Chapter 24
... 1. Carefully count and account for each of the atoms and charges in the equations for the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA, the synthesis of malonyl-CoA, and the overall reaction for the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA. Answer: Malonyl-CoA is synthesized as follows Acetyl-CoA + HCO3- + ATP4- ...
... 1. Carefully count and account for each of the atoms and charges in the equations for the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA, the synthesis of malonyl-CoA, and the overall reaction for the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA from acetyl-CoA. Answer: Malonyl-CoA is synthesized as follows Acetyl-CoA + HCO3- + ATP4- ...
Balancing between respiration and fermentation - UvA-DARE
... environment.. They have developed specific regulatory systems to sense the presence, type and concentrationn of a carbon source in order to carry out the metabolic functions most appropriate too the situation (figure 1). This provides the yeast cell with energy and reducing equivalents in thee form ...
... environment.. They have developed specific regulatory systems to sense the presence, type and concentrationn of a carbon source in order to carry out the metabolic functions most appropriate too the situation (figure 1). This provides the yeast cell with energy and reducing equivalents in thee form ...
Unit: Biochemistry of Macromolecules and - Edexcel
... fatty acids. They will develop an appreciation of how the structure and properties of macromolecules are determined by the chemical structure and functional group chemistry of the building block molecules. The structure of macromolecules, including proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids and lipids ...
... fatty acids. They will develop an appreciation of how the structure and properties of macromolecules are determined by the chemical structure and functional group chemistry of the building block molecules. The structure of macromolecules, including proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids and lipids ...
lecture4
... amphipathic molecules synthesized from cholesterol in the liver and secreted from the gall bladder. Incorporation of lipids into micelles orients the ester bonds of the lipid toward the surface of the micelle, rendering the bonds more susceptible to digestion by pancreatic lipases that are in aqueou ...
... amphipathic molecules synthesized from cholesterol in the liver and secreted from the gall bladder. Incorporation of lipids into micelles orients the ester bonds of the lipid toward the surface of the micelle, rendering the bonds more susceptible to digestion by pancreatic lipases that are in aqueou ...
- Wiley Online Library
... Aims: To investigate the relationship between the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) bypass and the production of pyruvate of a multi-vitamin auxotrophic yeast Torulopsis glabrata. Methods and Results: Torulopsis glabrata CCTCC M202019, a multi-vitamin auxotrophic yeast that requires acetate f ...
... Aims: To investigate the relationship between the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) bypass and the production of pyruvate of a multi-vitamin auxotrophic yeast Torulopsis glabrata. Methods and Results: Torulopsis glabrata CCTCC M202019, a multi-vitamin auxotrophic yeast that requires acetate f ...
Enzymes I - eCurriculum
... Have two or more subunits The substrate binding sites exhibit co-operativity Are modified by reversible non-covalent binding of regulators Allosteric activators lock the enzyme in a conformation that has high affinity for the substrate Aspartate transcarbamylase ...
... Have two or more subunits The substrate binding sites exhibit co-operativity Are modified by reversible non-covalent binding of regulators Allosteric activators lock the enzyme in a conformation that has high affinity for the substrate Aspartate transcarbamylase ...
Effect of alpha-lipoic acid on blood glucose, insulin resistance, and
... improved HOMA index with no significant changes in insulin sensitivity.26 This study also showed significant decrease in erythrocyte’s GH-Px enzyme level in ALA, although the difference between the 2 groups was not considerable. In support of this finding, significantly higher activities of antioxid ...
... improved HOMA index with no significant changes in insulin sensitivity.26 This study also showed significant decrease in erythrocyte’s GH-Px enzyme level in ALA, although the difference between the 2 groups was not considerable. In support of this finding, significantly higher activities of antioxid ...
Amino Acid Oxidation, the Production of Urea, and Amino Acid
... gluconeogenesis, or to be converted to fatty acids. The energy and precursors are generated during fasting or starvation, whereas fatty acids are made during times of plenty when the body has more amino acids than it needs. During energy poor times and/or starvation, amino acids are metabolized by a ...
