Ch. 9-11 Review ppt.
... 11.2 Fatty Acids Fatty Acid Almost exclusively the linear (unbranched) acids with even #’s C’s ...
... 11.2 Fatty Acids Fatty Acid Almost exclusively the linear (unbranched) acids with even #’s C’s ...
Serine Proteases Teaching Exercises
... 4. When these enzymes are made, they are initially in an inactive precursor state, called zymogens. In order for the enzymes to become active, they will be cleaved to arrange the linear amino acid sequence in such a fashion as to orient three particular residues to form an active site for substrates ...
... 4. When these enzymes are made, they are initially in an inactive precursor state, called zymogens. In order for the enzymes to become active, they will be cleaved to arrange the linear amino acid sequence in such a fashion as to orient three particular residues to form an active site for substrates ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
... 2) The branchpoint for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis is chorismate. What is the structure of chorismate? What are the three immediate products derived from chorismate that constitute the first unique steps in the synthesis of the three aromatic amino acids? 3) From where are the two carbons of th ...
yes - Learnblock
... Reactions with large negative ΔGo reach equilibrium quicker no relationship between delta G and speed ...
... Reactions with large negative ΔGo reach equilibrium quicker no relationship between delta G and speed ...
Protein Synthesis
... molecule of water. This is called a condensation reaction and usually occurs between amino acids. The resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond, and the resulting molecule is an amide. A peptide bond can be broken down by hydrolysis (the adding of water). The peptide bonds that are formed within ...
... molecule of water. This is called a condensation reaction and usually occurs between amino acids. The resulting CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond, and the resulting molecule is an amide. A peptide bond can be broken down by hydrolysis (the adding of water). The peptide bonds that are formed within ...
Protein Unit Study Guide/Review Sheets
... If you have questions, make sure to ask them. Come after school for extra help. Review: these topics are not completely inclusive of test questions. You must be able to synthesize responses using this information and also to apply this information in different ways or contexts. GENERAL PROTEIN STRUC ...
... If you have questions, make sure to ask them. Come after school for extra help. Review: these topics are not completely inclusive of test questions. You must be able to synthesize responses using this information and also to apply this information in different ways or contexts. GENERAL PROTEIN STRUC ...
aliphatic amino acid structures
... Cleaving the polypeptide chain Sequencing of peptides Ordering peptide fragments Locating disulfide bond ...
... Cleaving the polypeptide chain Sequencing of peptides Ordering peptide fragments Locating disulfide bond ...
#24926 HAAO A Antibod
... trryptophan metabolism. Itt employs on frrom 3-hydroxyanthranilicc acid. QUIN N is an exccitotoxin who ose toxicity is mediated d by its ability to activa ate glutamate N-methyl-D-asspartate recceptors. Inccreased cerebral levelss of QUIN may partic cipate in th he ammatory dissorders. HAA AO has be ...
... trryptophan metabolism. Itt employs on frrom 3-hydroxyanthranilicc acid. QUIN N is an exccitotoxin who ose toxicity is mediated d by its ability to activa ate glutamate N-methyl-D-asspartate recceptors. Inccreased cerebral levelss of QUIN may partic cipate in th he ammatory dissorders. HAA AO has be ...
Organic Molecules
... Each amino acid has • One carbon with 4 groups attached • The 4 groups are: amine group NH2 • Carboxyl group COOH • Hydrogen • R group—varies with each amino acid ...
... Each amino acid has • One carbon with 4 groups attached • The 4 groups are: amine group NH2 • Carboxyl group COOH • Hydrogen • R group—varies with each amino acid ...
Review Problems #2 (Enzyme Review, Phosphatases
... 14) Which amino acids are essential? What is meant by an essential amino acid? 15) What is meant by a conditionally essential amino acid? What amino acids qualify? 16) Why are both cysteine and methionine often combined together when estimating the content of essential amino acids? 17) What is mean ...
... 14) Which amino acids are essential? What is meant by an essential amino acid? 15) What is meant by a conditionally essential amino acid? What amino acids qualify? 16) Why are both cysteine and methionine often combined together when estimating the content of essential amino acids? 17) What is mean ...
Protein Synthesis Poster
... The process requires enzymes and ATP. The polypeptide chain gets longer. This process stops when a termination (stop) codon is reached. The polypeptide is then complete. The protein now has to undergo folding and the addition of bonds. Folding allows the Protein to reach its 3D (Tertiary Shape) whic ...
