximum initial input of Neanderthal genes into the Paleolithic European gene pool has been estimated to lie between 0.02% and 0.09%. ...
DNA
... code? Why or why not? How do the proteins made affect the type and function of cells? Cells do not make all of the proteins for which they have genes (DNA). The structure and function of each cell are determined by the types of proteins present. 2. Consider what you now know about genes and protein ...
... code? Why or why not? How do the proteins made affect the type and function of cells? Cells do not make all of the proteins for which they have genes (DNA). The structure and function of each cell are determined by the types of proteins present. 2. Consider what you now know about genes and protein ...
FINAL_FALL2005frmHw.doc
... c. intermediate between organisms that are homozygous for the recessive allele and organisms that are homozygous for the dominant allele ...
... c. intermediate between organisms that are homozygous for the recessive allele and organisms that are homozygous for the dominant allele ...
슬라이드 1
... Tight packing high melting point Solid at room temperature more double bonds liquid at room temperature ...
... Tight packing high melting point Solid at room temperature more double bonds liquid at room temperature ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.