The following are Biology 201 terms that will be used in Biology 202
... The following are Biology 201 terms that will be used in Biology 202. Biology 202 is a continuation of biology 201 and since we stress homeostasis in both courses there will be a fair amount of information from biology 201 that is used in 202. The following terms you are expected to know and be able ...
... The following are Biology 201 terms that will be used in Biology 202. Biology 202 is a continuation of biology 201 and since we stress homeostasis in both courses there will be a fair amount of information from biology 201 that is used in 202. The following terms you are expected to know and be able ...
File
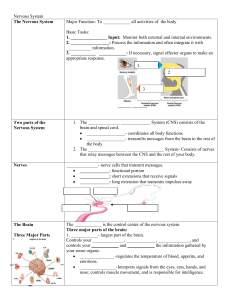
... d. There are two divisions of PNS 1. Somatic system – controls voluntary actions, from CNS to skeletal muscles. 2. Autonomic system – control of involuntary actions, heart rate, breathing, digestion. ...
... d. There are two divisions of PNS 1. Somatic system – controls voluntary actions, from CNS to skeletal muscles. 2. Autonomic system – control of involuntary actions, heart rate, breathing, digestion. ...
Iliopsoas Muscle Injury
... and it can be difficult to determine whether your pet’s limping is due to a muscle injury or some other underlying condition. Since a definitive diagnosis can only be made with specialized testing like ultrasound, CAT scan, or MRI (expensive), many times we will treat your pet for a muscle strain to ...
... and it can be difficult to determine whether your pet’s limping is due to a muscle injury or some other underlying condition. Since a definitive diagnosis can only be made with specialized testing like ultrasound, CAT scan, or MRI (expensive), many times we will treat your pet for a muscle strain to ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
... 3. Axon: long projection that carries impulses away from cell body ...
Chapter 13: Peripheral Nervous System and Reflexes
... the peripheral nerves. Describe the skin dermatomes. 9. Distinguish between autonomic and somatic reflexes, and compare and contrast stretch, flexor, and crossed extensor reflexes. ...
... the peripheral nerves. Describe the skin dermatomes. 9. Distinguish between autonomic and somatic reflexes, and compare and contrast stretch, flexor, and crossed extensor reflexes. ...
Module 1:Human Nervous System Lecture 2:Hindbrain The
... Cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata constitutes the hind brain. Cerebellum is of the size of fist and deals with fine motor coordination and muscular movement. It also has to do with sense of balance, posture and muscle tonus. Damage to it can cause tremor and shaking of the neck. Pons is the rel ...
... Cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata constitutes the hind brain. Cerebellum is of the size of fist and deals with fine motor coordination and muscular movement. It also has to do with sense of balance, posture and muscle tonus. Damage to it can cause tremor and shaking of the neck. Pons is the rel ...
Integrated Listening Systems
... Brain scans of ADHD individuals show the cortex as being hypo‐ or under‐active, particularly in the frontal and temporal lobes. This suggests that the cortex is the source of the problem, which is not necessarily the case. In fact, the cortical (higher brain) function in ADHD individuals is often ...
... Brain scans of ADHD individuals show the cortex as being hypo‐ or under‐active, particularly in the frontal and temporal lobes. This suggests that the cortex is the source of the problem, which is not necessarily the case. In fact, the cortical (higher brain) function in ADHD individuals is often ...
The Muscular System
... • a human has 600 muscles making up over 40% of your total body weight!! • the overall responsibility of the muscles is to provide movement, but also ...
... • a human has 600 muscles making up over 40% of your total body weight!! • the overall responsibility of the muscles is to provide movement, but also ...
UNIT 2: Internal geological agents
... are grouped in the sense organs ans their main characteristics are: - Are very specific for every type of stimulus. - They are stimulated as long as the stimulus exceeds a threshold of excitation. -They can suffer adaptation if the stimulus is persistent (do not respond). - A very intense stimulus c ...
... are grouped in the sense organs ans their main characteristics are: - Are very specific for every type of stimulus. - They are stimulated as long as the stimulus exceeds a threshold of excitation. -They can suffer adaptation if the stimulus is persistent (do not respond). - A very intense stimulus c ...
EXC 7770 Psychoneurological & Medical Issues in Special Education
... runs bodily functions without our awareness or control Sympathetic system: "fight-or-flight" response Parasympathetic system: slowing the heart, constricting the pupils, stimulating the gut and salivary glands, and other responses that are not a priority when being "chased by a tiger“ The state of t ...
... runs bodily functions without our awareness or control Sympathetic system: "fight-or-flight" response Parasympathetic system: slowing the heart, constricting the pupils, stimulating the gut and salivary glands, and other responses that are not a priority when being "chased by a tiger“ The state of t ...
Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the
... Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the dorsal root ganglion neuron specification Aditya Harisankar One of the most complex issues in developmental neurobiology is to understand how diversity in the nervous system is created. A classic model system in which to address this ...
... Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the dorsal root ganglion neuron specification Aditya Harisankar One of the most complex issues in developmental neurobiology is to understand how diversity in the nervous system is created. A classic model system in which to address this ...
chapter 4
... vestibular sense receptors are celia in the inner ear which detect head movements. Kinesthesia provides information about the movement and position of the limbs and other parts of the body relative to one another. Kinesthesia receptors are cells in the joints, muscles, and tendons. 4.16 Perception i ...
... vestibular sense receptors are celia in the inner ear which detect head movements. Kinesthesia provides information about the movement and position of the limbs and other parts of the body relative to one another. Kinesthesia receptors are cells in the joints, muscles, and tendons. 4.16 Perception i ...
Skeletal, Muscular and Nervous Systems
... An overstretched or torn ligament. R.I.C.E. to treat a sprain. ►Dislocation: Bone ends forced out of their proper location. The bones need to be put back into location and then braced until they heal. ►Torn Cartilage: Cartilage between bones is torn. Typically repaired with surgery. Quite common in ...
... An overstretched or torn ligament. R.I.C.E. to treat a sprain. ►Dislocation: Bone ends forced out of their proper location. The bones need to be put back into location and then braced until they heal. ►Torn Cartilage: Cartilage between bones is torn. Typically repaired with surgery. Quite common in ...
Chapter 13 - Integration
... Awareness of body position and movements of parts of the body is provided by the proprioceptive (one’s own), or kinesthetic (motion) sense. It informs us of: o the degree to which muscles are contracted o the amount of tension created in tendons o the change of position of a joint o the orientat ...
... Awareness of body position and movements of parts of the body is provided by the proprioceptive (one’s own), or kinesthetic (motion) sense. It informs us of: o the degree to which muscles are contracted o the amount of tension created in tendons o the change of position of a joint o the orientat ...
Ch on Drugs and Prep for Test
... * Contains the primary auditory cortex * Much of it is used for complex visual tasks in conjunction with the primary visual cortex * These include recognizing faces and perceiving motion * Also crucial to memory * In the left hemisphere, aids language skills ...
... * Contains the primary auditory cortex * Much of it is used for complex visual tasks in conjunction with the primary visual cortex * These include recognizing faces and perceiving motion * Also crucial to memory * In the left hemisphere, aids language skills ...
The Human Body Systems - Mr. Swan
... Cancellous Bone (Spongy): a highly vascular bone that contains red bone marrow, typically located at the end of bones. It contains high surface area, but less density. ...
... Cancellous Bone (Spongy): a highly vascular bone that contains red bone marrow, typically located at the end of bones. It contains high surface area, but less density. ...
• Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to It releases
... Axons branching out to muscle fibers ...
... Axons branching out to muscle fibers ...
Modeling and Imagery
... • Focal vision pathway = “what” pathway • Ambient vision pathway = “vision for action” pathway ...
... • Focal vision pathway = “what” pathway • Ambient vision pathway = “vision for action” pathway ...
Biological Bases Of Behaviour Central Nervous System
... is to transmit info to the brain from the sensory receptors and the motor function involves moving muscles attached to the body’s skeleton. Involves controlling skeletal muscles that are involved in movement If the spinal cord is severed, the somatic nervous system below the point of damage becomes ...
... is to transmit info to the brain from the sensory receptors and the motor function involves moving muscles attached to the body’s skeleton. Involves controlling skeletal muscles that are involved in movement If the spinal cord is severed, the somatic nervous system below the point of damage becomes ...
Chapter 9—Sensory Systems. I. Sensory receptors receive stimuli
... 1. These contain otolithic organs, with hair cells projecting into a jelly-like membrane containing otoliths. 2. These organs detect linear acceleration, and the head’s changing orientation relative to gravity. 3. These movements cause the otolithic organ to deform, bending the underlying hair cells ...
... 1. These contain otolithic organs, with hair cells projecting into a jelly-like membrane containing otoliths. 2. These organs detect linear acceleration, and the head’s changing orientation relative to gravity. 3. These movements cause the otolithic organ to deform, bending the underlying hair cells ...
Stephen Hawking
... muscles throughout the body. • Stephen Hawking is unable to move or speak* because of a disease called Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis ...
... muscles throughout the body. • Stephen Hawking is unable to move or speak* because of a disease called Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis ...
Navigating The Nervous System
... 6. What is the role of the dendrite? a. To receive nerve impulse messages. ...
... 6. What is the role of the dendrite? a. To receive nerve impulse messages. ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.