LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
... II. State whether the following are true or false, if false, give reason ...
Slide 1
... • Whether the organism is aerobic or anaerobic, that organism will undergo glycolysis. This is always the 1st step! • Glucose is converted to pyruvate (a 3-C compound) and 2 ATP are released. • This occurs in the cytoplasm ...
... • Whether the organism is aerobic or anaerobic, that organism will undergo glycolysis. This is always the 1st step! • Glucose is converted to pyruvate (a 3-C compound) and 2 ATP are released. • This occurs in the cytoplasm ...
3. CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... cycle) is a series of reactions in mitochondria that bring about the catabolism of acetyl residues, to CO2 and water in aerobic condition. • The hydrogen equivalents upon oxidation, lead to the release of most of the free energy which is captured as ATP of most of the available energy of tissue ...
... cycle) is a series of reactions in mitochondria that bring about the catabolism of acetyl residues, to CO2 and water in aerobic condition. • The hydrogen equivalents upon oxidation, lead to the release of most of the free energy which is captured as ATP of most of the available energy of tissue ...
Macromolecules
... Digestion is a process of hydrolysis where the starch is broken down into the various monosaccharides. A major product is glucose, which can be used immediately for metabolism to make energy. ...
... Digestion is a process of hydrolysis where the starch is broken down into the various monosaccharides. A major product is glucose, which can be used immediately for metabolism to make energy. ...
KINE 4010 Mock Midterm #1
... KINE 4010 Mock Midterm #1 Disclaimer: This exam does not cover the course material in its entirety and should NOT be used as the only source of studying. The questions were made by KAHSSO Peer Tutors. 1. Which of the following about ATP is false? a) It has three phosphates b) It contains a ribose su ...
... KINE 4010 Mock Midterm #1 Disclaimer: This exam does not cover the course material in its entirety and should NOT be used as the only source of studying. The questions were made by KAHSSO Peer Tutors. 1. Which of the following about ATP is false? a) It has three phosphates b) It contains a ribose su ...
What is a cell?
... No!! Not because of energy conservation. But because Q is a lower quality of energy. To convert it to mechanical energy, E, you will always get less than Q, E < Q -> Mechanical energy = high quality • Q is in the Brownian motion of atoms – larger if T grows. The randomness is measured by S (entropy) ...
... No!! Not because of energy conservation. But because Q is a lower quality of energy. To convert it to mechanical energy, E, you will always get less than Q, E < Q -> Mechanical energy = high quality • Q is in the Brownian motion of atoms – larger if T grows. The randomness is measured by S (entropy) ...
2002
... 10. A single carboxyl group and a long non-polar hydrocarbon chain is the characteristic of 1) nucleoside 2) amino acid 3) fatty acid 4) pyrimidine 11. The unique properties of water that make it necessary for life is due to its 1) pH 2) solvent nature 3) molecular structure 4) dissociation constant ...
... 10. A single carboxyl group and a long non-polar hydrocarbon chain is the characteristic of 1) nucleoside 2) amino acid 3) fatty acid 4) pyrimidine 11. The unique properties of water that make it necessary for life is due to its 1) pH 2) solvent nature 3) molecular structure 4) dissociation constant ...
SUCCINYL-CoA SYNTHETASE from a prokaryote (Lot 140901b)
... The enzyme is supplied as an ammonium sulphate suspension and should be stored at 4°C. For assay, this enzyme should be diluted in 100 mM glycylglycine buffer, pH 8.4 containing 10 mM MgCl2. Swirl to mix the enzyme suspension immediately prior to use. ...
... The enzyme is supplied as an ammonium sulphate suspension and should be stored at 4°C. For assay, this enzyme should be diluted in 100 mM glycylglycine buffer, pH 8.4 containing 10 mM MgCl2. Swirl to mix the enzyme suspension immediately prior to use. ...
