Principles of cell
... mutagenesis can be used to generate a specific nucleotide substitution in a coding sequence of a gene. This is achieved by using M13 vectors to generate singlestranded recombinant DNA ...
... mutagenesis can be used to generate a specific nucleotide substitution in a coding sequence of a gene. This is achieved by using M13 vectors to generate singlestranded recombinant DNA ...
Protein Synthesis
... monomers and they are formed at the ribosomes! Proteins can be enzymes, which catalyze and regulate chemical reactions. Proteins also make up our structure! ...
... monomers and they are formed at the ribosomes! Proteins can be enzymes, which catalyze and regulate chemical reactions. Proteins also make up our structure! ...
Why Should Our Community Care?
... how they work, the epigenetic factors involved, etc. Synthetic organisms may be both powerful and UNPREDICTABLE The synthetic biologist may not be able to correct the problems they cause. ...
... how they work, the epigenetic factors involved, etc. Synthetic organisms may be both powerful and UNPREDICTABLE The synthetic biologist may not be able to correct the problems they cause. ...
pARA-R Restriction Digest: An Introduction to Plasmids and
... pARA-R Restriction Digest: An Introduction to Plasmids and Restriction Enzymes ...
... pARA-R Restriction Digest: An Introduction to Plasmids and Restriction Enzymes ...
DNA, Protein Synth, Mutations
... 2.1 Mutations I. Types of Gene Mutations • mutations are often a bad thing because the protein does not work and your body needs it to function. These are known as NEGATIVE MUTATIONS and they DECREASE_ survival rates. • e.g. mutated gene SICKLE-CELL ANEMIA (misshapen red blood cells that don’t ca ...
... 2.1 Mutations I. Types of Gene Mutations • mutations are often a bad thing because the protein does not work and your body needs it to function. These are known as NEGATIVE MUTATIONS and they DECREASE_ survival rates. • e.g. mutated gene SICKLE-CELL ANEMIA (misshapen red blood cells that don’t ca ...
RNA Synthesis (Transcription)
... Process of DNA directed RNA synthesis (copying process) (genes in DNA ...
... Process of DNA directed RNA synthesis (copying process) (genes in DNA ...
Ninth Grade Biology Unit 3 – Growth and Heredity Asexual and
... Working in groups, students write down the name of all the diseases that they believe are genetically related. The students will write their responses on a small piece of whiteboard or poster board. The teacher will call on each group to share their responses and discuss. As the discussion progresse ...
... Working in groups, students write down the name of all the diseases that they believe are genetically related. The students will write their responses on a small piece of whiteboard or poster board. The teacher will call on each group to share their responses and discuss. As the discussion progresse ...
BIOL 1101 Introduction to Human Genetics
... 1. Recognize and explain the major concepts and principles of scientific theories of Classic, Molecular and Population Genetics. More important, they should be able to apply those concepts and principles to new situations in written exams. (2a, 3a) 2. Identify the basic steps of the scientific metho ...
... 1. Recognize and explain the major concepts and principles of scientific theories of Classic, Molecular and Population Genetics. More important, they should be able to apply those concepts and principles to new situations in written exams. (2a, 3a) 2. Identify the basic steps of the scientific metho ...
BACTERIAL TRANSFORMATION Lab 15
... of DNA so that this naturally occurring means of genetic alteration can take place more efficiently. In 1970, it was discovered that certain conditions can help bacterial cells absorb exogenous (free) DNA. Cells treated in this manner have been made "competent" to take up exogenous DNA, significantl ...
... of DNA so that this naturally occurring means of genetic alteration can take place more efficiently. In 1970, it was discovered that certain conditions can help bacterial cells absorb exogenous (free) DNA. Cells treated in this manner have been made "competent" to take up exogenous DNA, significantl ...
Chapter 4: DNA, Genes, and Protein Synthesis
... Describe the difference between haploid and diploid cells and where they are found. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ...
... Describe the difference between haploid and diploid cells and where they are found. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ...
Biological Science, 4e (Freeman)
... A) Post-translational control doesn’t cost a lot of energy, and is useful when a high efficiency of control is required. The downside is that it is relatively slow. B) Post-translational control is very fast and is useful when a quick response to a changing environment is required. The downside is t ...
... A) Post-translational control doesn’t cost a lot of energy, and is useful when a high efficiency of control is required. The downside is that it is relatively slow. B) Post-translational control is very fast and is useful when a quick response to a changing environment is required. The downside is t ...
Sample exam #1
... 7. [5 ] Watson & Crick s structure for DNA relied to a large extent upon X ray crystallography data from Maurice Wilkins and Roslyn Franklin, and also on an observation called Chargaff s Rule , which stated that in any DNA, Watson & Crick s structure consisted of 2 strand of DNA bound together by __ ...
