A.P. Psychology 4 (E)
... o The system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts ...
... o The system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts ...
Treatment May Consist of
... Relaxes and stretches muscles Breaks adhesions in muscle belly creating balance and pliability Restores balance to synchronize masticatory (chewing) system Pain and inflammation reduction with Ultra Sound, Electric Stimulation: Breaks adhesions in muscle belly and joint disc Decreases inflammation a ...
... Relaxes and stretches muscles Breaks adhesions in muscle belly creating balance and pliability Restores balance to synchronize masticatory (chewing) system Pain and inflammation reduction with Ultra Sound, Electric Stimulation: Breaks adhesions in muscle belly and joint disc Decreases inflammation a ...
Neuroscience 5a – Touch and Proprioception
... » Somatosensory I (SI) – is the primary somatosensory area. The body map is distorted according to the relative density of input from different parts of the body, i.e. the face and hands have the greatest area of processing. The response of neurons in SI varies, and most only respond to a particula ...
... » Somatosensory I (SI) – is the primary somatosensory area. The body map is distorted according to the relative density of input from different parts of the body, i.e. the face and hands have the greatest area of processing. The response of neurons in SI varies, and most only respond to a particula ...
Somatosensory system
... Dorsal root ganglia - spinal nerve - limb and trunk Trigeminal ganglia - cranial nerve - head and face ...
... Dorsal root ganglia - spinal nerve - limb and trunk Trigeminal ganglia - cranial nerve - head and face ...
Proprioception: - e
... tissues, such as ligaments and capsules, and also from those receptors located in extraarticular tissues, such as tendons and muscles [16,18]. Neuropathies, most notably diabetic neuropathy, can cause also significant loss of proprioception [19]. Proprioception has also shown decrease with age [1,13 ...
... tissues, such as ligaments and capsules, and also from those receptors located in extraarticular tissues, such as tendons and muscles [16,18]. Neuropathies, most notably diabetic neuropathy, can cause also significant loss of proprioception [19]. Proprioception has also shown decrease with age [1,13 ...
Human Body Systems - Whitehall District Schools
... pons, and MO. Controls involuntary functions • Hypothalamus: Controls hunger, thirst, body temp, anger, and fatigue. • Thalamus: receives info from sense organs and relays them to proper region of cortex. ...
... pons, and MO. Controls involuntary functions • Hypothalamus: Controls hunger, thirst, body temp, anger, and fatigue. • Thalamus: receives info from sense organs and relays them to proper region of cortex. ...
Input Involves all environmental stimuli – e.g. other players/the ball
... Receive the stimuli/include vision/audition and proprioceptors e.g. eyes see the ball coming. ...
... Receive the stimuli/include vision/audition and proprioceptors e.g. eyes see the ball coming. ...
Neuron
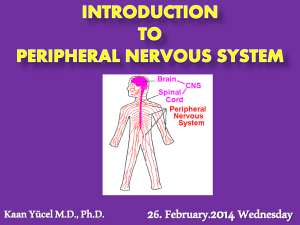
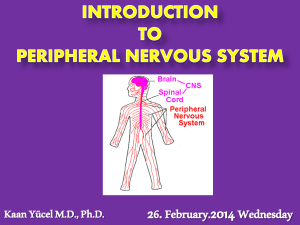
... SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM exteroceptors external stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) proprioception receptors @ tendons, joint capsules, and muscles convey position sense http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v4/n7/fig_tab/nrn1141_F1.html ...
... SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM exteroceptors external stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) proprioception receptors @ tendons, joint capsules, and muscles convey position sense http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v4/n7/fig_tab/nrn1141_F1.html ...
PowerPoint Sunusu
... SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM exteroceptors external stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) proprioception receptors @ tendons, joint capsules, and muscles convey position sense http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v4/n7/fig_tab/nrn1141_F1.html ...
... SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM exteroceptors external stimuli (pain, touch, and temperature) proprioception receptors @ tendons, joint capsules, and muscles convey position sense http://www.nature.com/nrn/journal/v4/n7/fig_tab/nrn1141_F1.html ...
PPT File - Holden R
... • Senses: Means by which brain receives information about environment and body – General: Distributed over large part of body • Somatic: Touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain • Visceral: Internal organs and consist mostly of pain and pressure ...
... • Senses: Means by which brain receives information about environment and body – General: Distributed over large part of body • Somatic: Touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain • Visceral: Internal organs and consist mostly of pain and pressure ...
Chapter 14
... • Senses: Means by which brain receives information about environment and body – General: Distributed over large part of body • Somatic: Touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain • Visceral: Internal organs and consist mostly of pain and pressure ...
... • Senses: Means by which brain receives information about environment and body – General: Distributed over large part of body • Somatic: Touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain • Visceral: Internal organs and consist mostly of pain and pressure ...
Touch
... Kinesthetic Sense System of receptors located in the muscles and joints that provides information about the location of the extremities. Sense receptors located in the joints and muscles send information to the brain concerning muscle tension and joint perception: determine location of limbs. ...
... Kinesthetic Sense System of receptors located in the muscles and joints that provides information about the location of the extremities. Sense receptors located in the joints and muscles send information to the brain concerning muscle tension and joint perception: determine location of limbs. ...
Control of Movement
... disproportionate amount of cortex for body parts high sensitivity: large cortical area ~ ...
... disproportionate amount of cortex for body parts high sensitivity: large cortical area ~ ...
Proprioception
... proprioceptors sending information to the nervous system from joints and ligaments. Depending on the amount, where in the body, and from what proprioceptors the different input is coming from, determines if the information will be made conscious or processed unconsciously. All the input coming into ...
... proprioceptors sending information to the nervous system from joints and ligaments. Depending on the amount, where in the body, and from what proprioceptors the different input is coming from, determines if the information will be made conscious or processed unconsciously. All the input coming into ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.