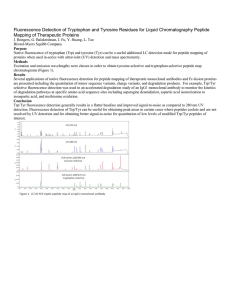
Carbon Isomers
... Ribonucleic acid (RNA) • RNA similar to DNA except – Contains ribose instead of deoxyribose – Contains uracil instead of thymine ...
... Ribonucleic acid (RNA) • RNA similar to DNA except – Contains ribose instead of deoxyribose – Contains uracil instead of thymine ...
Elements Found in Living Things
... Dehydration synthesis (removal of a water molecule) links amino acids link together to form chains called polypeptides. Polypeptide chains join to form proteins. The bonds holding amino acids to each other are known as peptide bonds. Use your textbook to make a sketch of a dipeptide (2 amino acids l ...
... Dehydration synthesis (removal of a water molecule) links amino acids link together to form chains called polypeptides. Polypeptide chains join to form proteins. The bonds holding amino acids to each other are known as peptide bonds. Use your textbook to make a sketch of a dipeptide (2 amino acids l ...
UNIT 4: Chapter 6.1 Yellow Box Questions AK
... 2. Name and describe and draw the process that builds macromolecules. The process that builds macromolecules is called dehydration synthesis. To form a covalent bond between two sub-unit molecules, an -0H (hydroxyl) group is removed from one sub-unit and a hydrogen atom is removed from the other sub ...
... 2. Name and describe and draw the process that builds macromolecules. The process that builds macromolecules is called dehydration synthesis. To form a covalent bond between two sub-unit molecules, an -0H (hydroxyl) group is removed from one sub-unit and a hydrogen atom is removed from the other sub ...
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... • Biological molecules consist predominantly of carbon atoms bonded to other carbon atoms or to atoms of oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or hydrogen. (p. 36) • Hydrocarbons are molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen; thus, they store considerable energy. (p. 36) • Functional groups have definite ...
... • Biological molecules consist predominantly of carbon atoms bonded to other carbon atoms or to atoms of oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or hydrogen. (p. 36) • Hydrocarbons are molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen; thus, they store considerable energy. (p. 36) • Functional groups have definite ...
Protein_hierarchy
... • (c) describe, with the aid of diagrams, the formation and breakage of peptide bonds in the synthesis and hydrolysis of dipeptides and polypeptides; • (d) explain, with the aid of diagrams, the term primary structure; • (e) explain, with the aid of diagrams, the term secondary structure with refere ...
... • (c) describe, with the aid of diagrams, the formation and breakage of peptide bonds in the synthesis and hydrolysis of dipeptides and polypeptides; • (d) explain, with the aid of diagrams, the term primary structure; • (e) explain, with the aid of diagrams, the term secondary structure with refere ...
Codon Practice
... 5. A certain mRNA molecule has the following sequence: 5’ G G U A U C C C G A U U 3’ A. How many codons are in this sequence? _________________ B. What amino acid sequences are in this sequence? _________________________ ...
... 5. A certain mRNA molecule has the following sequence: 5’ G G U A U C C C G A U U 3’ A. How many codons are in this sequence? _________________ B. What amino acid sequences are in this sequence? _________________________ ...
Teaching Notes
... Answers to Questions in Exercise: Q1. In PDB entry 1hla, how many polymer chains are there? What are they? A1: There are 3 protein chains - HLA, beta-2 microglobulin and the antigen peptide Q2. Where are the Cys residues located? Comment about how they are contributing to the stability of the struct ...
... Answers to Questions in Exercise: Q1. In PDB entry 1hla, how many polymer chains are there? What are they? A1: There are 3 protein chains - HLA, beta-2 microglobulin and the antigen peptide Q2. Where are the Cys residues located? Comment about how they are contributing to the stability of the struct ...
Chemistry part 2
... amino acid sequence • Determined by the sequence of amino acids • Amino acids linked by peptide bonds • Chain is called polypeptide • Sequence proceeds from “Nterminus” to “C-terminus” • Amino acid sequence determined by DNA code ...
... amino acid sequence • Determined by the sequence of amino acids • Amino acids linked by peptide bonds • Chain is called polypeptide • Sequence proceeds from “Nterminus” to “C-terminus” • Amino acid sequence determined by DNA code ...
Biosynthesis of non-amino acids from amino acid precursors
... AA to energy stores. Alanine plays important role in carbon transfers btwn liver and muscle during AA breakdown. Degradative conditions: Muscle protein degraded to individual AA. Transaminate with alpha-KG to form glutamate Glu will TA pyruvate to form alanine. Ala travels to liver, will ...