... gluconeogenesis, or to be converted to fatty acids. The energy and precursors are generated during fasting or starvation, whereas fatty acids are made during times of plenty when the body has more amino acids than it needs. During energy poor times and/or starvation, amino acids are metabolized by a ...
(metabolic pathways) based on functional group
... a multi-classification problem. For pathways with too few samples, such as energy metabolism and metabolism of other amino acids, the prediction accuracy is not as good as others. The prediction performance is anticipated to be improved if more samples could be collected. Totally, the overall succes ...
... a multi-classification problem. For pathways with too few samples, such as energy metabolism and metabolism of other amino acids, the prediction accuracy is not as good as others. The prediction performance is anticipated to be improved if more samples could be collected. Totally, the overall succes ...
Basic Principle in Plant Physiology
... •Amino acids released from protein turnover can be resynthesized into proteins. •Excess amino acids are degraded into specific compounds that can be used in other metabolic pathways. •This process begins with the removal of the amino group, which can be converted to urea and excreted. •The a-ketoids ...
... •Amino acids released from protein turnover can be resynthesized into proteins. •Excess amino acids are degraded into specific compounds that can be used in other metabolic pathways. •This process begins with the removal of the amino group, which can be converted to urea and excreted. •The a-ketoids ...
PPT2 - Ycmou
... therapeutic or pharmacopic values. By knowing key precursors in metabolic pathways one can also find some cure to correct the pathological condition arising out of defective metabolic pathway by targeting the key precursor. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. ...
... therapeutic or pharmacopic values. By knowing key precursors in metabolic pathways one can also find some cure to correct the pathological condition arising out of defective metabolic pathway by targeting the key precursor. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. ...
Co-enzyme derived from vitamin and their role in metabolic action
... Its phosphate derivatives are involved in many cellular processes. ...
... Its phosphate derivatives are involved in many cellular processes. ...
08_Lecture_Presentation_PC
... • Chemical chaos would result if a cell’s metabolic pathways were not tightly regulated • A cell does this by switching on or off the genes that encode specific enzymes or by regulating the activity of enzymes © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Chemical chaos would result if a cell’s metabolic pathways were not tightly regulated • A cell does this by switching on or off the genes that encode specific enzymes or by regulating the activity of enzymes © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chap. 6B Enzymes Introduction to Enzymes How Enzymes Work
... classic application of pre-steady state kinetics. In addition to its action on polypeptides, CT also catalyzes the hydrolysis of small esters and amides. These reactions are much slower than peptide hydrolysis because less binding energy is available with smaller substrates, and they are therefore e ...
... classic application of pre-steady state kinetics. In addition to its action on polypeptides, CT also catalyzes the hydrolysis of small esters and amides. These reactions are much slower than peptide hydrolysis because less binding energy is available with smaller substrates, and they are therefore e ...
Module 1 - Carbohydrates part A [1] Today, we want to talk about
... Let's begin to define carbohydrates. By name, they mean hydrates of carbon. Carbohydrates, hydrates of carbon. They are carbon surrounded by water. The simplest of carbohydrates is C6H12O6. C is for carbon, H is for hydrogen and O is for oxygen in those proportions: 6C, 12H, and 6O. Since, they are ...
... Let's begin to define carbohydrates. By name, they mean hydrates of carbon. Carbohydrates, hydrates of carbon. They are carbon surrounded by water. The simplest of carbohydrates is C6H12O6. C is for carbon, H is for hydrogen and O is for oxygen in those proportions: 6C, 12H, and 6O. Since, they are ...
Mitochondrial b
... hypoglycaemia and an inappropriate ketotic response to fasting may not be present. The concentrations of intermediary metabolites from patients with medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency and from patients with other causes of hypoketotic hypoglycaemia and hyperinsulinism, are shown in Table ...
... hypoglycaemia and an inappropriate ketotic response to fasting may not be present. The concentrations of intermediary metabolites from patients with medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency and from patients with other causes of hypoketotic hypoglycaemia and hyperinsulinism, are shown in Table ...
