242140_Fx_DNA-RNA
... 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there, and what about them determines the nature of the protein being built? 6. If there ar ...
... 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there, and what about them determines the nature of the protein being built? 6. If there ar ...
Transcription additions
... Over time, introns were lost from prokaryotes as a way to make proteins more efficiently. ... The mixing and matching of exons from the same gene can lead to proteins with different functions. Eukaryotes might need this diversity in proteins because they have many types of cells all with the same se ...
... Over time, introns were lost from prokaryotes as a way to make proteins more efficiently. ... The mixing and matching of exons from the same gene can lead to proteins with different functions. Eukaryotes might need this diversity in proteins because they have many types of cells all with the same se ...
Document
... Regulation of gene expression at the level of chromatin Sequence-independent linker histones: control DNA compaction and accessibility to trans-acting factors post-translational modifications of histone tails: control compaction of DNA and serve as docking sites for trans-acting factors Range: Can ...
... Regulation of gene expression at the level of chromatin Sequence-independent linker histones: control DNA compaction and accessibility to trans-acting factors post-translational modifications of histone tails: control compaction of DNA and serve as docking sites for trans-acting factors Range: Can ...
Bacterial Genetics Summary
... (a) hydrogen bond to complementary base (b) covalent bond to adjacent nucleotide in growing RNA molecule (6) when terminator sequence is reached one gene has been copied into RNA (7) RNA leaves DNA (8) DNA rezippers, recoils into double helix ...
... (a) hydrogen bond to complementary base (b) covalent bond to adjacent nucleotide in growing RNA molecule (6) when terminator sequence is reached one gene has been copied into RNA (7) RNA leaves DNA (8) DNA rezippers, recoils into double helix ...
2013 ProSyn PREAP
... Plant and animal breeders often take advantage of such beneficial mutations. ...
... Plant and animal breeders often take advantage of such beneficial mutations. ...
Protein Synthesis - Katy Independent School District
... Plant and animal breeders often take advantage of such beneficial mutations. ...
... Plant and animal breeders often take advantage of such beneficial mutations. ...
Gene Regulation - Marblehead High School
... TATA box – marks the beginning gene position for the RNA polymerase Enhancer sequences – areas on the DNA before the gene that regulate gene expression when proteins bind to it ...
... TATA box – marks the beginning gene position for the RNA polymerase Enhancer sequences – areas on the DNA before the gene that regulate gene expression when proteins bind to it ...
04/03
... elements and promoterproximal elements with RNA polymerase initiates transcription at appropriate levels. Architectural proteins allow bending of the DNA to bring all components together, both spatially and functionally. ...
... elements and promoterproximal elements with RNA polymerase initiates transcription at appropriate levels. Architectural proteins allow bending of the DNA to bring all components together, both spatially and functionally. ...
Mysterious Merlin and the Holy Grail
... The aim of this project was to understand how Grail interacts with Merlin. The presence of Grail in two cell types was examined using protein detection techniques. Subsequently production of Grail was inhibited. The novel gene silencing technique RNA interference was used to inhibit Grail. In RNA in ...
... The aim of this project was to understand how Grail interacts with Merlin. The presence of Grail in two cell types was examined using protein detection techniques. Subsequently production of Grail was inhibited. The novel gene silencing technique RNA interference was used to inhibit Grail. In RNA in ...
17-Gene to Protein
... • Initiation: RNA polymerase binds to promoter region,TATA box plays critical role during initiation • Elongation: Helicase unwinds DNA and RNA polymerase adds nucleotides, 10 bases long, grows 5' to 3' direction. • Termination: terminator sequence (AAUAAA) stops transcription • DNA reforms double h ...
... • Initiation: RNA polymerase binds to promoter region,TATA box plays critical role during initiation • Elongation: Helicase unwinds DNA and RNA polymerase adds nucleotides, 10 bases long, grows 5' to 3' direction. • Termination: terminator sequence (AAUAAA) stops transcription • DNA reforms double h ...
Molecular Biology - Gene Regulation
... • Describe how prokaryotic gene expression occurs at the transcriptional level • Understand that eukaryotic gene expression occurs at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels For a cell to function properly, necessary proteins must be synthe ...
... • Describe how prokaryotic gene expression occurs at the transcriptional level • Understand that eukaryotic gene expression occurs at the epigenetic, transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels For a cell to function properly, necessary proteins must be synthe ...
What is a protein? - Hicksville Public Schools
... Amino acids • They are formed from 20 different amino acids. ...
... Amino acids • They are formed from 20 different amino acids. ...
Lecture, Gene Expression
... template • mRNA is “read” from 5’ 3’ in triplets (“codons”) • Codons code for amino acids • Start codon is AUG but stop codon varies • Enzyme* that does this is called tRNA • Takes place in cytoplasm at a ribosome • After folding of polypeptide, a protein is formed! ...
... template • mRNA is “read” from 5’ 3’ in triplets (“codons”) • Codons code for amino acids • Start codon is AUG but stop codon varies • Enzyme* that does this is called tRNA • Takes place in cytoplasm at a ribosome • After folding of polypeptide, a protein is formed! ...
Chapter 17: RNA
... a gene carries the information for the primary structure of a protein. ie, the linear sequence of a.a. on the protein b. In transcription, a gene on the DNA strand provides a template ...
... a gene carries the information for the primary structure of a protein. ie, the linear sequence of a.a. on the protein b. In transcription, a gene on the DNA strand provides a template ...
Steps in gene expression: comparison of
... Six steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. In prokaryotic cells, genes do not have introns (no step 2) and transcription and translation are not separated in space and time (no step 3). ...
... Six steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. In prokaryotic cells, genes do not have introns (no step 2) and transcription and translation are not separated in space and time (no step 3). ...
Translation
... polymerase then the sigma factor is released. - Termination: RNA polymerase encounter a stop signal or transcription terminator (e.g. rho protein in procaryotes). - the RNA polymerase dissociate from the DNA template - the RNA transcript is released. ...
... polymerase then the sigma factor is released. - Termination: RNA polymerase encounter a stop signal or transcription terminator (e.g. rho protein in procaryotes). - the RNA polymerase dissociate from the DNA template - the RNA transcript is released. ...
5b Gene Expression
... • The Expression of Genes as Proteins: DNA gene --> RNA --> Protein - Transcription by RNA Polymerase (DNA gene --> mRNA) - The Three Types of RNA ...
... • The Expression of Genes as Proteins: DNA gene --> RNA --> Protein - Transcription by RNA Polymerase (DNA gene --> mRNA) - The Three Types of RNA ...
No Slide Title
... • Viral DNA injected into cells • Cells evolved nucleases in cytoplasm that chomp up any RNA or DNA out there • Nucleases can’t get through the nuclear envelope so DNA is safe • mRNA sent out into the cytoplasm must be protected – Methyl cap is a block – Poly A tail is a fuse ...
... • Viral DNA injected into cells • Cells evolved nucleases in cytoplasm that chomp up any RNA or DNA out there • Nucleases can’t get through the nuclear envelope so DNA is safe • mRNA sent out into the cytoplasm must be protected – Methyl cap is a block – Poly A tail is a fuse ...
Gene expression
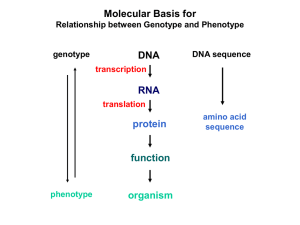
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.