Chapter 11: DNA and Genes
... when they discovered that a group of three nitrogenous bases in mRNA code for one amino acid. Each group is known as a codon. • Sixty-four combinations are possible when a sequence of three bases is used; thus, 64 different mRNA codons are in the genetic code. ...
... when they discovered that a group of three nitrogenous bases in mRNA code for one amino acid. Each group is known as a codon. • Sixty-four combinations are possible when a sequence of three bases is used; thus, 64 different mRNA codons are in the genetic code. ...
1 Introduction 2 Central Dogma of molecular biology 3 DNA
... the sense that it is also a polymer made up of repeated nucleotides. However, it is single stranded. It is made up of also a different sugar. Its nucleotides are A, U, G, and C, where U is the analog of T in DNA. While most of the RNA gets translated into proteins there are some other types of RNA t ...
... the sense that it is also a polymer made up of repeated nucleotides. However, it is single stranded. It is made up of also a different sugar. Its nucleotides are A, U, G, and C, where U is the analog of T in DNA. While most of the RNA gets translated into proteins there are some other types of RNA t ...
The Biotechnology Age: Issues and Impacts
... • Isomer: Different substances that have the same components. = Different molecules with same chemical formula • Alter chemical bonding --> different “shapes” --> activities and functions. •Isomerase: an enzyme that can make different molecular shapes out of the same substance. ...
... • Isomer: Different substances that have the same components. = Different molecules with same chemical formula • Alter chemical bonding --> different “shapes” --> activities and functions. •Isomerase: an enzyme that can make different molecular shapes out of the same substance. ...
2.2 PPT_Proteins and Nucleic Acids
... amino amino amino amino amino acid – acid – acid – acid – acid ...
... amino amino amino amino amino acid – acid – acid – acid – acid ...
Ch. 11 - Holden R-III School District
... assemble the amino acids in the correct order Transfer RNA (tRNA) Brings the amino acids to the ribosomes, where they are assembled into a protein ...
... assemble the amino acids in the correct order Transfer RNA (tRNA) Brings the amino acids to the ribosomes, where they are assembled into a protein ...
1 - optometrie.ch
... 8. All of the following are characteristics of autosomal recessive inheritance EXCEPT: a. Autosomal recessive traits are expressed only when both copies of a gene are mutant. b. The pattern of inheritance is horizontal (found in a single group of brothers and sisters. c. Except for a new mutation, ...
... 8. All of the following are characteristics of autosomal recessive inheritance EXCEPT: a. Autosomal recessive traits are expressed only when both copies of a gene are mutant. b. The pattern of inheritance is horizontal (found in a single group of brothers and sisters. c. Except for a new mutation, ...
From DNA to Protein
... The Process of Transcription RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a promoter (a specific binding site in DNA close to the start of a gene) RNA polymerase moves over the gene in a 5' to 3' direction, unwinds the DNA helix, reads the base sequence, and joins free RNA nucleotides into ...
... The Process of Transcription RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a promoter (a specific binding site in DNA close to the start of a gene) RNA polymerase moves over the gene in a 5' to 3' direction, unwinds the DNA helix, reads the base sequence, and joins free RNA nucleotides into ...
Document
... The Process of Transcription RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a promoter (a specific binding site in DNA close to the start of a gene) RNA polymerase moves over the gene in a 5' to 3' direction, unwinds the DNA helix, reads the base sequence, and joins free RNA nucleotides into ...
... The Process of Transcription RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a promoter (a specific binding site in DNA close to the start of a gene) RNA polymerase moves over the gene in a 5' to 3' direction, unwinds the DNA helix, reads the base sequence, and joins free RNA nucleotides into ...
DNA to Protein WS
... Write the complementary mRNA strand to this strand of DNA below it. 5’ T A C C T G C C A G T T A C C G A G G C T A T G C G A T C C C G T A C T 3’ _______________________________________________________________________ Match codons of the mRNA strand you’ve created with their corresponding amino acid ...
... Write the complementary mRNA strand to this strand of DNA below it. 5’ T A C C T G C C A G T T A C C G A G G C T A T G C G A T C C C G T A C T 3’ _______________________________________________________________________ Match codons of the mRNA strand you’ve created with their corresponding amino acid ...
Document
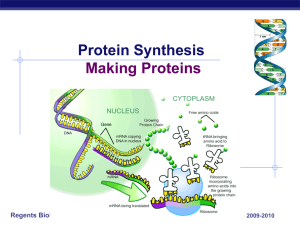
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
... How does mRNA code for proteins mRNA leaves nucleus mRNA goes to ribosomes in cytoplasm ...
DNA Workshop_Protein_Synthesis
... Translation: Match tRNA anticodon to mRNA codon Drag and drop from well: UAC (methionine; compl. of AUG) CCG (glycine; compl. of GGC) AGG (serine; compl. of UCC) Help Window: Like DNA, mRNA consists of four bases. The bases in mRNA are grouped into sets of three called codons. Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
... Translation: Match tRNA anticodon to mRNA codon Drag and drop from well: UAC (methionine; compl. of AUG) CCG (glycine; compl. of GGC) AGG (serine; compl. of UCC) Help Window: Like DNA, mRNA consists of four bases. The bases in mRNA are grouped into sets of three called codons. Transfer RNA (tRNA) ...
