Nerve cord
... Sensory Neuron: nerve cells that detect stimuli Interneurons: nerve cells that pass information between neurons Motor neurons: nerve cells that carry response information to muscles and other organs ...
... Sensory Neuron: nerve cells that detect stimuli Interneurons: nerve cells that pass information between neurons Motor neurons: nerve cells that carry response information to muscles and other organs ...
Chapter 21
... 1. Somatic sensations arise from stimulation of sensory receptors embedded in: i. skin or subcutaneous layer ii. mucous membranes of the mouth, vagina, and anus iii. muscles, tendons, and joints iv. internal ear 2. Some parts of the body are densely populated with receptors (e.g., tip of tongue, lip ...
... 1. Somatic sensations arise from stimulation of sensory receptors embedded in: i. skin or subcutaneous layer ii. mucous membranes of the mouth, vagina, and anus iii. muscles, tendons, and joints iv. internal ear 2. Some parts of the body are densely populated with receptors (e.g., tip of tongue, lip ...
Phantom Limbs
... continues to be associated with a hand movement despite the fact that the descending motor commands generated by this activation now result in stump muscle contractions. ...
... continues to be associated with a hand movement despite the fact that the descending motor commands generated by this activation now result in stump muscle contractions. ...
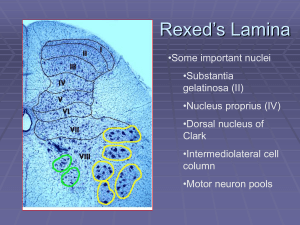
Rexed`s Lamina
... Fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus carry signals from arm and leg Decussation of 2nd order neuron in medulla 3rd order neuron in thalamus carries signal to cerebral cortex ...
... Fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus carry signals from arm and leg Decussation of 2nd order neuron in medulla 3rd order neuron in thalamus carries signal to cerebral cortex ...
First-order neuron
... • 1 million upper motor neurons in cerebral cortex • 90% of fibers decussate(cross over) in the medulla – right side of brain controls left side muscles ...
... • 1 million upper motor neurons in cerebral cortex • 90% of fibers decussate(cross over) in the medulla – right side of brain controls left side muscles ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... relays sensations from periphery of body to brain transmits signals from brain to motor neurons to move body’s muscles ...
... relays sensations from periphery of body to brain transmits signals from brain to motor neurons to move body’s muscles ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Impairs judgment, reasoning memory and muscle functions o Caffeine – _____, can cause physical dependence, stopping can cause headaches and nausea Aim: Senses Hearing – when an object vibrates/moves, it causes the air around it to move. This produces sound waves. Sound waves – bones in ear to nerv ...
... Impairs judgment, reasoning memory and muscle functions o Caffeine – _____, can cause physical dependence, stopping can cause headaches and nausea Aim: Senses Hearing – when an object vibrates/moves, it causes the air around it to move. This produces sound waves. Sound waves – bones in ear to nerv ...
7-6_TheGenOfSpecResp_MajorosMyrtill
... This activation of the Ia afferent causes the monosynaptic activation of the alpha motor neuron that causes the muscle to contract. Alpha motor neurons are lower motor neurons that travel from the spinal cord to the muscle and they innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle. Axons of gamm ...
... This activation of the Ia afferent causes the monosynaptic activation of the alpha motor neuron that causes the muscle to contract. Alpha motor neurons are lower motor neurons that travel from the spinal cord to the muscle and they innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle. Axons of gamm ...
Soccer Specific Warmups
... Dynamic stretches are more appropriate to the warm up as they help reduce muscle stiffness. Static exercises do not reduce muscle stiffness. What are the benefits of a warm up? Performance may be improved, as an appropriate warm up will result in an: ...
... Dynamic stretches are more appropriate to the warm up as they help reduce muscle stiffness. Static exercises do not reduce muscle stiffness. What are the benefits of a warm up? Performance may be improved, as an appropriate warm up will result in an: ...
PowerPoint from lab
... that cause the extensor muscles of the left leg to contract to support the body. • Contralateral reflex arc • Also reciprocal innervation. ...
... that cause the extensor muscles of the left leg to contract to support the body. • Contralateral reflex arc • Also reciprocal innervation. ...
ANTERIOR LEG MASSAGE 1 Session 11
... Irene’s Myomassology Institute ANTERIOR LEG MASSAGE 1 Session 11 A. Definition/Description Systematic and scientific use of pressure, movement and reflex points to affect the musculoskeletal, circulatory, nervous and lymphatic system B. Effects of techniques a. Movement to stretch soft tissue to mai ...
