Chapter 15- Lateral mesoderm and endoderm
... Note: Blood vessels form independently of the heart, then link up Some background Info ...
... Note: Blood vessels form independently of the heart, then link up Some background Info ...
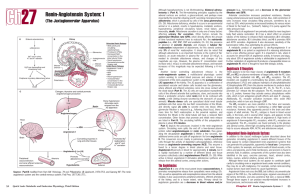
Renin-Angiotensin System: I
... pressure (e.g., hemorrhage), and a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Arteriolar constriction increases peripheral resistance, thereby raising arterial pressure back toward normal. Also, mild constriction of veins increases mean circulatory filling pressure, sometimes by as much as 20 ...
... pressure (e.g., hemorrhage), and a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR). Arteriolar constriction increases peripheral resistance, thereby raising arterial pressure back toward normal. Also, mild constriction of veins increases mean circulatory filling pressure, sometimes by as much as 20 ...
Review Sheet – Human Body Systems
... The function of the digestive system is to break down food into small nutrient molecules. The nutrient molecules are absorbed into the blood and carried to the cells of your body. You eat a slice of pizza for lunch. Your pizza consists of bread, tomato sauce, and cheese. The pizza will travel throug ...
... The function of the digestive system is to break down food into small nutrient molecules. The nutrient molecules are absorbed into the blood and carried to the cells of your body. You eat a slice of pizza for lunch. Your pizza consists of bread, tomato sauce, and cheese. The pizza will travel throug ...
Models of Cheyne-Stokes Respiration with Cardiovascular
... carbon dioxide, and this may interfere with the operation of the respiratory control center. We conjecture that poor circulation of blood in the brain may be a cause of Cheyne-Stokes respiration during ...
... carbon dioxide, and this may interfere with the operation of the respiratory control center. We conjecture that poor circulation of blood in the brain may be a cause of Cheyne-Stokes respiration during ...
Human Body Systems PPT
... Digestive: stimulates metabolism of sugars Immune: helps with immune responses Circulatory: provides main transport medium for hormones Respiration: Epinephrine increases respiration by dilating ...
... Digestive: stimulates metabolism of sugars Immune: helps with immune responses Circulatory: provides main transport medium for hormones Respiration: Epinephrine increases respiration by dilating ...
Annelida
... aortic arches *5 pairs of muscular tubes connecting the 2 vessels together *located in the anterior end *contractions cause blood to move ...
... aortic arches *5 pairs of muscular tubes connecting the 2 vessels together *located in the anterior end *contractions cause blood to move ...
External Gas Exchange
... To maintain the concentration gradients of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the alveoli. The body needs oxygen to make ATP via cell respiration. The body needs to get rid of carbon dioxide, a product of cell respiration. Oxygen needs to diffuse from the alveoli into the blood. Carbon dioxide needs to di ...
... To maintain the concentration gradients of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the alveoli. The body needs oxygen to make ATP via cell respiration. The body needs to get rid of carbon dioxide, a product of cell respiration. Oxygen needs to diffuse from the alveoli into the blood. Carbon dioxide needs to di ...
BIO 202 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
... Students are expected to attend all classes for which they are registered. Students who are unable to attend class regularly, regardless of the reason or circumstance, should withdraw from that class before poor attendance interferes with the student’s ability to achieve the objectives required in ...
... Students are expected to attend all classes for which they are registered. Students who are unable to attend class regularly, regardless of the reason or circumstance, should withdraw from that class before poor attendance interferes with the student’s ability to achieve the objectives required in ...
Animals: Circulation
... Key Concepts: How important is your circulatory system? 50% of all deaths in this country: heart disease; heart attack; diabetes; etc. 1. All cells survive by exchanging substances with their surroundings 2. Blood is the transport medium of the circulatory system 3. There are two types of circulator ...
... Key Concepts: How important is your circulatory system? 50% of all deaths in this country: heart disease; heart attack; diabetes; etc. 1. All cells survive by exchanging substances with their surroundings 2. Blood is the transport medium of the circulatory system 3. There are two types of circulator ...
Cardiovascular System Webquest
... 3. Your blood pressure is at its ______________________ when the heart ___________________, pumping the blood. This is called _______________________________________________________. 4. When the heart is at __________________, between _________________, your blood pressure ________________________. ...
