Osmoregulation and excretion
... Controlling the internal environment Osmoregulation Nitrogenous wastes Excretory systems Mammalian excretory systems ...
... Controlling the internal environment Osmoregulation Nitrogenous wastes Excretory systems Mammalian excretory systems ...
Chapter 32 Circulation
... ventricular relaxation – Pulse – expansion & contraction of artery walls during heartbeat ...
... ventricular relaxation – Pulse – expansion & contraction of artery walls during heartbeat ...
Circulatory System
... take in a good breath of air, the oxygen passes into your blood stream. The blood travels to your heart, where it is pumped out the left side, through your aorta, to all parts of your body. Blood carries its supply of oxygen through your arteries, then through smaller capillaries, and finally delive ...
... take in a good breath of air, the oxygen passes into your blood stream. The blood travels to your heart, where it is pumped out the left side, through your aorta, to all parts of your body. Blood carries its supply of oxygen through your arteries, then through smaller capillaries, and finally delive ...
Physiological responses to exercise
... around the body where it provides the muscles with the energy it needs to perform work. The cardio respiratory system draws more oxygen into the body as a response to exercise. It does this by increasing both its breathing and heart rate to deliver an increased quality of oxygen to working muscles. ...
... around the body where it provides the muscles with the energy it needs to perform work. The cardio respiratory system draws more oxygen into the body as a response to exercise. It does this by increasing both its breathing and heart rate to deliver an increased quality of oxygen to working muscles. ...
how fish swim
... The blood flows thorough the gill filaments and secondary lamellae in the opposite direction from the water passing the gills. This is very important for getting all of the available oxygen out of the water and into the blood. If the blood flowed in the same direction as the water passing it, then t ...
... The blood flows thorough the gill filaments and secondary lamellae in the opposite direction from the water passing the gills. This is very important for getting all of the available oxygen out of the water and into the blood. If the blood flowed in the same direction as the water passing it, then t ...
the respiratory system
... thin capillary walls. At the same time CO2 & other waste move from the cells to the blood in the capillaries. The blood is now deoxygenated. The blood travels back to the heart through the veins where O2 is loaded into the blood through external respiration again. ...
... thin capillary walls. At the same time CO2 & other waste move from the cells to the blood in the capillaries. The blood is now deoxygenated. The blood travels back to the heart through the veins where O2 is loaded into the blood through external respiration again. ...
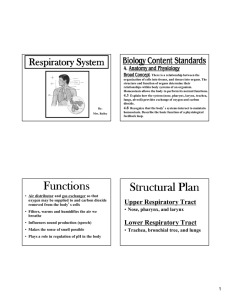
Functions Structural Plan
... organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. 4.3 Explain how the system (nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, alveoli) ...
... organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. 4.3 Explain how the system (nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lungs, alveoli) ...
Respiratory System
... the aorta and arteries to the capillaries that are in contact with individual cells The blood in the body capillaries has more oxygen than the body cells, so oxygen diffuses from the blood into the body cells The body cells have more carbon dioxide than the blood, so carbon dioxide diffuses from the ...
... the aorta and arteries to the capillaries that are in contact with individual cells The blood in the body capillaries has more oxygen than the body cells, so oxygen diffuses from the blood into the body cells The body cells have more carbon dioxide than the blood, so carbon dioxide diffuses from the ...
Unit IV-B Outline
... sinuses of the liver; fluids, nutrients, and some blood proteins flow into these spaces, maintaining the balance of glucose in the blood by removing excess amounts converting it into glycogen which is then stored. If no food has been eaten for a long time, blood reaching the liver will be low in glu ...
... sinuses of the liver; fluids, nutrients, and some blood proteins flow into these spaces, maintaining the balance of glucose in the blood by removing excess amounts converting it into glycogen which is then stored. If no food has been eaten for a long time, blood reaching the liver will be low in glu ...
ANPS 020 Black 03-28-12
... Vial capacity: maximum amount of air one can into or out of lungs in a single respiratory cycle Totally lung capacity: Total volume of lungs = vital capacity and residual capacity (avg = 6000ml males, 4200 females) GAS EXCHANGE How do you get oxygen from the air into your cells? -principle of diffus ...
... Vial capacity: maximum amount of air one can into or out of lungs in a single respiratory cycle Totally lung capacity: Total volume of lungs = vital capacity and residual capacity (avg = 6000ml males, 4200 females) GAS EXCHANGE How do you get oxygen from the air into your cells? -principle of diffus ...
