Biosimilars PPTX
... The most common DNA shape illustrated by artists and scientists looks a lot like a twisting ladder that scientists call a double helix. DNA also folds and coils itself into more complex shapes. The coiled shape makes it very small. In fact, it is small enough to easily fit inside and any of our cell ...
... The most common DNA shape illustrated by artists and scientists looks a lot like a twisting ladder that scientists call a double helix. DNA also folds and coils itself into more complex shapes. The coiled shape makes it very small. In fact, it is small enough to easily fit inside and any of our cell ...
Nutrigenomics? Epigenetics? The must-know
... nutrigenomics enables us avoid developing that same disease by choosing foods or supplements known to improve the expression of the defective gene(s). ...
... nutrigenomics enables us avoid developing that same disease by choosing foods or supplements known to improve the expression of the defective gene(s). ...
GENE TECHNOLOGY - mf011
... Bacterial restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules at specific DNA sequences called restriction sites A restriction enzyme usually makes many cuts, yielding restriction fragments The most useful restriction enzymes cut DNA in a staggered way, producing fragments with “sticky ends” that bond with comple ...
... Bacterial restriction enzymes cut DNA molecules at specific DNA sequences called restriction sites A restriction enzyme usually makes many cuts, yielding restriction fragments The most useful restriction enzymes cut DNA in a staggered way, producing fragments with “sticky ends” that bond with comple ...
End of chapter 14 questions and answers from the text book
... The sequence of bases in a molecule of DNA codes for proteins. Different sequences of bases code for different proteins. The genetic code, however, is degenerate. Although the base sequence for AGT codes for serine, other sequences may also code for this same amino acid. There are 4 base sequences w ...
... The sequence of bases in a molecule of DNA codes for proteins. Different sequences of bases code for different proteins. The genetic code, however, is degenerate. Although the base sequence for AGT codes for serine, other sequences may also code for this same amino acid. There are 4 base sequences w ...
Document
... Bodies Cells DNA Bodies are made up of cells All cells run on a set of instructions spelled out in DNA ...
... Bodies Cells DNA Bodies are made up of cells All cells run on a set of instructions spelled out in DNA ...
File
... addition of ribose nucleotides into an RNA molecule (pink). The nucleotides in the RNA are complementary to the template strand of the DNA. Begins at 5 and works to 3 C) Termination – At the end of a gene, RNA polymerase encounters a DNA sequence called a termination signal. RNA polymerase detaches ...
... addition of ribose nucleotides into an RNA molecule (pink). The nucleotides in the RNA are complementary to the template strand of the DNA. Begins at 5 and works to 3 C) Termination – At the end of a gene, RNA polymerase encounters a DNA sequence called a termination signal. RNA polymerase detaches ...
Ch8MicrobialGenetics
... Genetic Transfer and Recombination Vertical gene transfer: Occurs during reproduction between generations of cells. Horizontal (lateral) gene transfer: Transfer of genes between cells of the same generation. Leads to genetic recombination Three mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer: ...
... Genetic Transfer and Recombination Vertical gene transfer: Occurs during reproduction between generations of cells. Horizontal (lateral) gene transfer: Transfer of genes between cells of the same generation. Leads to genetic recombination Three mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer: ...
Slide 1
... Two genes, A and B, exist in a population. If the frequency of chromosomes with AB=Ab=aB=ab then the genes are in equilibrium. If the frequency of one allele of gene A is seen more frequently with a particular allele of gene B, then the genes are in linkage disequilibrium. ...
... Two genes, A and B, exist in a population. If the frequency of chromosomes with AB=Ab=aB=ab then the genes are in equilibrium. If the frequency of one allele of gene A is seen more frequently with a particular allele of gene B, then the genes are in linkage disequilibrium. ...
PowerPoint file
... Genetic Transfer and Recombination Vertical gene transfer: Occurs during reproduction between generations of cells. Horizontal (lateral) gene transfer: Transfer of genes between cells of the same generation. Leads to genetic recombination Three mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer: ...
... Genetic Transfer and Recombination Vertical gene transfer: Occurs during reproduction between generations of cells. Horizontal (lateral) gene transfer: Transfer of genes between cells of the same generation. Leads to genetic recombination Three mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer: ...
How was DNA shown to be the genetic material?
... elements and that these genetic elements were probably carried on or by chromosomes. The burning question of the day was what type of molecule carried the genetic information. During the 1940's it was known that chromosomes contained both DNA and small basic proteins called histones. It was also cle ...
... elements and that these genetic elements were probably carried on or by chromosomes. The burning question of the day was what type of molecule carried the genetic information. During the 1940's it was known that chromosomes contained both DNA and small basic proteins called histones. It was also cle ...
Part 2 - Latona
... a. A stop codon signals the finished polypeptide to be released. b. The polypeptide may or may not join with other chains, then it begins folding into its unique 3-D shape ...
... a. A stop codon signals the finished polypeptide to be released. b. The polypeptide may or may not join with other chains, then it begins folding into its unique 3-D shape ...
IB Topics DNA HL
... many points in eukaryotic chromosomes. 1. replication begins at origin, strands separate b/c helicase breaks H bonds 2. Replication fork at each end of bubble (DBL strand opens to expose 2 template strands) ...
... many points in eukaryotic chromosomes. 1. replication begins at origin, strands separate b/c helicase breaks H bonds 2. Replication fork at each end of bubble (DBL strand opens to expose 2 template strands) ...
Bacterial Genome Structure, Replication and Gene regulation
... Microarray - Measuring Gene Expression of Many Genes at a Time ...
