Muscle Structure
... The term kinesthesia means conscious recognition of the position of the body parts with respect to on another as well as recognition of limb movement rates These functions are accomplished by extensive sensory devices in and around joints There are three principal types of proprioceptors: (1) free n ...
... The term kinesthesia means conscious recognition of the position of the body parts with respect to on another as well as recognition of limb movement rates These functions are accomplished by extensive sensory devices in and around joints There are three principal types of proprioceptors: (1) free n ...
The nervous system - Mr T Pities the Fool
... The Peripheral system Consists of: Sensory division and Motor division -includes all sensory neurons, motor neurons, and sense organs ...
... The Peripheral system Consists of: Sensory division and Motor division -includes all sensory neurons, motor neurons, and sense organs ...
The Nervous System - Centennial Christian School
... • You had the maximum number of neurons when you were born • 1000’s of neurons are lost every day and are never replaced • Don’t notice this until later in life when the loss is so large – This is why elderly people often become forgetful ...
... • You had the maximum number of neurons when you were born • 1000’s of neurons are lost every day and are never replaced • Don’t notice this until later in life when the loss is so large – This is why elderly people often become forgetful ...
Where does breathing start?
... It comes from the respiratory centres called medulla oblongata and the pons which are located in the lower brainstem. The medulla oblongata contains the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG) and the Dorsal Respiratory Group and the pons contains the Pneumotaxic (PNG) and the Apneustic centres (APN). The f ...
... It comes from the respiratory centres called medulla oblongata and the pons which are located in the lower brainstem. The medulla oblongata contains the Ventral Respiratory Group (VRG) and the Dorsal Respiratory Group and the pons contains the Pneumotaxic (PNG) and the Apneustic centres (APN). The f ...
Strabismus following posterior segment surgery
... Evaluation • Look for epiretinal membranes • Amsler grid testing • Lights on-off test ...
... Evaluation • Look for epiretinal membranes • Amsler grid testing • Lights on-off test ...
File
... know is that it's the organ that makes us human, giving people the capacity for art, language, judgments, and rational thought. It's also responsible for each individual's personality, memories, movements, and how we sense the world. • All this comes from a jellylike mass of fat and protein weighing ...
... know is that it's the organ that makes us human, giving people the capacity for art, language, judgments, and rational thought. It's also responsible for each individual's personality, memories, movements, and how we sense the world. • All this comes from a jellylike mass of fat and protein weighing ...
Neurologic System
... • 3 – Full ROM against gravity • 4 – Full ROM against gravity, some resistance • 5 – Full ROM against gravity full resistance without evident fatigue = Normal Muscle Strength ...
... • 3 – Full ROM against gravity • 4 – Full ROM against gravity, some resistance • 5 – Full ROM against gravity full resistance without evident fatigue = Normal Muscle Strength ...
Chapter Summary Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception • Sensation
... The frequency and amplitude of sound waves produce our perceptions of pitch and loudness of sounds. When sounds enter the ear, they move the ear drum, which sets in motion the ossicles. The last of these, the stirrup, vibrates the oval window, setting into motion fluid in the cochlea. Hair cells on ...
... The frequency and amplitude of sound waves produce our perceptions of pitch and loudness of sounds. When sounds enter the ear, they move the ear drum, which sets in motion the ossicles. The last of these, the stirrup, vibrates the oval window, setting into motion fluid in the cochlea. Hair cells on ...
Chapter 7
... nerve matches the frequency of the sound. That is, the basilar membrane vibrates in synchrony with the sound wave. • We now know that the firing rate matches the frequency because of the volley principle: • while one group of neurons in the auditory nerve is firing, another group is recovering from ...
... nerve matches the frequency of the sound. That is, the basilar membrane vibrates in synchrony with the sound wave. • We now know that the firing rate matches the frequency because of the volley principle: • while one group of neurons in the auditory nerve is firing, another group is recovering from ...
Sensation
... • provides the parietal cortex of the brain with information on the relative positions of the parts of the body • describes how much we know about where we are in space and where all of our parts are in relationship to each other • Our kinesthetic sense helps us move with greater precision, avoid in ...
... • provides the parietal cortex of the brain with information on the relative positions of the parts of the body • describes how much we know about where we are in space and where all of our parts are in relationship to each other • Our kinesthetic sense helps us move with greater precision, avoid in ...
10 Control of Movement
... instructions coming from higher levels in the motor program • Adjusting motor unit activity to local conditions (obstacles to movement, pain) ...
... instructions coming from higher levels in the motor program • Adjusting motor unit activity to local conditions (obstacles to movement, pain) ...
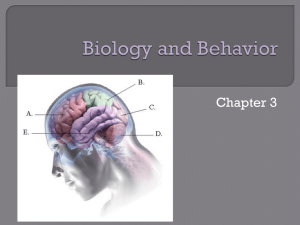
Ch 3 biology and Behavioir Notes
... Cerebrum is the largest part of your brain Cerebral cortex -The outermost layer of the cerebrum ...
