Chapter 17: Microbial taxonomy
... classification and determination of phylogenetic relationships Genomic Finger Printing does not involve nucleotide sequencing Can be used because of multicopies of highly conserved and repetitive DNA sequences present in most gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria Multicopies can be obt ...
... classification and determination of phylogenetic relationships Genomic Finger Printing does not involve nucleotide sequencing Can be used because of multicopies of highly conserved and repetitive DNA sequences present in most gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria Multicopies can be obt ...
Molecular Genetics II (cont.) Mutation
... genes or translocations of genes from one chromosome to f h t another. Major rearrangements may or may not have phenotypic consequences. ...
... genes or translocations of genes from one chromosome to f h t another. Major rearrangements may or may not have phenotypic consequences. ...
1406 Topics for Practical Exam II
... purpose of each reagent, all starting materials and ending products of respiration by yeast, and any chemical detection reagent used. Be able to interpret the results obtained from the experiments that were performed and demonstrated. What would have happened if the yeast had been boiled before use? ...
... purpose of each reagent, all starting materials and ending products of respiration by yeast, and any chemical detection reagent used. Be able to interpret the results obtained from the experiments that were performed and demonstrated. What would have happened if the yeast had been boiled before use? ...
recombinant DNA. Lesson Overview
... In nature this bacterium inserts a small DNA plasmid that produces tumors in a plant’s cells. Scientists can deactivate the plasmid’s tumor-producing gene and replace it with a piece of recombinant DNA.The recombinant plasmid can then be used to infect and transform plant cells. The transformed cell ...
... In nature this bacterium inserts a small DNA plasmid that produces tumors in a plant’s cells. Scientists can deactivate the plasmid’s tumor-producing gene and replace it with a piece of recombinant DNA.The recombinant plasmid can then be used to infect and transform plant cells. The transformed cell ...
document
... Craig Venter (leading scientists of the human genome project): “This tells me that genes can’t possibly explain all of what makes us what we are.” Venter, 2001, Science 291, 1304 Human Genome Project, 2001 ...
... Craig Venter (leading scientists of the human genome project): “This tells me that genes can’t possibly explain all of what makes us what we are.” Venter, 2001, Science 291, 1304 Human Genome Project, 2001 ...
TT2007 Lecture 8 HB
... fertilization. This is explained in modern terms by reassortment during meiosis allele- any one of the alternative forms of a gene homozygous organism- organism having the same allele of a gene on the two homologous chromosomes heterozygous organism- carrying dissimilar alleles of a gene(s); not hom ...
... fertilization. This is explained in modern terms by reassortment during meiosis allele- any one of the alternative forms of a gene homozygous organism- organism having the same allele of a gene on the two homologous chromosomes heterozygous organism- carrying dissimilar alleles of a gene(s); not hom ...
A different PowerPoint that combines the
... order of nucleotides on mRNA and have that tell us the order of amino acids within each protein • As there are 20 amino acids and only 4 different bases each nucleotide on its own cant specify the position of a different amino acid ...
... order of nucleotides on mRNA and have that tell us the order of amino acids within each protein • As there are 20 amino acids and only 4 different bases each nucleotide on its own cant specify the position of a different amino acid ...
Bchm 2000 Problem Set 3 Spring 2008 1. You
... b. Provide three characteristics which differ between A-DNA and BDNA. c. Provide two characteristics which are the same in A-DNA and BDNA. d. What is the name of the third type of double helical DNA next to Aand B-DNA? 12. mRNA processing: a. List the three main events in eucaryotic mRNA processing ...
... b. Provide three characteristics which differ between A-DNA and BDNA. c. Provide two characteristics which are the same in A-DNA and BDNA. d. What is the name of the third type of double helical DNA next to Aand B-DNA? 12. mRNA processing: a. List the three main events in eucaryotic mRNA processing ...
FAQ on Genetic Engineering
... One of the earliest discoveries on what DNA does, besides providing for its own replication, is that certain stretches, called genes, specifies the structure of proteins that are made, through a ‘genetic code’. Three successive bases, a ‘triplet’, codes for one of twenty different amino acids that a ...
... One of the earliest discoveries on what DNA does, besides providing for its own replication, is that certain stretches, called genes, specifies the structure of proteins that are made, through a ‘genetic code’. Three successive bases, a ‘triplet’, codes for one of twenty different amino acids that a ...
One Gene-one polypeptide:
... - Each gene codes for the production of a specific polypeptide -Beadle and Tatum first showed a direct relationship between genes and enzymes, which they put forward as the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis -Since a different gene encodes each distinct polypeptide, their hypothesis was restated as the ...
... - Each gene codes for the production of a specific polypeptide -Beadle and Tatum first showed a direct relationship between genes and enzymes, which they put forward as the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis -Since a different gene encodes each distinct polypeptide, their hypothesis was restated as the ...