Topic: Exchange and functions of carbohydrates
... Glucose coming from intestinal by means of portal vena system gets to liver, where one portion of it is detained and another portion by means of general circulation gets into the cells of other organs and tissues. Glucose consumption by circulation cells occurs with the help of reduced diffusion wit ...
... Glucose coming from intestinal by means of portal vena system gets to liver, where one portion of it is detained and another portion by means of general circulation gets into the cells of other organs and tissues. Glucose consumption by circulation cells occurs with the help of reduced diffusion wit ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... • Temperature – increasing it increases rate of reaction • Temperature coefficient or Q10 is a value for the reaction that shows how much the rate increases when you increase the temperature by 10oC • At temperatures before optimum if the Q10 is 2 then the rate doubles for 10oC increase • A value of ...
... • Temperature – increasing it increases rate of reaction • Temperature coefficient or Q10 is a value for the reaction that shows how much the rate increases when you increase the temperature by 10oC • At temperatures before optimum if the Q10 is 2 then the rate doubles for 10oC increase • A value of ...
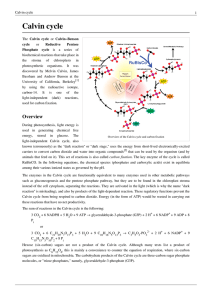
Calvin cycle
... known (erroneously) as the "dark reaction" or "dark stage," uses the energy from short-lived electronically-excited carriers to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds[2] that can be used by the organism (and by animals that feed on it). This set of reactions is also called carbon fi ...
... known (erroneously) as the "dark reaction" or "dark stage," uses the energy from short-lived electronically-excited carriers to convert carbon dioxide and water into organic compounds[2] that can be used by the organism (and by animals that feed on it). This set of reactions is also called carbon fi ...
presentation of preclinical data at the 25 th
... lower lipids through regulation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Reverse lipid transport (RLT), driven by high-density lipo- ...
... lower lipids through regulation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Reverse lipid transport (RLT), driven by high-density lipo- ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... • It consists of two, irreversible oxidative reactions, followed by a series of reversible sugar-phosphate interconversions. • No ATP is directly consumed or produced in the cycle. Carbon one of G-6-P is released as CO2, & 2 NADPH are produced for each G-6-P molecule entering the oxidative part of t ...
... • It consists of two, irreversible oxidative reactions, followed by a series of reversible sugar-phosphate interconversions. • No ATP is directly consumed or produced in the cycle. Carbon one of G-6-P is released as CO2, & 2 NADPH are produced for each G-6-P molecule entering the oxidative part of t ...
lecture notes
... produce products. maltase that converts maltose to glucose • Be regulated from a state of low activity to high activity and vice versa. e.g. some enzyme activity is inhibited by the product. • Be versatile: More than 3000 enzymes are identified ...
... produce products. maltase that converts maltose to glucose • Be regulated from a state of low activity to high activity and vice versa. e.g. some enzyme activity is inhibited by the product. • Be versatile: More than 3000 enzymes are identified ...
Carbon Flow of Heliobacteria Is Related More to Clostridia than to
... with fluoroacetate; (ii) isotopomer data; (iii) mass spectrum of photosynthetic pigments; and (iv) transcriptomic profiles. Pyruvate is the best known organic carbon source for supporting the phototrophic growth of H. modesticaldum (3, 4) and several other heliobacteria (1), and it was used for prob ...
... with fluoroacetate; (ii) isotopomer data; (iii) mass spectrum of photosynthetic pigments; and (iv) transcriptomic profiles. Pyruvate is the best known organic carbon source for supporting the phototrophic growth of H. modesticaldum (3, 4) and several other heliobacteria (1), and it was used for prob ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑















![Module 1 - Carbohydrates part A [1] Today, we want to talk about](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011192405_1-ea6cb8b8d47f58e0f04db66c477b38f9-300x300.png)