File
... Creatine phosphate breaks down to release energy and phosphate that is used to convert ADP to ATP at a fast rate. This system can only support strenuous muscle activity for around 10 seconds, when the creatine phosphate supply runs out. It is restored when energy demands are low. Lactic acid metabol ...
... Creatine phosphate breaks down to release energy and phosphate that is used to convert ADP to ATP at a fast rate. This system can only support strenuous muscle activity for around 10 seconds, when the creatine phosphate supply runs out. It is restored when energy demands are low. Lactic acid metabol ...
The Central Role of Acetyl-CoA
... • The oxidation uses oxidised forms of coenzymes ultimately producing CO2, H2O and stored energy • Energy is stored directly as ATP or as reduced forms of coenzymes that ultimately reduce oxygen to H2O • Reduction of oxygen to H2O yields more ATP and oxidised form of coenzymes ...
... • The oxidation uses oxidised forms of coenzymes ultimately producing CO2, H2O and stored energy • Energy is stored directly as ATP or as reduced forms of coenzymes that ultimately reduce oxygen to H2O • Reduction of oxygen to H2O yields more ATP and oxidised form of coenzymes ...
CH2 - SCF Faculty Site Homepage
... are more likely to be converted into cholesterol than unsaturated fats. Excess cholesterol forms ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ plaques in coronary arteries reducing the blood supply to the heart. _______________________________ ...
... are more likely to be converted into cholesterol than unsaturated fats. Excess cholesterol forms ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ plaques in coronary arteries reducing the blood supply to the heart. _______________________________ ...
Organic Molecules
... Function: make any part Test to Identify: of an organism; muscle contraction Biurets Test Last source of energy ...
... Function: make any part Test to Identify: of an organism; muscle contraction Biurets Test Last source of energy ...
AP Biology Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration
... without oxygen. It only releases a small amount of ATP. Glycolysis: the first step of breaking down glucose—it splits glucose (6C) into 2 pyruvic acid molecules (3C each) ...
... without oxygen. It only releases a small amount of ATP. Glycolysis: the first step of breaking down glucose—it splits glucose (6C) into 2 pyruvic acid molecules (3C each) ...
Chapter 32 - How Animals Harvest Energy Stored in Nutrients
... Animals require a constant supply of energy to perform biological work. The energy-rich molecule ATP usually provides this energy. All animals can generate ATP by breaking down organic nutrients (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins). The energy released is used to join ADP and phosphate (Pi) to form A ...
... Animals require a constant supply of energy to perform biological work. The energy-rich molecule ATP usually provides this energy. All animals can generate ATP by breaking down organic nutrients (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins). The energy released is used to join ADP and phosphate (Pi) to form A ...
Document
... We obtain energy from fuels (carbohydrate, protein and fat) in the presence of oxygen by means of aerobic metabolic pathways. The controlled release of energy during aerobic metabolism allows for a large amount of energy in glucose to be stored as energy in ATP: Glucose + 6 O2 + 38 ADP + 39 Phosphat ...
... We obtain energy from fuels (carbohydrate, protein and fat) in the presence of oxygen by means of aerobic metabolic pathways. The controlled release of energy during aerobic metabolism allows for a large amount of energy in glucose to be stored as energy in ATP: Glucose + 6 O2 + 38 ADP + 39 Phosphat ...
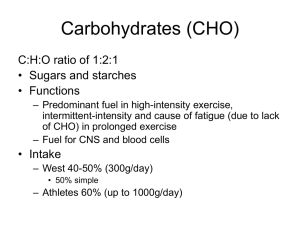
Carbohydrates (CHO)
... – Predominant fuel in high-intensity exercise, intermittent-intensity and cause of fatigue (due to lack of CHO) in prolonged exercise – Fuel for CNS and blood cells ...
... – Predominant fuel in high-intensity exercise, intermittent-intensity and cause of fatigue (due to lack of CHO) in prolonged exercise – Fuel for CNS and blood cells ...
Tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle, also called the Krebs cycle or
... acceptor (ADP) or inorganic phosphate. The rate of oxidative phosphorylation is proportional to [ADP][Pi]/[ATP]; this is known as respiratory control of energy production. The oxidation of NADH and FADH2 by the electron transport chain also stops if ADP is limiting. This is because the processes of ...
... acceptor (ADP) or inorganic phosphate. The rate of oxidative phosphorylation is proportional to [ADP][Pi]/[ATP]; this is known as respiratory control of energy production. The oxidation of NADH and FADH2 by the electron transport chain also stops if ADP is limiting. This is because the processes of ...
Reactions of the citric acid cycle
... phosphate acceptor (ADP) or inorganic phosphate. The rate of oxidative phosphorylation is proportional to [ADP][Pi]/[ATP]; this is known as respiratory control of energy production. The oxidation of NADH and FADH2 by the electron transport chain also stops if ADP is limiting. This is because the pro ...
... phosphate acceptor (ADP) or inorganic phosphate. The rate of oxidative phosphorylation is proportional to [ADP][Pi]/[ATP]; this is known as respiratory control of energy production. The oxidation of NADH and FADH2 by the electron transport chain also stops if ADP is limiting. This is because the pro ...
Cellular Respiration Food to Energy Food to Energy Calorie Questions
... • 1st – Your body uses the stored ATP (only good for a few seconds of energy) • 2nd – Your body produces ATP through lactic acid fermentation (lasts up to 90 seconds) • 3rd –Your body must go through cellular respiration for anything longer than 90 ...
... • 1st – Your body uses the stored ATP (only good for a few seconds of energy) • 2nd – Your body produces ATP through lactic acid fermentation (lasts up to 90 seconds) • 3rd –Your body must go through cellular respiration for anything longer than 90 ...
Chapter 4 - Cellular Metabolism 4.1 Introduction (p. 74) A. A living
... cytoplasm where the protein will be constructed in a process called translation. Protein Synthesis (p. 87; Fig. 4.18; Table 4.3) ...
... cytoplasm where the protein will be constructed in a process called translation. Protein Synthesis (p. 87; Fig. 4.18; Table 4.3) ...
P-glycoprotein Activation Monitored via ATP Hydrolysis and ATP
... anaesthetics, cyclic peptides, and cytotoxic drugs. ATP hydrolysis was assessed by spectroscopically monitoring the release of inorganic phosphate in inside-out cellular vesicles of MDR1-transfected cells and ATP synthesis was assessed by measuring the extracellular acidification rate, ECAR, which c ...
... anaesthetics, cyclic peptides, and cytotoxic drugs. ATP hydrolysis was assessed by spectroscopically monitoring the release of inorganic phosphate in inside-out cellular vesicles of MDR1-transfected cells and ATP synthesis was assessed by measuring the extracellular acidification rate, ECAR, which c ...
Summary of Metabolic Pathways
... • Under aerobic conditions, pyruvic acid is oxidized to acetyl coenzyme A. -Oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A yields energy in the form of NADH. -Oxidation of pyruvate can only occur if the oxidized coenzyme (NAD+) is available. • Under anaerobic conditions, the NADH which accumulates is no ...
... • Under aerobic conditions, pyruvic acid is oxidized to acetyl coenzyme A. -Oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A yields energy in the form of NADH. -Oxidation of pyruvate can only occur if the oxidized coenzyme (NAD+) is available. • Under anaerobic conditions, the NADH which accumulates is no ...
Cellular Respiration
... flowing through the ATP synthase “turbine” can generate energy that is used to combine ADP and Pi to form ATP. Since H+ has built up at high levels in the intermembrane space, it flows through ATP synthase into the matrix from its area of high concentration to its area of low concentration. As H+ fl ...
... flowing through the ATP synthase “turbine” can generate energy that is used to combine ADP and Pi to form ATP. Since H+ has built up at high levels in the intermembrane space, it flows through ATP synthase into the matrix from its area of high concentration to its area of low concentration. As H+ fl ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