... The process requires enzymes and ATP. The polypeptide chain gets longer. This process stops when a termination (stop) codon is reached. The polypeptide is then complete. The protein now has to undergo folding and the addition of bonds. Folding allows the Protein to reach its 3D (Tertiary Shape) whic ...
Revision - Mr C Biology
... The process requires enzymes and ATP. The polypeptide chain gets longer. This process stops when a termination (stop) codon is reached. The polypeptide is then complete. The protein now has to undergo folding and the addition of bonds. Folding allows the Protein to reach its 3D (Tertiary Shape) whic ...
... The process requires enzymes and ATP. The polypeptide chain gets longer. This process stops when a termination (stop) codon is reached. The polypeptide is then complete. The protein now has to undergo folding and the addition of bonds. Folding allows the Protein to reach its 3D (Tertiary Shape) whic ...
Peptide Library Synthesis
... Jamie M. R. Moore 11/9/04 Solid phase peptide synthesis consists of assembling amino acids from the C-terminal to the N-terminal. The a-carboxyl group is attached via an acidlabile linker to a solid support, "resin" (Figure 1). Resins commonly used are composed of polystyrene (P). The amino termina ...
... Jamie M. R. Moore 11/9/04 Solid phase peptide synthesis consists of assembling amino acids from the C-terminal to the N-terminal. The a-carboxyl group is attached via an acidlabile linker to a solid support, "resin" (Figure 1). Resins commonly used are composed of polystyrene (P). The amino termina ...
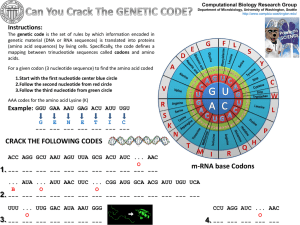
Slide 1
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
Chemistry 464 Biochemistry First Hour Exam
... Actually the COO- is close to its pKa so it is only about ½ protonated at pH2 ...
... Actually the COO- is close to its pKa so it is only about ½ protonated at pH2 ...
LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea
... 1. The enzyme RNA-polymerase reads the DNA molecule in the 3’ to 5’ direction and synthesizes complementary mRNA molecules that determine the order of amino acids in the polypeptide. 2. In eukaryotic cells the mRNA transcript undergoes a series of enzymeregulated modifications. ...
... 1. The enzyme RNA-polymerase reads the DNA molecule in the 3’ to 5’ direction and synthesizes complementary mRNA molecules that determine the order of amino acids in the polypeptide. 2. In eukaryotic cells the mRNA transcript undergoes a series of enzymeregulated modifications. ...
4f03125
... Which of the following statements concerning metabolism of proteins is true: proteins are stored in the pancreas for later use proteins can be removed from the diet with almost no adverse effects proteins are broken down into amino acids, which circulate in the body’s amino acid pool for use in buil ...
... Which of the following statements concerning metabolism of proteins is true: proteins are stored in the pancreas for later use proteins can be removed from the diet with almost no adverse effects proteins are broken down into amino acids, which circulate in the body’s amino acid pool for use in buil ...
a sample task
... polypeptide chains, A and B, shown in the diagram below. Each chain has its own set of amino acids, assembled in a particular order. For instance, the sequence of the A chain starts with glycine at the N-terminus and ends with an asparagine at the C-terminus, and is different from the sequence of th ...
... polypeptide chains, A and B, shown in the diagram below. Each chain has its own set of amino acids, assembled in a particular order. For instance, the sequence of the A chain starts with glycine at the N-terminus and ends with an asparagine at the C-terminus, and is different from the sequence of th ...
Amino Acids
... ionized and positively charged • Histidine is weakly basic, free aa is largely uncharged at physiologic pH. When in protein, His R-group can be either positive or neutral depending on the ionic env. provided by the polypeptide chains of the protein. • This contributes to role of His in functioning o ...
... ionized and positively charged • Histidine is weakly basic, free aa is largely uncharged at physiologic pH. When in protein, His R-group can be either positive or neutral depending on the ionic env. provided by the polypeptide chains of the protein. • This contributes to role of His in functioning o ...
Basic Chemistry and Biochemistry Unit Review Sheet File
... 11. Measurement of the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution may be given in terms of _________________. 12. Glucose is a __________________________________, maltose is a __________________________, and starch is a _________________________________. 13. The type of reaction by which proteins are ...
... 11. Measurement of the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution may be given in terms of _________________. 12. Glucose is a __________________________________, maltose is a __________________________, and starch is a _________________________________. 13. The type of reaction by which proteins are ...