ORGANELLES AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Worksheet #3
... A. Organelle Functions and Protein Synthesis 1) Organelle Functions: a. Define the function of the following items and indicate if it is an organelle or not CELLULAR STRUCTURES: Plasma Membrane ...
... A. Organelle Functions and Protein Synthesis 1) Organelle Functions: a. Define the function of the following items and indicate if it is an organelle or not CELLULAR STRUCTURES: Plasma Membrane ...
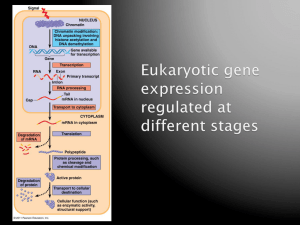
Regulation of gene expression: Eukaryotic
... 2. Problems to look over: Ch. 11: 4, 5, 8, 15; Ch. 12: 3, 10, 21, 22; Ch. 13: 2, 6, 7, 13, 15, 23. 3. Homework due next Friday, 11/1. 4. Last day to withdraw is next Fri. Nov. 1. If you have concerns, talk to me. ...
... 2. Problems to look over: Ch. 11: 4, 5, 8, 15; Ch. 12: 3, 10, 21, 22; Ch. 13: 2, 6, 7, 13, 15, 23. 3. Homework due next Friday, 11/1. 4. Last day to withdraw is next Fri. Nov. 1. If you have concerns, talk to me. ...
Brief description of pGLO
... The 3 genes for arabinose metabolism; araB , araA, and araD are transcribed, in that order, onto a single polycistronic mRNA from the promoter PBAD. Transcription from PBAD is subject to both positive and negative regulation (as is Plac) by the same regulatory protein. This regulatory protein is the ...
... The 3 genes for arabinose metabolism; araB , araA, and araD are transcribed, in that order, onto a single polycistronic mRNA from the promoter PBAD. Transcription from PBAD is subject to both positive and negative regulation (as is Plac) by the same regulatory protein. This regulatory protein is the ...
Gene Expression/Mutations
... - bacteria will break down lactose (into glucose + galactose) from dairy products in intestine to use as energy source (will only do so in presence of lactose) - three enzymes needed to do this (each has a different gene) - allows bacteria to conserve energy when gene is off - lac operon: cluster of ...
... - bacteria will break down lactose (into glucose + galactose) from dairy products in intestine to use as energy source (will only do so in presence of lactose) - three enzymes needed to do this (each has a different gene) - allows bacteria to conserve energy when gene is off - lac operon: cluster of ...
Introduction to Microarray Data Analysis and Gene Networks
... denoted by their initial letters, A,C ,G and T 5' C-G-A-T-T-G-C-A-A-C-G-A-T-G-C 3' ...
... denoted by their initial letters, A,C ,G and T 5' C-G-A-T-T-G-C-A-A-C-G-A-T-G-C 3' ...
Chapter 10
... 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: c. Students know how prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), an ...
... 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism's cells. As a basis for understanding this concept: c. Students know how prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells (including those from plants and animals), an ...
Protein Interactions in an Organism Compose the Interactome
... Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype ...
... Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype ...
DNA RNA
... 3. Termination: RNA polymerase reaches sequence of DNA bases called a terminator signaling the end of the gene and polymerase molecule detaches ...
... 3. Termination: RNA polymerase reaches sequence of DNA bases called a terminator signaling the end of the gene and polymerase molecule detaches ...
Gene Expression
... Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Each protein has a specific sequence of amino acids. The shape of the protein determines the function of the protein. The DNA code holds the key for the sequence of amino acids for each protein. ...
... Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Each protein has a specific sequence of amino acids. The shape of the protein determines the function of the protein. The DNA code holds the key for the sequence of amino acids for each protein. ...
Document
... • Both siRNA and miRNA molecules combine with proteins to form an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). • The RISC pairs with a mRNA molecule that possesses a sequence complementary to its siRNA or miRNA component and either: - cleaves the mRNA (leading to degradation or mRNA) or - represses transla ...
... • Both siRNA and miRNA molecules combine with proteins to form an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). • The RISC pairs with a mRNA molecule that possesses a sequence complementary to its siRNA or miRNA component and either: - cleaves the mRNA (leading to degradation or mRNA) or - represses transla ...
What meaning(s) do these two photos represent? (Hint* dna,rna
... DNA and converting it into an amino acid sequence. ...
... DNA and converting it into an amino acid sequence. ...
Genes
... repressor protein triggering repressor to bind to DNA – blocks (represses) transcription – tend to be anabolic pathways ...
... repressor protein triggering repressor to bind to DNA – blocks (represses) transcription – tend to be anabolic pathways ...
Protein Synthesis Continued
... After a strand of RNA is constructed by transcription, it must be altered before it moves to the cytoplasm Introns are sections of the RNA that do not code for a protein and are “cut out” of the RNA strand (they stay IN the nucleus) Exons are then spliced back together because they code for the prot ...
... After a strand of RNA is constructed by transcription, it must be altered before it moves to the cytoplasm Introns are sections of the RNA that do not code for a protein and are “cut out” of the RNA strand (they stay IN the nucleus) Exons are then spliced back together because they code for the prot ...
Name:
... 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there, and what about them determines the nature of the protein being built? 6. If there ar ...
... 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there, and what about them determines the nature of the protein being built? 6. If there ar ...
Unit 4: DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... packaging and modifying different proteins Phenotype as a function of gene expression (DNA to protein to phenotype) Different types of gene mutations Possible effect of mutation (change in the DNA sequence) on phenotype Environmental influences on phenotype ...
... packaging and modifying different proteins Phenotype as a function of gene expression (DNA to protein to phenotype) Different types of gene mutations Possible effect of mutation (change in the DNA sequence) on phenotype Environmental influences on phenotype ...
Ch 18.2-18.5 PPT
... Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
... Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription & Translation
... • Codon: 3-base code on mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid – Ex. CGU = alanine GUU = valine ...
... • Codon: 3-base code on mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid – Ex. CGU = alanine GUU = valine ...
Exam 1 Review KEY
... a. Glycolysis: cytoplasm b. Transition reaction: Moving from cytoplasm to mitochondrial matrix c. Kreb’s Cycle: mitochondrial matrix d. Electron transport chain: mitochondrial cristae (inner membrane) e. Cori Cycle: From muscles to liver and back 31.) What type of energy storage provides the greates ...
... a. Glycolysis: cytoplasm b. Transition reaction: Moving from cytoplasm to mitochondrial matrix c. Kreb’s Cycle: mitochondrial matrix d. Electron transport chain: mitochondrial cristae (inner membrane) e. Cori Cycle: From muscles to liver and back 31.) What type of energy storage provides the greates ...
12.3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • RNA polymerase will only bind to regions of DNA known as promoters. ...
... • During transcription, RNA polymerase binds to DNA and separates the DNA strands. RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template from which nucleotides are assembled into a strand of RNA. • RNA polymerase will only bind to regions of DNA known as promoters. ...
24 October - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the fidelity of replication during DNA synthesis? 2. Define “promoter” and disc ...
... posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the fidelity of replication during DNA synthesis? 2. Define “promoter” and disc ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.