... Cerebrum is the largest part of your brain Cerebral cortex -The outermost layer of the cerebrum ...
Acute necrotizing myopathy
... Patients that are prescribed neuromuscular blocking agents and/or steroids should be monitored for the development of neuropathy and myopathy, including serial serum creatinine kinase measurements and repeated ...
... Patients that are prescribed neuromuscular blocking agents and/or steroids should be monitored for the development of neuropathy and myopathy, including serial serum creatinine kinase measurements and repeated ...
Golgi Tendon Reflux
... The stretch reflex operates as a feedback mechanism to control muscle length by causing muscle contraction. In contrast, the tendon reflex operates as a feedback mechanism to control muscle tension by causing muscle relaxation before muscle force becomes so great that tendons might be torn. Althou ...
... The stretch reflex operates as a feedback mechanism to control muscle length by causing muscle contraction. In contrast, the tendon reflex operates as a feedback mechanism to control muscle tension by causing muscle relaxation before muscle force becomes so great that tendons might be torn. Althou ...
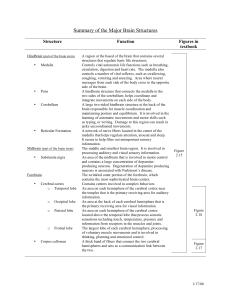
Nervous System
... The five main sections of the brain are: Cerebrum-largest part/conscious activity in the body/intelligence, learning, judgment Cerebellum- located at back of the skull/ coordinates muscles so body can move gracefully Brain Stem-connects brain and spinal cord/regulates flow of information between bra ...
... The five main sections of the brain are: Cerebrum-largest part/conscious activity in the body/intelligence, learning, judgment Cerebellum- located at back of the skull/ coordinates muscles so body can move gracefully Brain Stem-connects brain and spinal cord/regulates flow of information between bra ...
File - Schuette Science
... a. Movement of body parts – muscles attach to the bones to make movement possible b. Transport within the body – muscles help move digestive organs in order to transport food c. Stability – some muscles are always contracted to give us stability (posture) d. Maintain Homeostasis – muscles give off h ...
... a. Movement of body parts – muscles attach to the bones to make movement possible b. Transport within the body – muscles help move digestive organs in order to transport food c. Stability – some muscles are always contracted to give us stability (posture) d. Maintain Homeostasis – muscles give off h ...
Neurological Control of Movement
... the body’s internal environment. Thalamus: interprets sensory input and relays it to the appropriate area of the brain. Hypothalamus: maintains homeostasis. ...
... the body’s internal environment. Thalamus: interprets sensory input and relays it to the appropriate area of the brain. Hypothalamus: maintains homeostasis. ...
Rexed`s Lamina
... Processing at the Perceptual Level Motor cortex Somatosensory cortex Thalamus ...
... Processing at the Perceptual Level Motor cortex Somatosensory cortex Thalamus ...
Zmysły chemiczne
... moved perpendicualarly to the cortical surface responded to activation of only one modality (shown by shading). Electrodes moved at angle to the cortical surface responded to activation of more than one modality. It led to the discovery of columnar organization of the somatosensory cortex. The neuro ...
... moved perpendicualarly to the cortical surface responded to activation of only one modality (shown by shading). Electrodes moved at angle to the cortical surface responded to activation of more than one modality. It led to the discovery of columnar organization of the somatosensory cortex. The neuro ...
The Mechanical Senses: Vestibular and Somatosensation
... For this course, don’t worry about the different pathways to the brain for the different types of sensory neurons, although I will show the pain pathways. ...
... For this course, don’t worry about the different pathways to the brain for the different types of sensory neurons, although I will show the pain pathways. ...
Unit 2 bio-behavior review guide
... Use your book to answer these questions. This will help be your study guide for your test. 1. The right hemisphere, in most people, is primarily responsible for a. counting b. sensation c. emotions d. speech 2. If a person's left hemisphere is dominant, they will probably be a. left-handed b. right- ...
... Use your book to answer these questions. This will help be your study guide for your test. 1. The right hemisphere, in most people, is primarily responsible for a. counting b. sensation c. emotions d. speech 2. If a person's left hemisphere is dominant, they will probably be a. left-handed b. right- ...
The human body contains more than 650 individual muscles which
... The human body contains more than 650 individual muscles which are attached to the skeleton, which provides the pulling power for us to move around. The main job of the muscular system is to provide movement for the body. The muscular system consist of three different types of muscle tissues : skele ...
... The human body contains more than 650 individual muscles which are attached to the skeleton, which provides the pulling power for us to move around. The main job of the muscular system is to provide movement for the body. The muscular system consist of three different types of muscle tissues : skele ...
The Nervous System Lesson Outline LESSON 1 A.
... such as dilating blood vessels and the beating of the heart. It also controls cardiac muscles and ...
... such as dilating blood vessels and the beating of the heart. It also controls cardiac muscles and ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.