... AA to energy stores. Alanine plays important role in carbon transfers btwn liver and muscle during AA breakdown. Degradative conditions: Muscle protein degraded to individual AA. Transaminate with alpha-KG to form glutamate Glu will TA pyruvate to form alanine. Ala travels to liver, will ...
Chapter 3. The Concept of Protecting Functional Groups
... t-Butyl esters t-BuO group provides steric shielding of the carbonyl carbon, thereby lowering its susceptibility to attack by nucleophilic reagents. It is cleaved by CF3CO2H or HCO2H in refluxing benzene. ...
... t-Butyl esters t-BuO group provides steric shielding of the carbonyl carbon, thereby lowering its susceptibility to attack by nucleophilic reagents. It is cleaved by CF3CO2H or HCO2H in refluxing benzene. ...
Amino Acids
... is attached to four different chemical groups is a chiral or optically active carbon atom. Glycine is the exception. amino acids exist in two forms, D and L, that are mirror images of each other. All amino acids found in proteins are of the Lconfiguration. ...
... is attached to four different chemical groups is a chiral or optically active carbon atom. Glycine is the exception. amino acids exist in two forms, D and L, that are mirror images of each other. All amino acids found in proteins are of the Lconfiguration. ...
Homework1
... Describe acidosis and alkalosis, give examples of how each arise, and predict how each will shift the bicarbonate equilibrium. Describe the processes by which the body attempts to compensate for acidosis or alkalosis. ...
... Describe acidosis and alkalosis, give examples of how each arise, and predict how each will shift the bicarbonate equilibrium. Describe the processes by which the body attempts to compensate for acidosis or alkalosis. ...
Chapter 22, Proteins
... ¾All R-groups on any one chain alternate, first above, then below the plane of the sheet, etc. ¾The distinction between secondary structure (α-helix, β-pleated sheets) and tertiary structure is that secondary structures are stabilized only by hydrogen bonds arising through the peptide units, while t ...
... ¾All R-groups on any one chain alternate, first above, then below the plane of the sheet, etc. ¾The distinction between secondary structure (α-helix, β-pleated sheets) and tertiary structure is that secondary structures are stabilized only by hydrogen bonds arising through the peptide units, while t ...
3. Proteins Classification (2017)
... there are more it becomes a polypeptide. Short polypeptide chains are usually called peptides while longer ones are called proteins. ...
... there are more it becomes a polypeptide. Short polypeptide chains are usually called peptides while longer ones are called proteins. ...
4 Amino Acids - School of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Pyrrolysine (Pyl or O) is a genetically coded amino acid used by some methanogenic archaea and one known bacterium. Pyrrolysine is used in enzymes that are part of methaneproducing metabolism. Pyrrolysine is similar to lysine, but with an added pyrroline ring linked to the end of the lysine side cha ...
... Pyrrolysine (Pyl or O) is a genetically coded amino acid used by some methanogenic archaea and one known bacterium. Pyrrolysine is used in enzymes that are part of methaneproducing metabolism. Pyrrolysine is similar to lysine, but with an added pyrroline ring linked to the end of the lysine side cha ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
... From the Greek word proteio “Proteios” - first rank, most important Play central roles in all biological processes ...
... From the Greek word proteio “Proteios” - first rank, most important Play central roles in all biological processes ...
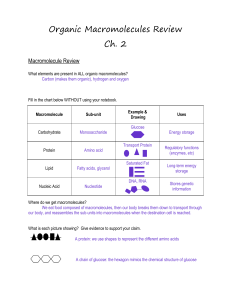
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... A glucose molecule is a specific type of monosaccharide. A monosaccharide is a single sugar, so it could also mean ribose (a 5-carbon sugar found in nucleic acids). ...
... A glucose molecule is a specific type of monosaccharide. A monosaccharide is a single sugar, so it could also mean ribose (a 5-carbon sugar found in nucleic acids). ...
Gene Action
... Translation 2. The large ribosomal subunit attaches to the small subunit, creating a functional ribosome – The initiator tRNA binds to the start codon – One end of the tRNA carries a specific amino acid, the other consists of a triplet of bases ...
... Translation 2. The large ribosomal subunit attaches to the small subunit, creating a functional ribosome – The initiator tRNA binds to the start codon – One end of the tRNA carries a specific amino acid, the other consists of a triplet of bases ...
large molecule consisting of many identical or similar subunits
... primary (1) structure: the sequence of amino acids. This is determined by genes. A slight change can affect the structure and function as in sickle cell anemia. secondary (2) structure: regular, repeated folding of a protein’s peptide backbone which stabilizes H bonds. This 2 structure contains a ...
... primary (1) structure: the sequence of amino acids. This is determined by genes. A slight change can affect the structure and function as in sickle cell anemia. secondary (2) structure: regular, repeated folding of a protein’s peptide backbone which stabilizes H bonds. This 2 structure contains a ...