TWO-DAY COURSE, Saturday and Sunday 12 Peptides and
... of proteins. This course is designed as an introduction for researchers needing to expand their knowledge of the use of mass spectrometry-based methods for the identification, characterization, and quantification of peptides and proteins. Background material in basic protein chemistry will be provid ...
... of proteins. This course is designed as an introduction for researchers needing to expand their knowledge of the use of mass spectrometry-based methods for the identification, characterization, and quantification of peptides and proteins. Background material in basic protein chemistry will be provid ...
A Biology Primer for Computer Scientists
... Figure 5: Diagrammatic illustration of the ”central dogma” and of its subsequent amendments (in light broken line). Three major processes occur in the cell: DNA replication, DNA-RNA transcription, and RNA-protein translation, referred to briefly as replication, transcription, and translation. These ...
... Figure 5: Diagrammatic illustration of the ”central dogma” and of its subsequent amendments (in light broken line). Three major processes occur in the cell: DNA replication, DNA-RNA transcription, and RNA-protein translation, referred to briefly as replication, transcription, and translation. These ...
RNAi
... recognizes a DNA sequence called the UAS (upstream activating sequence) • We can use this to control expression of YFG in a tissue specific manner by using enhancer elements specific for the tissue we are interested in ...
... recognizes a DNA sequence called the UAS (upstream activating sequence) • We can use this to control expression of YFG in a tissue specific manner by using enhancer elements specific for the tissue we are interested in ...
INDUCTION OF ß-GALACTOSIDASE IN E.COLI
... The structure genes of the lac operon encode the information of three proteins (ß-galactosidase, transacetylase and lactose permease) necessary to be synthesized by the cells utilizing lactose as energy source. ß-galactosidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactose into glucose and galactose. Besides t ...
... The structure genes of the lac operon encode the information of three proteins (ß-galactosidase, transacetylase and lactose permease) necessary to be synthesized by the cells utilizing lactose as energy source. ß-galactosidase catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactose into glucose and galactose. Besides t ...
From DNA to Protein WS
... Write the complementary mRNA strand to this strand of DNA below it. 5’ T A C C T G C C A G T T A T C G A G G C T A T C C G A T C C C G T T A T 3’ _______________________________________________________________________ Match codons of the mRNA strand you’ve created with their corresponding amino acid ...
... Write the complementary mRNA strand to this strand of DNA below it. 5’ T A C C T G C C A G T T A T C G A G G C T A T C C G A T C C C G T T A T 3’ _______________________________________________________________________ Match codons of the mRNA strand you’ve created with their corresponding amino acid ...
DNA - Madison County Schools
... ribosome in the cytoplasm. mRNA is read as codons: (three base pairs in a row.) tRNA brings amino acids to the mRNA that is specific for the codon and forms a peptide ...
... ribosome in the cytoplasm. mRNA is read as codons: (three base pairs in a row.) tRNA brings amino acids to the mRNA that is specific for the codon and forms a peptide ...
Assessing the Affect of RNA and cDNA Freeze
... freeze thaw-related gene expression changes for RNA when analyzed using Affymetrix microarray analysis and Real-Time qPCR. Interestingly, when cDNA was freeze thawed repeatedly, the measured gene expression using Real-Time qPCR for HPRT was slightly reduced each freeze thaw cycle with a total reduce ...
... freeze thaw-related gene expression changes for RNA when analyzed using Affymetrix microarray analysis and Real-Time qPCR. Interestingly, when cDNA was freeze thawed repeatedly, the measured gene expression using Real-Time qPCR for HPRT was slightly reduced each freeze thaw cycle with a total reduce ...
Von Neumann`s Quintessential Message: Genotype C Ribotype D
... double helix, put forward what he called the central dogma of molecular biology: Proteins are not made directly from genes—there must be an intermediary between them, and this intermediary is RNA [2]. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains the information needed by a biological organism to carry out i ...
