Unit 7: Protein Synthesis
... What is this unit/lesson about? In this unit, students will explore further the nucleic acids, in particular, DNA and RNA, which are biochemicals of life. This unit focuses on DNA replication, transcription, and translation. We will then delve into mutations and biotechnology once we have a sound un ...
... What is this unit/lesson about? In this unit, students will explore further the nucleic acids, in particular, DNA and RNA, which are biochemicals of life. This unit focuses on DNA replication, transcription, and translation. We will then delve into mutations and biotechnology once we have a sound un ...
Powerpoint file - revised
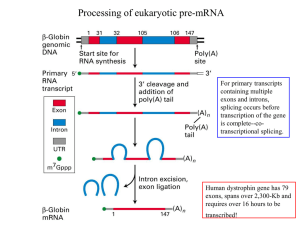
... •Five snRNPs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles) containing 5 snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs, ranging from 107 to 210 nucleotides) and their associated proteins (6-10 per snRNP) assemble on the pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome. •There are a total of ~1 ...
... •Five snRNPs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles) containing 5 snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs, ranging from 107 to 210 nucleotides) and their associated proteins (6-10 per snRNP) assemble on the pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome. •There are a total of ~1 ...
Baker - International School of Crystallography
... TB structural genomics consortium – a different model for large scale structure determination - access to centralised facilities ...
... TB structural genomics consortium – a different model for large scale structure determination - access to centralised facilities ...
6.4 RNA - Part 2 - Translation rna_2_s12
... There are 20 amino acids used in proteins, all with different “side groups.” ...
... There are 20 amino acids used in proteins, all with different “side groups.” ...
DNA WebQuest
... Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready to move on. ...
... Read the animation page by page – just click the “next” button when you are ready to move on. ...
Intro Cell Physiolog..
... Transcription - complementary mRNA is made at the DNA gene. Three-base sequences, or triplets, on the DNA specify a particular amino acid. The corresponding three-base sequences on mRNA are called codons. The form is different, but the information is the same. Translation – The mRNA is "decoded" to ...
... Transcription - complementary mRNA is made at the DNA gene. Three-base sequences, or triplets, on the DNA specify a particular amino acid. The corresponding three-base sequences on mRNA are called codons. The form is different, but the information is the same. Translation – The mRNA is "decoded" to ...
Replication - UniMAP Portal
... 4) DNA polymerase III also performs a proofreading function. About 1 out of every 100,000 nucleotides is mismatched with its template; for instance, a guanine might become incorrectly paired with a thymine. DNA polymerase III recognizes most such errors and removes the ...
... 4) DNA polymerase III also performs a proofreading function. About 1 out of every 100,000 nucleotides is mismatched with its template; for instance, a guanine might become incorrectly paired with a thymine. DNA polymerase III recognizes most such errors and removes the ...
• •
... A mutation is any physical change in the genetic material (such as a gene or a chromosome). A gene that contains a mutation ( change in the base sequence of the DNA) will produce an altered mRNA molecule that will produce an altered sequence of amino acids in the resulting protein General Types of M ...
... A mutation is any physical change in the genetic material (such as a gene or a chromosome). A gene that contains a mutation ( change in the base sequence of the DNA) will produce an altered mRNA molecule that will produce an altered sequence of amino acids in the resulting protein General Types of M ...
DNA- The Molecule of Life
... Before translation can begin, transcription of the DNA into mRNA must occur. ...
... Before translation can begin, transcription of the DNA into mRNA must occur. ...
DNA is the genetic material DNA structure
... phosphate group, no extension of the DNA strand there ...
... phosphate group, no extension of the DNA strand there ...
File
... polynucleotide, Primase must first add a primer, made of RNA nucleotides, to the origin of replication ...
... polynucleotide, Primase must first add a primer, made of RNA nucleotides, to the origin of replication ...
Exam #1
... What are the four steps or tests a microbe must pass in order for it to be shown to cause a disease? (What are Koch’s postulates?) 4 points ...
... What are the four steps or tests a microbe must pass in order for it to be shown to cause a disease? (What are Koch’s postulates?) 4 points ...
No Slide Title
... The gene for ribosomal RNAs occur as repetitive sequence and together with the genes for some transfer RNAs in several thousand of copies Structural genes are present in only a few copies, sometimes just single copy. Structural genes encoding for structurally and functionally related proteins of ...
... The gene for ribosomal RNAs occur as repetitive sequence and together with the genes for some transfer RNAs in several thousand of copies Structural genes are present in only a few copies, sometimes just single copy. Structural genes encoding for structurally and functionally related proteins of ...
opinion - Insight Cruises
... the opportunity to explore niches available to more complex organisms. In any case, although Lamarck’s ideas of evolution by learnt adaptation, rather than by selection, have been widely rejected in favour of the more fundamental and compelling explanation offered by Darwin, their hypotheses are not ...
... the opportunity to explore niches available to more complex organisms. In any case, although Lamarck’s ideas of evolution by learnt adaptation, rather than by selection, have been widely rejected in favour of the more fundamental and compelling explanation offered by Darwin, their hypotheses are not ...
̚Ꮈ̂ጯ Ⴧ̀٢Ϡ ྏྏᗟ
... 29. Which of the following statements about protein synthesis is correct? (A) Protein synthesis stops at the amino end. (B) Transcription of mRNAs and translation into proteins are uncoupled in most eukaryotic systems. (C) Protein synthesis proceeds in the 3’ to 5’ direction of the mRNA. (D) Amino a ...
... 29. Which of the following statements about protein synthesis is correct? (A) Protein synthesis stops at the amino end. (B) Transcription of mRNAs and translation into proteins are uncoupled in most eukaryotic systems. (C) Protein synthesis proceeds in the 3’ to 5’ direction of the mRNA. (D) Amino a ...
Nucleic Acids and DNA
... rRNA – forms complex of 2/3 RNA, 1/3 protein to form protein in ribosome tRNA – carries the amino acids to the mRNA snRNA – helps splice exons Ribozymes – RNA capable of catalytic activity Antisense RNA – act to bind RNA to stop ...
... rRNA – forms complex of 2/3 RNA, 1/3 protein to form protein in ribosome tRNA – carries the amino acids to the mRNA snRNA – helps splice exons Ribozymes – RNA capable of catalytic activity Antisense RNA – act to bind RNA to stop ...
Gene Expression Data Sets
... a given data set. Downloading such files is straightforward but extracting numerical information is not so as different files stores gene expression data mixed with textual headers and other text information. In order to access gene expression data, one needs to write a separate script or program fo ...
... a given data set. Downloading such files is straightforward but extracting numerical information is not so as different files stores gene expression data mixed with textual headers and other text information. In order to access gene expression data, one needs to write a separate script or program fo ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... amino acids, nucleobases, sugars, lipids, oligomers of biochemical compounds ...
... amino acids, nucleobases, sugars, lipids, oligomers of biochemical compounds ...
Slide 1
... (2) How to change the rate of a specific cellular activity? (3) Rapid vs slower change (4) Varying amount vs specific activity of a protein (5) Coordinating simultaneous changes in related proteins (6) How to achieve fine/differential regulation ...
... (2) How to change the rate of a specific cellular activity? (3) Rapid vs slower change (4) Varying amount vs specific activity of a protein (5) Coordinating simultaneous changes in related proteins (6) How to achieve fine/differential regulation ...
Nucleic Acids
... – stored information is passed from parent to offspring • need to copy accurately ...
... – stored information is passed from parent to offspring • need to copy accurately ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.