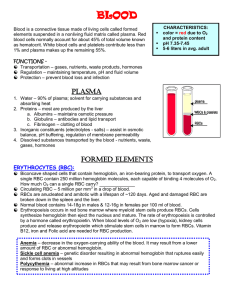
Bio 20 Blood and Immunity
... Red blood cells (erythrocytes) • Contain special protein units called hemoglobin, which is made up of 4 polypeptide chains (globin) and iron (heme). The function of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen. Also these do not have a nucleus • Carbon monoxide has a higher affinity for hemoglobin than oxygen doe ...
... Red blood cells (erythrocytes) • Contain special protein units called hemoglobin, which is made up of 4 polypeptide chains (globin) and iron (heme). The function of hemoglobin is to carry oxygen. Also these do not have a nucleus • Carbon monoxide has a higher affinity for hemoglobin than oxygen doe ...
1. Atoms & Molecules
... Molecules want to move from an area of HIGH concentration to an area of LOW concentration. This is DIFFUSION. Rate of diffusion is affected by ...
... Molecules want to move from an area of HIGH concentration to an area of LOW concentration. This is DIFFUSION. Rate of diffusion is affected by ...
Human body
... 12. The respiratory system starts at the nasal passages (nose), where air is breathed in during inspiration. There the air is filtered and its temperature regulated. It then passes through the larynx (voice box) and trachea (windpipe) into the bronchi and bronchioles, and ends in little air pockets ...
... 12. The respiratory system starts at the nasal passages (nose), where air is breathed in during inspiration. There the air is filtered and its temperature regulated. It then passes through the larynx (voice box) and trachea (windpipe) into the bronchi and bronchioles, and ends in little air pockets ...
Nervous System Vocab
... from the sense organs to the central nervous system. The motor division transmits impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles or glands. Stimulants increase heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. In addition, stimulants increase the release of neurotransmitters at some synapses ...
... from the sense organs to the central nervous system. The motor division transmits impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles or glands. Stimulants increase heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing rate. In addition, stimulants increase the release of neurotransmitters at some synapses ...
Chapter 4 - Tracy Jubenville Nearing
... Most CO2 in the blood combines with water to form carbonic acid ◦ –The carbonic acid breaks down to form H+ions and bicarbonate ions ◦ –These help buffer the blood ...
... Most CO2 in the blood combines with water to form carbonic acid ◦ –The carbonic acid breaks down to form H+ions and bicarbonate ions ◦ –These help buffer the blood ...
File - Science with Ms. Friess
... • The right side has a higher water concentration • Water would move from right to left…. The water level on the right would go down to balance the solution on the other side ...
... • The right side has a higher water concentration • Water would move from right to left…. The water level on the right would go down to balance the solution on the other side ...
CARDIOVASCULAR notes
... Arterial Pulse – the alternating expansion and recoil of an artery that occurs with each beat of the left ventricle creates a pressure wave – a pulse – that travels through the entire arterial system. Normally, pulse rate (pressure surges/min) equals heart rate (beats/min) ---- average 70 beats/min ...
... Arterial Pulse – the alternating expansion and recoil of an artery that occurs with each beat of the left ventricle creates a pressure wave – a pulse – that travels through the entire arterial system. Normally, pulse rate (pressure surges/min) equals heart rate (beats/min) ---- average 70 beats/min ...
B - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... This feedback system is one way that the human body (1) circulates gases (3) destroys viruses (2) maintains equilibrium (4) transports nutrients ...
... This feedback system is one way that the human body (1) circulates gases (3) destroys viruses (2) maintains equilibrium (4) transports nutrients ...
The Human Body - Madison County Schools
... The stomach has a thick muscular wall that contracts to mash up the food Stomach acids and enzymes begin to break down the nutrients in the food we eat, particularly the proteins The liquefied contents of the stomach enter the small intestine for further processing As the food is digested in the sma ...
... The stomach has a thick muscular wall that contracts to mash up the food Stomach acids and enzymes begin to break down the nutrients in the food we eat, particularly the proteins The liquefied contents of the stomach enter the small intestine for further processing As the food is digested in the sma ...
Presentation - Megan Semel
... vessels/arterioles (less blood to tissues) • Increases blood pressure • Caused by a nerve impulse that contracts smooth muscle • Less O2 to tissues ...
... vessels/arterioles (less blood to tissues) • Increases blood pressure • Caused by a nerve impulse that contracts smooth muscle • Less O2 to tissues ...
human body system worksheet
... 21. _______ is a tissue made up of cells and cell parts that are carried in a liquid (color is a dark red). 22. ___________ cells carry oxygen and carbon dioxide. 23. ______________ cells help you fight disease. 24.What is the function of B cells? T cells? Macrophages? ...
... 21. _______ is a tissue made up of cells and cell parts that are carried in a liquid (color is a dark red). 22. ___________ cells carry oxygen and carbon dioxide. 23. ______________ cells help you fight disease. 24.What is the function of B cells? T cells? Macrophages? ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.