... double helix, put forward what he called the central dogma of molecular biology: Proteins are not made directly from genes—there must be an intermediary between them, and this intermediary is RNA [2]. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains the information needed by a biological organism to carry out i ...
Operons: The Basic Concept
... • In bacteria, genes are often clustered into operons, composed of – An operator, an “on-off” switch – A promoter – Genes for metabolic enzymes ...
... • In bacteria, genes are often clustered into operons, composed of – An operator, an “on-off” switch – A promoter – Genes for metabolic enzymes ...
Puredown Protein A/G-Agarose Conjugate
... be coupled to a solid substrate at some point in the procedure. Protein A is a 40-60 kDa MSCRAMM surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-com ...
... be coupled to a solid substrate at some point in the procedure. Protein A is a 40-60 kDa MSCRAMM surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-com ...
Intro-Cell-Physiology
... Transcription - complementary mRNA is made at the DNA gene. Three-base sequences, or triplets, on the DNA specify a particular amino acid. The corresponding three-base sequences on mRNA are called codons. The form is different, but the information is the same. Translation – The mRNA is "decoded" to ...
... Transcription - complementary mRNA is made at the DNA gene. Three-base sequences, or triplets, on the DNA specify a particular amino acid. The corresponding three-base sequences on mRNA are called codons. The form is different, but the information is the same. Translation – The mRNA is "decoded" to ...
Slide 1
... • Amino acids link - polypeptides combine to form proteins. • Amino acids made of hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, amino group, variable R group (or side chain). • R group makes amino acids different from one another. • R groups have different properties (i.e. hydrophobic) - form amino acids with dif ...
... • Amino acids link - polypeptides combine to form proteins. • Amino acids made of hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, amino group, variable R group (or side chain). • R group makes amino acids different from one another. • R groups have different properties (i.e. hydrophobic) - form amino acids with dif ...
Nanotechnology in Medicine Krešimir Pavelić Division of Molecular
... Antisense Therapy and Nanoparticles Problems: poor stability of antisense oligonucleotides versus nuclease activity in vitro and in vivo, and their low intracellular penetration have limited their use in therapeutics. Solutions: to increase antisense stability, to improve cell penetration and also ...
... Antisense Therapy and Nanoparticles Problems: poor stability of antisense oligonucleotides versus nuclease activity in vitro and in vivo, and their low intracellular penetration have limited their use in therapeutics. Solutions: to increase antisense stability, to improve cell penetration and also ...
Slide 1 - helmricht
... Denaturation- the loss of the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of a protein by chemical or physical agent that leaves the primary structure intact Enzymes lose their catalytic activity and other proteins can’t carry out their biological functions when denatured ...
... Denaturation- the loss of the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of a protein by chemical or physical agent that leaves the primary structure intact Enzymes lose their catalytic activity and other proteins can’t carry out their biological functions when denatured ...
Network Dynamics
... The parameters of reactions of metabolism is incompletely known and if if known, then the system becomes extremely complex. Thus a series of techniques have been evolved for analysis of metabolisms. •Kinetic Modeling Rarely undertaken since all reactions are sufficiently well known or parameters kno ...
... The parameters of reactions of metabolism is incompletely known and if if known, then the system becomes extremely complex. Thus a series of techniques have been evolved for analysis of metabolisms. •Kinetic Modeling Rarely undertaken since all reactions are sufficiently well known or parameters kno ...
GENE MUTATION = POINT MUTATION at the DNA level: at the level
... Retrieval of Genetic Information: Central to any information storage system is the ability to access and retrieve the information and to convert it to a usable form. In addition to the sequence information that will be translated into protein via the triplet code, a gene also contains sequence info ...
... Retrieval of Genetic Information: Central to any information storage system is the ability to access and retrieve the information and to convert it to a usable form. In addition to the sequence information that will be translated into protein via the triplet code, a gene also contains sequence info ...
What do genes do? - The Open University
... v4.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.en_GB. Within that The Open University interprets this licence in the following way: www.open.edu/openlearn/about-openlearn/frequently-asked-questions-on-openlearn. Copyright and rights falling outside the terms of the Creative Commons Licen ...