... 7. [5 ] Watson & Crick s structure for DNA relied to a large extent upon X ray crystallography data from Maurice Wilkins and Roslyn Franklin, and also on an observation called Chargaff s Rule , which stated that in any DNA, Watson & Crick s structure consisted of 2 strand of DNA bound together by __ ...
Slide 1
... Where y is the initial number of DNA copies and n is the number of thermal cycles If you start with 1000 copies, how many copies are made in 32 cycles? ...
... Where y is the initial number of DNA copies and n is the number of thermal cycles If you start with 1000 copies, how many copies are made in 32 cycles? ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... significant affect as it can “knock out” large segments of the DNA (100 to 1000s of genes ...
... significant affect as it can “knock out” large segments of the DNA (100 to 1000s of genes ...
DNA Replication
... • When completed the replication bubbles will create four strands of DNA • One original strand (daughter strand) will be attached to an older strand (parental strand) • This means that DNA conserved through the process of DNA replication ...
... • When completed the replication bubbles will create four strands of DNA • One original strand (daughter strand) will be attached to an older strand (parental strand) • This means that DNA conserved through the process of DNA replication ...
1 What makes a family? Cells, Genes, Chromosomes and Traits
... What makes a family? Cells, Genes, Chromosomes and Traits Genes ...
... What makes a family? Cells, Genes, Chromosomes and Traits Genes ...
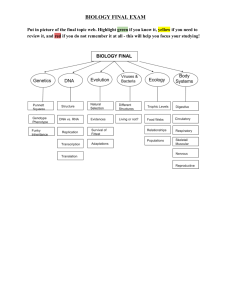
biology final exam - bhsbiologycheever
... supports the evolutionary relationship of these animals? a. the animals have different ancestries but have adapted to similar environments b. the animals share a common ancestry but have adapted to different environments c. the animals at one time lived in different environments but how share an ...
... supports the evolutionary relationship of these animals? a. the animals have different ancestries but have adapted to similar environments b. the animals share a common ancestry but have adapted to different environments c. the animals at one time lived in different environments but how share an ...
Gregor Mendel Mendel`s 7 Pea Plant Traits
... characteristic are called TRAITS. •Some forms are DOMINANT •Some forms are RECESSIVE ...
... characteristic are called TRAITS. •Some forms are DOMINANT •Some forms are RECESSIVE ...
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
... resistance (Ampr) protein. • After the transformation, the cells are grown on a solid medium called an agar plate. This medium will contain the antibiotic ampicillin. • In the presence of the ampicillin, only the bacteria containing the pGLO plasmid will have the Ampr protein which will break down t ...
... resistance (Ampr) protein. • After the transformation, the cells are grown on a solid medium called an agar plate. This medium will contain the antibiotic ampicillin. • In the presence of the ampicillin, only the bacteria containing the pGLO plasmid will have the Ampr protein which will break down t ...
Lecture 27
... Watson-Crick bp structure will allow any sequence on one polynucleotide strand as long as the opposite strand has complementary sequence. Each polynucleotide strand can act as the template for its complementary strand. In order to replicate, the parental strands must separate so that a complementary ...
... Watson-Crick bp structure will allow any sequence on one polynucleotide strand as long as the opposite strand has complementary sequence. Each polynucleotide strand can act as the template for its complementary strand. In order to replicate, the parental strands must separate so that a complementary ...
PPT File
... • The foreign allele replaces the native allele in the bacterial chromosome by genetic recombination. • The resulting cell is now recombinant with DNA derived from two different cells. ...
... • The foreign allele replaces the native allele in the bacterial chromosome by genetic recombination. • The resulting cell is now recombinant with DNA derived from two different cells. ...
Biology 155 Practice Exam 3 Name
... recessive trait. If a man who is noncolorblind marries a noncolorblind woman whose father was colorblind, what proportion of their sons and daughters should be colorblind? a. all sons, 1/2 daughters b. no sons, 1/2 daughters c. 1/2 sons, no daughters d. 1/2 sons, 1/2 daughters 12. For a single trait ...
... recessive trait. If a man who is noncolorblind marries a noncolorblind woman whose father was colorblind, what proportion of their sons and daughters should be colorblind? a. all sons, 1/2 daughters b. no sons, 1/2 daughters c. 1/2 sons, no daughters d. 1/2 sons, 1/2 daughters 12. For a single trait ...
Powerpoint Slides
... CONCENTRATION of nucleic acid. •Plots of this are called Cot curves, which are much like ...
... CONCENTRATION of nucleic acid. •Plots of this are called Cot curves, which are much like ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.