2.6 Natural Polymers
... Nucleotides Have Three Parts 3) A phosphoric acid molecule (phosphate group) ...
... Nucleotides Have Three Parts 3) A phosphoric acid molecule (phosphate group) ...
PS6 - Hormones KEY
... Trace the path of testosterone from its synthesis to one of its many target sites. Testosterone is produced in the testes and travels through the blood in carrier proteins such as serum albumin or sex hormone binding globulin. It passively diffuses through the cell membranes of target cells. ...
... Trace the path of testosterone from its synthesis to one of its many target sites. Testosterone is produced in the testes and travels through the blood in carrier proteins such as serum albumin or sex hormone binding globulin. It passively diffuses through the cell membranes of target cells. ...
Project Presentation
... being inserted into a lipid membrane on OSC’s supercomputer clusters 2. Determine how various mutations of the fusion peptide affects its ability to penetrate a lipid membrane ...
... being inserted into a lipid membrane on OSC’s supercomputer clusters 2. Determine how various mutations of the fusion peptide affects its ability to penetrate a lipid membrane ...
Peptide synthesis – chemistry and modifications
... Since the different side chains of the DNA-encoded amino acids encompass the majority of the common functional groups in organic chemistry, several different types of side chain protecting groups are required for peptide synthesis. These PGs are usually based on the Bzl or tBu group. Amino acids wit ...
... Since the different side chains of the DNA-encoded amino acids encompass the majority of the common functional groups in organic chemistry, several different types of side chain protecting groups are required for peptide synthesis. These PGs are usually based on the Bzl or tBu group. Amino acids wit ...
omproteinsandnucleicacids
... Note: The “R” shows represents where the carboxyl group attaches to an amino acid (also where it would attach to carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids) ...
... Note: The “R” shows represents where the carboxyl group attaches to an amino acid (also where it would attach to carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids) ...
the code of translation
... 5. The first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon. 6. The next tRNA brings in the next amino acid, and a peptide bond is formed between this amino acid and the growing amino acid chain. 7. The process continues with the ribosome moving along the mRNA molecule and the ...
... 5. The first tRNA leaves, and the ribosome moves along the mRNA to the next codon. 6. The next tRNA brings in the next amino acid, and a peptide bond is formed between this amino acid and the growing amino acid chain. 7. The process continues with the ribosome moving along the mRNA molecule and the ...
Lecture 3
... • A peptide bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two amino acids when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the another molecule. – Peptide bonds between amino acids are formed by dehydration synthesis. ...
... • A peptide bond is a covalent bond that is formed between two amino acids when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the another molecule. – Peptide bonds between amino acids are formed by dehydration synthesis. ...
molecular biology and phylogeny
... PROCEDURES: You have already done and discussed the activity entitled "Making Cladograms". The final cladogram produced in that activity (using anatomical similarities) is shown below. The provided chart shows the amino acid sequence in a protein that is homologous (same) for the 20 organisms shown, ...
... PROCEDURES: You have already done and discussed the activity entitled "Making Cladograms". The final cladogram produced in that activity (using anatomical similarities) is shown below. The provided chart shows the amino acid sequence in a protein that is homologous (same) for the 20 organisms shown, ...
Organic Compounds The Big Four
... All organic compounds have Carbon as their core element. Large molecules made up of repeating units are called Polymers. The building blocks of organic compounds are called Monomers. All 20 amino acids have the same structural blueprint; a central Carbon, an Amine group, a Carboxyl acid group, a sin ...
... All organic compounds have Carbon as their core element. Large molecules made up of repeating units are called Polymers. The building blocks of organic compounds are called Monomers. All 20 amino acids have the same structural blueprint; a central Carbon, an Amine group, a Carboxyl acid group, a sin ...
Amino Acids Proteins, and Enzymes
... Involves interactions and cross-links between R groups in different areas of the peptide chain ...
... Involves interactions and cross-links between R groups in different areas of the peptide chain ...
syllabus - Wofford
... Section I – Course Introduction – Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins – Enzymes In this section, you will need to learn the structures of the amino acids. It isn’t so difficult, because you really only need to remember the R groups. Amino acid structures are important for your understanding protein stru ...
... Section I – Course Introduction – Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins – Enzymes In this section, you will need to learn the structures of the amino acids. It isn’t so difficult, because you really only need to remember the R groups. Amino acid structures are important for your understanding protein stru ...
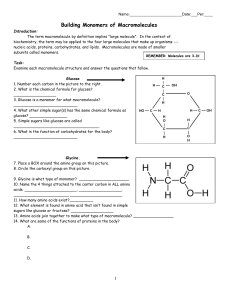
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... 11. How many amino acids exist?__________ 12. What element is found in amino acid that isn’t found in simple sugars like glucose or fructose? __________________ 13. Amino acids join together to make what type of macromolecule? _________________ 14. What are some of the functions of proteins in the b ...
... 11. How many amino acids exist?__________ 12. What element is found in amino acid that isn’t found in simple sugars like glucose or fructose? __________________ 13. Amino acids join together to make what type of macromolecule? _________________ 14. What are some of the functions of proteins in the b ...
Chapter 21 Antimicrobial Medications
... Block binding sites for tRNA/rRNA Inhibit peptide bond formation Prevent shift of reading frame ...
... Block binding sites for tRNA/rRNA Inhibit peptide bond formation Prevent shift of reading frame ...
Protein mteabolism
... Removal of α-amino group: Transamination: is the transfer of α-amino group from α-amino acid to α-keto acid to yield α-keto acid of the original amino acid and a new amino acid. The enzymes that catalyze transamination are called transaminases or ...
... Removal of α-amino group: Transamination: is the transfer of α-amino group from α-amino acid to α-keto acid to yield α-keto acid of the original amino acid and a new amino acid. The enzymes that catalyze transamination are called transaminases or ...