... v4.0 http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/deed.en_GB. Within that The Open University interprets this licence in the following way: www.open.edu/openlearn/about-openlearn/frequently-asked-questions-on-openlearn. Copyright and rights falling outside the terms of the Creative Commons Licen ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... Dissociate fairly easily from polymerase Found in substoichiometric quantities Might shuttle from one polymerase II to another Rpb4 may help anchor Rpb7 to the enzyme Mutants without Rpb4 and Rpb7 transcribes well, but cannot initiate at a real promoter ...
... Dissociate fairly easily from polymerase Found in substoichiometric quantities Might shuttle from one polymerase II to another Rpb4 may help anchor Rpb7 to the enzyme Mutants without Rpb4 and Rpb7 transcribes well, but cannot initiate at a real promoter ...
Document
... 8.4 Transcription Transcription makes three types of RNA. 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) - carries the message that will be translated to form a protein. 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome. ...
... 8.4 Transcription Transcription makes three types of RNA. 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) - carries the message that will be translated to form a protein. 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - forms part of ribosomes where proteins are made. 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) - brings amino acids from the cytoplasm to a ribosome. ...
Whole Genome Polymorphism Analysis of Regulatory Elements in
... Genetic disease may also be caused by differential expression of vital proteins ...
... Genetic disease may also be caused by differential expression of vital proteins ...
Recombinant DNA and gene cloning To use an unique feature(s) of
... To use an unique feature(s) of your gene/gene product to isolate the DNA fragment containing your gene from a library of DNA fragments. Difficulty in isolating genes (needle in a long line of connected needles): A gene is a small part of a large DNA (0.01% of an average chromosome); DNA pieces all h ...
... To use an unique feature(s) of your gene/gene product to isolate the DNA fragment containing your gene from a library of DNA fragments. Difficulty in isolating genes (needle in a long line of connected needles): A gene is a small part of a large DNA (0.01% of an average chromosome); DNA pieces all h ...
RNA Seq: A (soon to be outdated) Tutorial
... Differential Gene Expression Analysis: Sampling Variance Consider a bag of balls with K number of red balls where K is much less than the total number of balls. You can sample n number of balls. P represents the proportion of red balls in your sample. Estimate of the number of balls (u) = pn K (the ...
... Differential Gene Expression Analysis: Sampling Variance Consider a bag of balls with K number of red balls where K is much less than the total number of balls. You can sample n number of balls. P represents the proportion of red balls in your sample. Estimate of the number of balls (u) = pn K (the ...
Practice Benchmark I Page 1 of 12 Directions: Please choose the
... 20. Which of these BEST describes the sequence of steps in protein synthesis? RNA is replicated in the nucleus DNA is A. assembled from RNA at the ribosomes proteins are assembled at the ribosomes RNA is replicated in the ribosomes RNA is B. transcribed to DNA in the cytoplasm proteins are assembled ...
... 20. Which of these BEST describes the sequence of steps in protein synthesis? RNA is replicated in the nucleus DNA is A. assembled from RNA at the ribosomes proteins are assembled at the ribosomes RNA is replicated in the ribosomes RNA is B. transcribed to DNA in the cytoplasm proteins are assembled ...
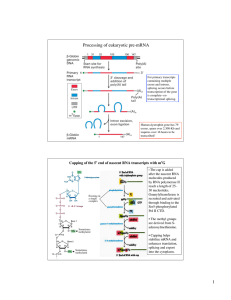
1 Processing of eukaryotic pre-mRNA
... •Five snRNPs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles) containing 5 snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs, ranging from 107 to 210 nucleotides) and their associated proteins (6-10 per snRNP) assemble on the pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome. •There are a total of ~1 ...
... •Five snRNPs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles) containing 5 snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 small nuclear RNAs, ranging from 107 to 210 nucleotides) and their associated proteins (6-10 per snRNP) assemble on the pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome. •There are a total of ~1 ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.