Pedigree Charts and Detecting Disorders
... 3. Ultrasound – non-invasive procedure of bouncing sound waves off of a fetus to produce its image. a. Can detect abnormalities in bone & muscle but may be disruptive to developing cells (ADD/ADHD). 4. Amniocentesis – invasive procedure by which a long needle is placed into the amniotic sac of cells ...
... 3. Ultrasound – non-invasive procedure of bouncing sound waves off of a fetus to produce its image. a. Can detect abnormalities in bone & muscle but may be disruptive to developing cells (ADD/ADHD). 4. Amniocentesis – invasive procedure by which a long needle is placed into the amniotic sac of cells ...
Exam - National Biology Competition
... the protein forms a covalent bond with a substrate molecule as part of the catalytic process. Which statement is CORRECT? a. As a catalyst, the enzyme changes the equilibrium of the reaction. b. Enzymes do not form covalent bonds with substrates during reactions, thus the experimental finding is in ...
... the protein forms a covalent bond with a substrate molecule as part of the catalytic process. Which statement is CORRECT? a. As a catalyst, the enzyme changes the equilibrium of the reaction. b. Enzymes do not form covalent bonds with substrates during reactions, thus the experimental finding is in ...
Genetics 314 - Spring 2005
... b) Why would synthesizing a gene based on the mRNA base sequence produce the desired protein? If the DNA sequence of the gene is based on the mRNA isolated from the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell the introns will not be presence in the sequence because mRNA in the cytoplasm has been processed so no ...
... b) Why would synthesizing a gene based on the mRNA base sequence produce the desired protein? If the DNA sequence of the gene is based on the mRNA isolated from the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell the introns will not be presence in the sequence because mRNA in the cytoplasm has been processed so no ...
Messenger RNA profiling: a prototype method to supplant
... Why use mRNA to identify body fluids? ...
... Why use mRNA to identify body fluids? ...
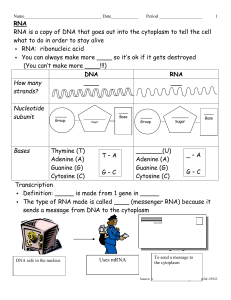
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... RNA is a copy of DNA that goes out into the cytoplasm to tell the cell what to do in order to stay alive RNA: ribonucleic acid You can always make more ____ so it’s ok if it gets destroyed (You can’t make more ____!!!) DNA RNA How many ____ ___ strands? Nucleotide subunit ...
... RNA is a copy of DNA that goes out into the cytoplasm to tell the cell what to do in order to stay alive RNA: ribonucleic acid You can always make more ____ so it’s ok if it gets destroyed (You can’t make more ____!!!) DNA RNA How many ____ ___ strands? Nucleotide subunit ...
revision notes - Victoria University
... At Metaphase 1, the double chromosomes line up in homologous (or matching) pairs. Crossing over (exchange of genetic material) can occur at one or more places between adjacent chromatids from different chromosomes. The point where crossing over occurs is a chiasma. The centromeres DO NOT separate at ...
... At Metaphase 1, the double chromosomes line up in homologous (or matching) pairs. Crossing over (exchange of genetic material) can occur at one or more places between adjacent chromatids from different chromosomes. The point where crossing over occurs is a chiasma. The centromeres DO NOT separate at ...
Linkage, Recombination, and Crossing Over
... genes are unlinked. There are two ways in which genes maybe unlinked: – They may be on separate chromosomes. – They may be far apart on the same chromosome. ...
... genes are unlinked. There are two ways in which genes maybe unlinked: – They may be on separate chromosomes. – They may be far apart on the same chromosome. ...
Lecture 14: Nucleic Acids and DNA Replication
... Does not limit linear sequence along the length of a DNA strand (iii) Suggests a general mechanism for DNA replication--bases form specific pairs, therefore the information in one strand compliments the other IV. ...
... Does not limit linear sequence along the length of a DNA strand (iii) Suggests a general mechanism for DNA replication--bases form specific pairs, therefore the information in one strand compliments the other IV. ...
BLOOM HELICASE (and BLOOM SYNDROME)
... delATCTGA/insTAGATTC @ position 2281 which is known as a blmAsh mutation ...
... delATCTGA/insTAGATTC @ position 2281 which is known as a blmAsh mutation ...
DNA & RNA
... carries code from DNA to ribosomes rRNA and t-RNA images from © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved mRNA image from http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/tmp/labeling/1140654_dyn.gif ...
... carries code from DNA to ribosomes rRNA and t-RNA images from © Pearson Education Inc, publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved mRNA image from http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/tmp/labeling/1140654_dyn.gif ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.