... 3. Your blood pressure is at its ______________________ when the heart ___________________, pumping the blood. This is called _______________________________________________________. 4. When the heart is at __________________, between _________________, your blood pressure ________________________. ...
Document
... The diaphragm and intercostal muscles: mechanical ventilation Breath: the diaphragm and intercostal muscles stretch Exhalation: diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax Gas exchange: oxygen is replaced with carbon dioxide in the alveolar sacs through the capillaries Oxygen enters the blood into cells ...
... The diaphragm and intercostal muscles: mechanical ventilation Breath: the diaphragm and intercostal muscles stretch Exhalation: diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax Gas exchange: oxygen is replaced with carbon dioxide in the alveolar sacs through the capillaries Oxygen enters the blood into cells ...
Levels of Structural Organization Levels of Structural
... • Transport of large particles and macromolecules across plasma membranes • Exocytosis – moves substance from the cell interior to the extracellular space • Endocytosis – enables large particles and macromolecules to enter the cell • Receptor-mediated transport – uses clathrin-coated pits as the maj ...
... • Transport of large particles and macromolecules across plasma membranes • Exocytosis – moves substance from the cell interior to the extracellular space • Endocytosis – enables large particles and macromolecules to enter the cell • Receptor-mediated transport – uses clathrin-coated pits as the maj ...
B3 gcse revision notes
... In the lungs: o Oxygen diffuses into the red blood cells. o Haemoglobin combines with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. In the other organs: o Oxyhaemoglobin splits up into haemoglobin and oxygen. o Oxygen diffuses out of the red blood cell. They have a biconcave shape. This increases their surface are ...
... In the lungs: o Oxygen diffuses into the red blood cells. o Haemoglobin combines with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. In the other organs: o Oxyhaemoglobin splits up into haemoglobin and oxygen. o Oxygen diffuses out of the red blood cell. They have a biconcave shape. This increases their surface are ...
Quick Quiz
... 2. Effects on the Vascular (Blood) System High concentrations of antidiuretic hormone also cause constriction of arterioles (vasoconstriction), which leads to increased arterial pressure. A negative feedback loop exists so that increased blood pressure blocks the secretion of more ADH. ...
... 2. Effects on the Vascular (Blood) System High concentrations of antidiuretic hormone also cause constriction of arterioles (vasoconstriction), which leads to increased arterial pressure. A negative feedback loop exists so that increased blood pressure blocks the secretion of more ADH. ...
nervous system
... Bones support and protect our body The Muscular System (3 claps) Moving and grooving, muscles make us stronger The Endocrine System (3 claps) Chemical hormones cause our body to change The Reproductive System (3 claps) ...
... Bones support and protect our body The Muscular System (3 claps) Moving and grooving, muscles make us stronger The Endocrine System (3 claps) Chemical hormones cause our body to change The Reproductive System (3 claps) ...
List the eleven organ systems we will study in this unit
... 2.Homeostasis in living things is regulated by the action of a. b. c. d. ...
... 2.Homeostasis in living things is regulated by the action of a. b. c. d. ...
Functions of each organ in each organ system
... known as sweat, so it cools you and releases wastes at the same time. Kidney These organs filter from the blood a certain mixture of water, salt, and urea into what is known as urine. Ureter They are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. ...
... known as sweat, so it cools you and releases wastes at the same time. Kidney These organs filter from the blood a certain mixture of water, salt, and urea into what is known as urine. Ureter They are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. ...
Chapter 19: Blood
... Components for Building red blood cells – amino acids – iron – vitamins B12, B6, and folic acid ...
... Components for Building red blood cells – amino acids – iron – vitamins B12, B6, and folic acid ...
A Trip Through The Human Body
... 9. What hormone regulates water balance __________________ What organ produces it? P. 1037 ________________________ 10. The main endocrine organ that regulates many of the other endocrine organs is the pituitary gland. Where is the pituitary gland located? P. 1033 ...
... 9. What hormone regulates water balance __________________ What organ produces it? P. 1037 ________________________ 10. The main endocrine organ that regulates many of the other endocrine organs is the pituitary gland. Where is the pituitary gland located? P. 1033 ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.