... Microarray - Measuring Gene Expression of Many Genes at a Time ...
CHAPTER 14: DNA: THE GENETIC MATERIAL
... DNA molecule. A key point of the model was the complementarity of the DNA strands, a result of the bonding of their bases, adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine. The Meselson Stahl experiments began to explain DNA replication by determining that it was a semiconservative process; each strand se ...
... DNA molecule. A key point of the model was the complementarity of the DNA strands, a result of the bonding of their bases, adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine. The Meselson Stahl experiments began to explain DNA replication by determining that it was a semiconservative process; each strand se ...
Daily Warm Ups, Q1
... element are called:______ • An atom’s Atomic Number is equal to that element’s number of :______________ • An element’s Atomic Mass is equal to its number of _________ plus its number of __________ . • To determine the number of neutrons, the ________is subtracted from the ________ ...
... element are called:______ • An atom’s Atomic Number is equal to that element’s number of :______________ • An element’s Atomic Mass is equal to its number of _________ plus its number of __________ . • To determine the number of neutrons, the ________is subtracted from the ________ ...
Protein Synthesis Practice
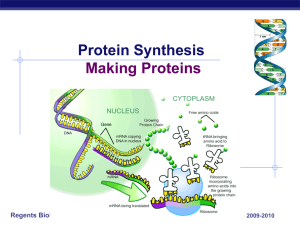
... Protein synthesis begins with DNA in the nucleus. Transcription takes place in the nucleus of the cell. During transcription messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies DNA's nucleotide sequence in the form of a complimentary RNA strand. Then the mRNA carries the DNA's information in the form of codons to ...
... Protein synthesis begins with DNA in the nucleus. Transcription takes place in the nucleus of the cell. During transcription messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies DNA's nucleotide sequence in the form of a complimentary RNA strand. Then the mRNA carries the DNA's information in the form of codons to ...
Bioinformatics - Welcome to the Official Website of
... The Motif Finding Problem: Formulation • Goal: Given a set of DNA sequences, find a set of l-mers, one from each sequence, that maximizes the consensus score • Input: A t x n matrix of DNA, and l, the length of the pattern to find • Output: An array of t starting positions s = (s1, s2, … st) maximi ...
... The Motif Finding Problem: Formulation • Goal: Given a set of DNA sequences, find a set of l-mers, one from each sequence, that maximizes the consensus score • Input: A t x n matrix of DNA, and l, the length of the pattern to find • Output: An array of t starting positions s = (s1, s2, … st) maximi ...
WAI_3024254_1_AIPLA Myriad powerpoint
... thirty years. In the early 1980s, the Office granted the first human gene patents. It is estimated that the PTO has issued 2,645 patents claiming “isolated DNA” over the past twenty-nine years, and that by 2005, had granted 40,000 DNA-related patents covering, in non-native form, twenty percent of t ...
... thirty years. In the early 1980s, the Office granted the first human gene patents. It is estimated that the PTO has issued 2,645 patents claiming “isolated DNA” over the past twenty-nine years, and that by 2005, had granted 40,000 DNA-related patents covering, in non-native form, twenty percent of t ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... – Imparts uniform negative charge to DNA / RNA • Negative charge repels nucleophilic species (e.g. hydroxyl) thus the phosphodiester bond resists hydrolytic attack. • Separation by agarose gel electrophoresis ...
... – Imparts uniform negative charge to DNA / RNA • Negative charge repels nucleophilic species (e.g. hydroxyl) thus the phosphodiester bond resists hydrolytic attack. • Separation by agarose gel electrophoresis ...
Protein-DNA interaction dataset Understanding the molecular
... Protein-DNA interaction dataset Understanding the molecular details of protein-DNA interactions is critical for deciphering the mechanisms of gene regulation. This dataset contains 56 proteins bound to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), 427 protein-DNA complexes with resolution better than 3.0 Å were extr ...
... Protein-DNA interaction dataset Understanding the molecular details of protein-DNA interactions is critical for deciphering the mechanisms of gene regulation. This dataset contains 56 proteins bound to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), 427 protein-DNA complexes with resolution better than 3.0 Å were extr ...
Protein Synthesis Lab
... DNA is organized in sections called genes. Genes code for proteins, and it is proteins that do all the work in the cell. They function as structural proteins — serving as the building blocks of cells and bodies. And they function as enzymes — directing all the chemical reactions in living organisms. ...
... DNA is organized in sections called genes. Genes code for proteins, and it is proteins that do all the work in the cell. They function as structural proteins — serving as the building blocks of cells and bodies. And they function as enzymes — directing all the chemical reactions in living organisms. ...
Worksheet
... evidence that DNA is a double helix. (1.8) Rosalind Franklin’s careful observation and interpretation of the photographic evidence was crucial to Crick’s and Watson’s successful discovery of the structure of DNA. Her work and her calculations were shown to Crick and Watson without her permission and ...
... evidence that DNA is a double helix. (1.8) Rosalind Franklin’s careful observation and interpretation of the photographic evidence was crucial to Crick’s and Watson’s successful discovery of the structure of DNA. Her work and her calculations were shown to Crick and Watson without her permission and ...
Modeling Protein Synthesis
... may cause only minor effects to the phenotype of an organism. But sometimes mutations can cause great changes to the gene and therefore greatly alter the protein that is made from that gene. This will likely have great effects on the organism, since the protein will not be able to perform its normal ...
... may cause only minor effects to the phenotype of an organism. But sometimes mutations can cause great changes to the gene and therefore greatly alter the protein that is made from that gene. This will likely have great effects on the organism, since the protein will not be able to perform its normal ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.