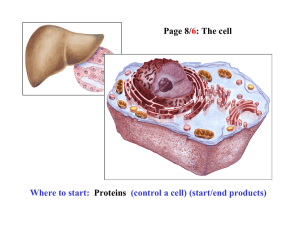
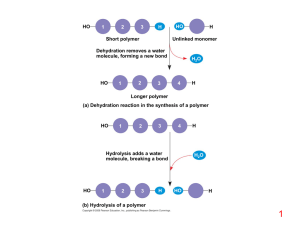
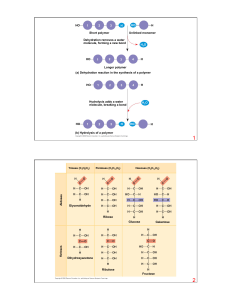
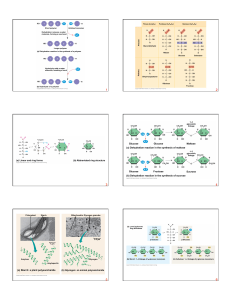
Macromolecules: Proteins and Nucleic Acids
... A typical protein contains 200–300 amino acids some are much smaller (smallest are peptides) -some much larger (titin a protein in skeletal and ...
... A typical protein contains 200–300 amino acids some are much smaller (smallest are peptides) -some much larger (titin a protein in skeletal and ...
Chapter 4: The Chemical Basis of Life
... o Forms by the attraction of the oily parts of lipid molecules for each other and by the attraction of the other parts of the lipid molecules for the surrounding water ...
... o Forms by the attraction of the oily parts of lipid molecules for each other and by the attraction of the other parts of the lipid molecules for the surrounding water ...
TECHNICAL NOTES Aurich, H .
... of the remaining water to dryness, the residue was taken up in 5.0 ml of 0. IN HCI. Aliquots of the solution were brought to pH 2.0 or 7.0 and diluted to a final volume dependent upon the dry weight of the mycelia from which it was extracted (m 15Omg/ml). Water extraction of dried mycelia, as used b ...
... of the remaining water to dryness, the residue was taken up in 5.0 ml of 0. IN HCI. Aliquots of the solution were brought to pH 2.0 or 7.0 and diluted to a final volume dependent upon the dry weight of the mycelia from which it was extracted (m 15Omg/ml). Water extraction of dried mycelia, as used b ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 21. Polymers are broken apart by the process of ___hydrolysis________________. 22. The monomer of a nucleic acid is called a ____nucleotide_______________________. 23. The three parts that make up a nucleotide include _____phosphate group_________, _______5 carbon sugar____________ and ____nitrogen ...
... 21. Polymers are broken apart by the process of ___hydrolysis________________. 22. The monomer of a nucleic acid is called a ____nucleotide_______________________. 23. The three parts that make up a nucleotide include _____phosphate group_________, _______5 carbon sugar____________ and ____nitrogen ...
pptx
... The stability of helices and sheets depends on their sequence of amino acids • Intrinsic propensity of an amino acid to adopt a helical or extended (strand) conformation • Interactions between adjacent R-groups ...
... The stability of helices and sheets depends on their sequence of amino acids • Intrinsic propensity of an amino acid to adopt a helical or extended (strand) conformation • Interactions between adjacent R-groups ...
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1948 Arne Tiselius
... TESS The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1948 Arne Tiselius ...
... TESS The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1948 Arne Tiselius ...
Chapter 30
... • 2) Base at position 73 “Discriminator base” • (3) In many, at least one anticodon base ...
... • 2) Base at position 73 “Discriminator base” • (3) In many, at least one anticodon base ...
Jan. 28 Bio II Answer to warm up Protein Synthesis
... DNA does not however make proteins directly. DNA is used to make RNA inside of the nucleus. Then the RNA exits the nucleus where it can be used to make proteins in the cytoplasm. ...
... DNA does not however make proteins directly. DNA is used to make RNA inside of the nucleus. Then the RNA exits the nucleus where it can be used to make proteins in the cytoplasm. ...
Functions
... Controlling the rate of reactions (enzymes). •Peptide bonds connect the amino acids Regulating cell processes (enzymes). •Enough amino acids connected together will Forming bones and muscles. cause the protein to fold and create a new Transporting substances into or out of cells. shape Helping to fi ...
... Controlling the rate of reactions (enzymes). •Peptide bonds connect the amino acids Regulating cell processes (enzymes). •Enough amino acids connected together will Forming bones and muscles. cause the protein to fold and create a new Transporting substances into or out of cells. shape Helping to fi ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... cylinder from one end. the folding of the polypeptide. ...
... cylinder from one end. the folding of the polypeptide. ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
Peptide microarrays for detailed, high-throughput
... the numbers indicate the position of the first and last amino acids of the peptide in the complete protein (UniProt annotation and numbering). ...
... the numbers indicate the position of the first and last amino acids of the peptide in the complete protein (UniProt annotation and numbering). ...
Structure-function study of the C-terminal tail of Thioredoxin Reductase
... homeostasis and protecting the cell from oxidative damage. TR is the only enzyme that reduces the protein thioredoxin, which functions in further reducing proteins and other cellular substrates. This system works as an antioxidant that protects the cell from damaging molecules like hydrogen peroxide ...
... homeostasis and protecting the cell from oxidative damage. TR is the only enzyme that reduces the protein thioredoxin, which functions in further reducing proteins and other cellular substrates. This system works as an antioxidant that protects the cell from damaging molecules like hydrogen peroxide ...
Week 2 Handout with No answers
... Water’s _____ and _______ allow it to form __________ bonds which are central to the behavior of macromolecules dissolved in it. When lipids are placed in a water solvent the corresponding effect is that water forms a hydration shell around the lipid. This highly ordered water shell results in decre ...
... Water’s _____ and _______ allow it to form __________ bonds which are central to the behavior of macromolecules dissolved in it. When lipids are placed in a water solvent the corresponding effect is that water forms a hydration shell around the lipid. This highly ordered water shell results in decre ...
Macromolecules
... Proteins are made up of amino acid monomer units. The amino end (-NH2) of one amino acid join up with the acid end (-COOH) of another amino acid to form a peptide bond. ...
... Proteins are made up of amino acid monomer units. The amino end (-NH2) of one amino acid join up with the acid end (-COOH) of another amino acid to form a peptide bond. ...
Chapter 13: Carbohydrates
... At the ribosome, each codon on the RNA codes for a single amino acid, and these are joined together to form the polypeptide chain ...
... At the ribosome, each codon on the RNA codes for a single amino acid, and these are joined together to form the polypeptide chain ...
Document
... • Two carbons at a time are cleaved from a fatty acyl-CoA as acetyl-CoA. • This cleavage continues until the entire fatty acid has been converted into acetyl-CoA. ...
... • Two carbons at a time are cleaved from a fatty acyl-CoA as acetyl-CoA. • This cleavage continues until the entire fatty acid has been converted into acetyl-CoA. ...
Chapter 14: Carbohydrates
... • The nonapeptides oxytocin and vasopressin have similar 1o structures. • Only the amino acids at positions 3 and 8 differ. ...
... • The nonapeptides oxytocin and vasopressin have similar 1o structures. • Only the amino acids at positions 3 and 8 differ. ...