... Irene’s Myomassology Institute ANTERIOR LEG MASSAGE 1 Session 11 A. Definition/Description Systematic and scientific use of pressure, movement and reflex points to affect the musculoskeletal, circulatory, nervous and lymphatic system B. Effects of techniques a. Movement to stretch soft tissue to mai ...
Bio_246_files/Motor Control
... muscles are located anterior to the motor neurons that innervate the flexor muscles. Proximal vs. distal: motor neurons that innervate proximal muscles are located medial to motor neurons that innervate distal muscles. ...
... muscles are located anterior to the motor neurons that innervate the flexor muscles. Proximal vs. distal: motor neurons that innervate proximal muscles are located medial to motor neurons that innervate distal muscles. ...
Control of Movement
... Plasticity of motor cortex Occurs: Denervation, stroke, intensive use of muscles After denervation, many function can be regained, but need training ...
... Plasticity of motor cortex Occurs: Denervation, stroke, intensive use of muscles After denervation, many function can be regained, but need training ...
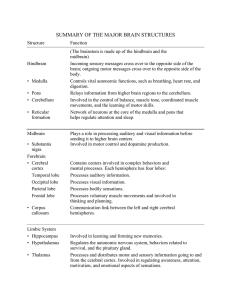
SUMMARY OF THE MAJOR BRAIN STRUCTURES
... Function (The brainstem is made up of the hindbrain and the midbrain) Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays ...
... Function (The brainstem is made up of the hindbrain and the midbrain) Incoming sensory messages cross over to the opposite side of the brain; outgoing motor messages cross over to the opposite side of the body. Controls vital autonomic functions, such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion. Relays ...
E4-D5-12
... Superior oblique eye muscle Muscles of mastication Lateral rectus eye muscle Muscles of facial ...
... Superior oblique eye muscle Muscles of mastication Lateral rectus eye muscle Muscles of facial ...
Nervous System Notes
... nerve pathway that consists of a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron ...
... nerve pathway that consists of a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron ...
Document
... moulded to each other in such a manner as to permit motion only in one plane, forward and backward, the extent of motion at the same time being considerable (elbow and knees). ...
... moulded to each other in such a manner as to permit motion only in one plane, forward and backward, the extent of motion at the same time being considerable (elbow and knees). ...
Sprint Adaptive Swimwear - Post
... Adaptive Bathing suit might be for you. Designed to be easy on and easy off, it offers the look of traditional swimwear and can be put on or removed with little or no assistance from a caregiver, giving more independence to girls and women with dexterity problems. The stylish v-neck design with mode ...
... Adaptive Bathing suit might be for you. Designed to be easy on and easy off, it offers the look of traditional swimwear and can be put on or removed with little or no assistance from a caregiver, giving more independence to girls and women with dexterity problems. The stylish v-neck design with mode ...
Sher`s Neurology Pre-Quiz Quiz
... 22. Posterior, sensory, sensory 23. Autonomic, internal organs 24. T1-L2 & S2-S4 25. Roots 26. False – They are made up of unipolar neurons 27. True REFLEXES 28. Unconscious 29. False – they can not be improved. Work with what you/re born with. 30. 1)Segmental response rule: for every stimulus there ...
... 22. Posterior, sensory, sensory 23. Autonomic, internal organs 24. T1-L2 & S2-S4 25. Roots 26. False – They are made up of unipolar neurons 27. True REFLEXES 28. Unconscious 29. False – they can not be improved. Work with what you/re born with. 30. 1)Segmental response rule: for every stimulus there ...
Nervous System
... Visual & auditory sensory input passes through the midbrain before being relayed to the higher brain centers Coordinates movements of the head related to vision and hearing (e.g. turning towards sound or flashing lights) Controls eye movement and pupil size Monitors unconscious movement of skeletal ...
... Visual & auditory sensory input passes through the midbrain before being relayed to the higher brain centers Coordinates movements of the head related to vision and hearing (e.g. turning towards sound or flashing lights) Controls eye movement and pupil size Monitors unconscious movement of skeletal ...
28.1_Responses
... nerve cells in the nervous system Acquire information from their surroundings, interpret that information, and then “decide” what to do about it. ...
... nerve cells in the nervous system Acquire information from their surroundings, interpret that information, and then “decide” what to do about it. ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.