Mutations Worksheet
... BONUS: You have a DNA sequence that codes for a protein and is 105 nucleotides long. A frameshift mutation occurs at the 85th base - how many amino acids will be correct in this protein? SHOW YOUR WORK. ...
... BONUS: You have a DNA sequence that codes for a protein and is 105 nucleotides long. A frameshift mutation occurs at the 85th base - how many amino acids will be correct in this protein? SHOW YOUR WORK. ...
Document
... Once mRNA was synthesized (via transcription), it leaves the nucleus of the cell and goes to the cytoplasm (aka cytosol) In the cytoplasm, there is an organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) which contains ribosomes Ribosomes facilitate protein synthesis ...
... Once mRNA was synthesized (via transcription), it leaves the nucleus of the cell and goes to the cytoplasm (aka cytosol) In the cytoplasm, there is an organelle called the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) which contains ribosomes Ribosomes facilitate protein synthesis ...
Gene Expression and Regulation
... Hormones can function as chemical regulators of gene expression in their target cells. A steroid hormone can bind to a receptor protein in the cytosol that then acts as a transcription activator. The activator will be recognized by all genes that respond to that particular hormone. For example: • Bi ...
... Hormones can function as chemical regulators of gene expression in their target cells. A steroid hormone can bind to a receptor protein in the cytosol that then acts as a transcription activator. The activator will be recognized by all genes that respond to that particular hormone. For example: • Bi ...
Cytoplasm: Within cells, the cytoplasm is made up of a jelly
... Nucleus: Brains/blueprints. DNA located here on 46 compact units called chromosomes. Transcription occurs when proteins copy segments of DNA onto mRNA! DNA is so awesome it never leaves nucleus. ...
... Nucleus: Brains/blueprints. DNA located here on 46 compact units called chromosomes. Transcription occurs when proteins copy segments of DNA onto mRNA! DNA is so awesome it never leaves nucleus. ...
Information Extraction from Biomedical Text
... What is known about protein X (subcellular & tissue localization, associations with diseases, interactions with drugs, …)? –! assisting scientific discovery by detecting previously unknown relationships, annotating experimental data ...
... What is known about protein X (subcellular & tissue localization, associations with diseases, interactions with drugs, …)? –! assisting scientific discovery by detecting previously unknown relationships, annotating experimental data ...
Comparative Genomics 2015 File
... Aim: This exercise will demonstrate how the advent of molecular evidence supports previously established evolutionary lines and give students the opportunity to use an online database. 1. Go to the NCBI website: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 2. In the search bar at the top, from the scroll down menu ...
... Aim: This exercise will demonstrate how the advent of molecular evidence supports previously established evolutionary lines and give students the opportunity to use an online database. 1. Go to the NCBI website: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 2. In the search bar at the top, from the scroll down menu ...
Non-translational synthesis of poly-amino
... in a simpler fashion--i.e., non-translationally. Such a peptide is simple enough [in sequence] … that a non-translational synthesis by some simple alternating process is definitely not ruled out. … ...
... in a simpler fashion--i.e., non-translationally. Such a peptide is simple enough [in sequence] … that a non-translational synthesis by some simple alternating process is definitely not ruled out. … ...
Appendices Enzyme Endurance Review of Protein Structure Great
... evolved so that the binding of a small ligand can induce a significant change in protein shape. Most enzymes are allosteric proteins that can exist in two conformations that differ in catalytic activity, and the enzyme can be turned on or off by ligands that bind to a distinct regulatory site to sta ...
... evolved so that the binding of a small ligand can induce a significant change in protein shape. Most enzymes are allosteric proteins that can exist in two conformations that differ in catalytic activity, and the enzyme can be turned on or off by ligands that bind to a distinct regulatory site to sta ...
Genomes 3/e - Illinois Institute of Technology
... of transcription initiation Primary regulation occurs at the level of transcription initiation & decides which gene is expressed in a particular cell & relative rate Secondary regulation is during the posttranscription (e.g. mRNA modification) and the protein synthesis & modification. Figure 11.22 G ...
... of transcription initiation Primary regulation occurs at the level of transcription initiation & decides which gene is expressed in a particular cell & relative rate Secondary regulation is during the posttranscription (e.g. mRNA modification) and the protein synthesis & modification. Figure 11.22 G ...
Everything you wanted to know about ENCODE
... Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter region together turn a gene on or off. These proteins are themselves regulated by their own promoters leading to a gene regulatory network with many of the same properties as a neural network. ...
... Proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences in the promoter region together turn a gene on or off. These proteins are themselves regulated by their own promoters leading to a gene regulatory network with many of the same properties as a neural network. ...