Carbohydrates
... Molecular building blocks of nucleic acids Formed by sugar (pentose) and phosphate groups joined in long chain with nitrogenous base open for metabolic activity ...
... Molecular building blocks of nucleic acids Formed by sugar (pentose) and phosphate groups joined in long chain with nitrogenous base open for metabolic activity ...
Folding in the cell Cytosolic proteins
... inactivate a protein unless it is in the active site of an enzyme, a ligand binding site or in an essential structural position (such as a sharp turn where only certain conformations can occur, or in amino acids involved in salt bridges in the interior of the molecule). Many single amino acid mutati ...
... inactivate a protein unless it is in the active site of an enzyme, a ligand binding site or in an essential structural position (such as a sharp turn where only certain conformations can occur, or in amino acids involved in salt bridges in the interior of the molecule). Many single amino acid mutati ...
Proteins
... Genes direct the order of amino acids Two types of nucleic acids – DNA – RNA - RiboNucleic Acid ...
... Genes direct the order of amino acids Two types of nucleic acids – DNA – RNA - RiboNucleic Acid ...
Macromolecule Review
... 2. Which of the molecules listed above can often be composed of C, H, and O alone? 3. Which of the compounds can be identified by looking at the C:H:O ratios alone? 4. What other elements are commonly associated with each of these four types of macromolecules? ...
... 2. Which of the molecules listed above can often be composed of C, H, and O alone? 3. Which of the compounds can be identified by looking at the C:H:O ratios alone? 4. What other elements are commonly associated with each of these four types of macromolecules? ...
Document
... • Unwind DNA helix • One acts as template for synthesis of mRNA • Build-up of complementary nucleotides along template DNA strand : enzyme RNA polymerase • According to Base pairing principle DNA : A C G T mRNA: U G C A ...
... • Unwind DNA helix • One acts as template for synthesis of mRNA • Build-up of complementary nucleotides along template DNA strand : enzyme RNA polymerase • According to Base pairing principle DNA : A C G T mRNA: U G C A ...
all of the above - Holy Trinity Diocesan High School
... Many pseudogenes (which no longer produce functional proteins) in vertebrate genomes lack introns. What process may account for such pseudogenes? Remember mRNA processing. A. gene duplication followed by DNA splicing to remove introns B. recombination between duplicated copies of genes C. reverse t ...
... Many pseudogenes (which no longer produce functional proteins) in vertebrate genomes lack introns. What process may account for such pseudogenes? Remember mRNA processing. A. gene duplication followed by DNA splicing to remove introns B. recombination between duplicated copies of genes C. reverse t ...
A Gene Group Database - Research | www.stowers.org
... attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore during meiosis I nuclear pore posttranslational protein targeting to membrane centromeric DNA binding cellular morphogenesis establishment and/or maintenance of cell polarity (sensu Fungi) ATPase activity transcription initiation from RNA polymerase ...
... attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore during meiosis I nuclear pore posttranslational protein targeting to membrane centromeric DNA binding cellular morphogenesis establishment and/or maintenance of cell polarity (sensu Fungi) ATPase activity transcription initiation from RNA polymerase ...
Proteins - West Branch Schools
... Proteins can have up to 4 levels of structure: 1. The number of amino acids in a chain and the order in which amino acids are joined define the proteins primary structure. 2. After an amino acid chain is formed, it folds into a unique three-dimensional shape Helix and a Pleat ...
... Proteins can have up to 4 levels of structure: 1. The number of amino acids in a chain and the order in which amino acids are joined define the proteins primary structure. 2. After an amino acid chain is formed, it folds into a unique three-dimensional shape Helix and a Pleat ...
Biological Modelling Gene Expression Data
... – Intrinsic Intracellualar factors (The Stage of the Cell Cycle). – Extrinsic factors (Signals from other cells). ...
... – Intrinsic Intracellualar factors (The Stage of the Cell Cycle). – Extrinsic factors (Signals from other cells). ...
T7 In Vitro Transcription Kit esiSCRIBE 100 Reactions (10 µl each
... generation of double-stranded (ds)RNA and guide (g)RNA for RNA interference (RNAi) experiments and CRISPR/Cas systems, respectively. Ready-totransfect esiRNAs (endoribonuclease-prepared siRNAs) and gRNAs are also available from Eupheria Biotech (www.eupheria.com). Reaction Conditions This kit contai ...
... generation of double-stranded (ds)RNA and guide (g)RNA for RNA interference (RNAi) experiments and CRISPR/Cas systems, respectively. Ready-totransfect esiRNAs (endoribonuclease-prepared siRNAs) and gRNAs are also available from Eupheria Biotech (www.eupheria.com). Reaction Conditions This kit contai ...
Lect 6 JF 2012.pptx
... - can’t grow if supplied with the ornithine - but can grow if they are supplied with citrulline or arginine - therefore the enzymatic block must be in the enzymatic step that converts ornithine citrulline ...
... - can’t grow if supplied with the ornithine - but can grow if they are supplied with citrulline or arginine - therefore the enzymatic block must be in the enzymatic step that converts ornithine citrulline ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.