LabM3bioinformatics
... Bioinformatics can be used to suggest the functions of newly identified genes and proteins. As the proteins with similar functions contain homologus amino acid sequences that corresponds to important functional domains in the three dimensional structure of the proteins, so the function of a protei ...
... Bioinformatics can be used to suggest the functions of newly identified genes and proteins. As the proteins with similar functions contain homologus amino acid sequences that corresponds to important functional domains in the three dimensional structure of the proteins, so the function of a protei ...
THE lac OPERON
... • These are the genes that are involved in of vital biochemical processes such as respiration • Other genes are not expressed all the time • They are switched on an off at need ...
... • These are the genes that are involved in of vital biochemical processes such as respiration • Other genes are not expressed all the time • They are switched on an off at need ...
Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes Short Answer
... a. A-T and C-G in DNA; b. A-U and C-G in RNA; c. complementary base pairing in replication ensures identical nucleotide sequence of new complementary strands; d. semi-conservative replication; e. transcription produces RNA sequence complementary to the DNA sequence (of the gene); f. triplets of nucl ...
... a. A-T and C-G in DNA; b. A-U and C-G in RNA; c. complementary base pairing in replication ensures identical nucleotide sequence of new complementary strands; d. semi-conservative replication; e. transcription produces RNA sequence complementary to the DNA sequence (of the gene); f. triplets of nucl ...
Document
... Surrounded by double membrane and contain own DNA, but codes for very few proteins! (a few dozen) Instead, most genes from prokaryotic ancestor have been transferred to the nucleus, so proteins must be imported ...
... Surrounded by double membrane and contain own DNA, but codes for very few proteins! (a few dozen) Instead, most genes from prokaryotic ancestor have been transferred to the nucleus, so proteins must be imported ...
Document
... • Then goes back into the cytoplasm to look for a free amino acid and repeats • The ribosome keeps reading the mRNA taking the amino acids from tRNA and sticking them together to make a protein chain ...
... • Then goes back into the cytoplasm to look for a free amino acid and repeats • The ribosome keeps reading the mRNA taking the amino acids from tRNA and sticking them together to make a protein chain ...
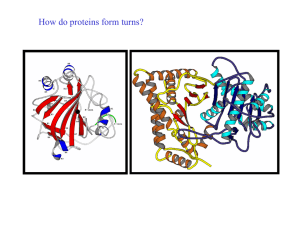
How do proteins form turns? - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... A reverse turn is region of the polypeptide having a hydrogen bond from one main chain carbonyl oxygen to the main chain N-H group 3 residues along the chain (i.e. O(i) to N(i+3)) Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and g ...
... A reverse turn is region of the polypeptide having a hydrogen bond from one main chain carbonyl oxygen to the main chain N-H group 3 residues along the chain (i.e. O(i) to N(i+3)) Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and g ...
Molecules of life 2.4 - Madison County Schools
... a. A variety of bonds (covalent, ionic, hydrogen) between distant amino acids causes large folds in the protein. These help provide stability to the folded protein. 4. Quaternary Structure (4’ ) “Quarter” means “fourth” a. This is when two or more polypeptides are woven together. b. Hemoglobin (Red ...
... a. A variety of bonds (covalent, ionic, hydrogen) between distant amino acids causes large folds in the protein. These help provide stability to the folded protein. 4. Quaternary Structure (4’ ) “Quarter” means “fourth” a. This is when two or more polypeptides are woven together. b. Hemoglobin (Red ...
Issue
... Plant genomes are mosaics of compositionally homogenous DNA segments with defined GC content, termed isochores. Because the GC content of genes of different origins, insertion of foreign DNA into an isochore may mark this region for inactivation and methylation. In this respect, modification of tran ...
... Plant genomes are mosaics of compositionally homogenous DNA segments with defined GC content, termed isochores. Because the GC content of genes of different origins, insertion of foreign DNA into an isochore may mark this region for inactivation and methylation. In this respect, modification of tran ...
Organic Molecule Notes
... 5. Terpenes=some pigments in plants & animals. 6. Phospholipids=form the cell membrane. ...
... 5. Terpenes=some pigments in plants & animals. 6. Phospholipids=form the cell membrane. ...
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.The process of gene expression is used by all known life - eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses - to generate the macromolecular machinery for life.Several steps in the gene expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, translation, and post-translational modification of a protein. Gene regulation gives the cell control over structure and function, and is the basis for cellular differentiation, morphogenesis and the versatility and adaptability of any organism. Gene regulation may also serve as a substrate for evolutionary change, since control of the timing, location, and amount of gene expression can have a profound effect on the functions (actions) of the gene in a cell or in a multicellular organism.In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, i.e. observable trait. The genetic code stored in DNA is ""interpreted"" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape, or that act as enzymes catalysing specific metabolic pathways characterising the organism.