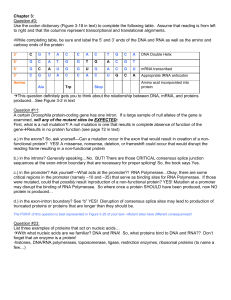
Proteins Large, complex polymer consists of carbon, oxygen
... Contain detailed instructions to build proteins. Polymers that are made up of monomers called nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of a sugar, phosphate group and nitrogencontaining molecule (base) Two general types: RNA and DNA Nucleic acids have just one function DNA and RNA work together to ...
... Contain detailed instructions to build proteins. Polymers that are made up of monomers called nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of a sugar, phosphate group and nitrogencontaining molecule (base) Two general types: RNA and DNA Nucleic acids have just one function DNA and RNA work together to ...
Proteins
... parts towards the centre and hydrophilic parts towards the edges – therefore water soluble – metabolic Fibrous – long fibres of repeated sequences of AA’s so therefore they are insoluble in water – and these are structural – Keratin and Collagen ...
... parts towards the centre and hydrophilic parts towards the edges – therefore water soluble – metabolic Fibrous – long fibres of repeated sequences of AA’s so therefore they are insoluble in water – and these are structural – Keratin and Collagen ...
Biological Chemistry II: Problem Set 1
... How long is the molecule? (b) A 40 amino acid peptide fragment forms a two-stranded, antiparallel β-sheet with a hairpin loop consisting of 4 residues. What is the largest dimension of this motif? (c) Although β-hairpin structures are often unstable in solution, incorporation of D-ProXaa sequences h ...
... How long is the molecule? (b) A 40 amino acid peptide fragment forms a two-stranded, antiparallel β-sheet with a hairpin loop consisting of 4 residues. What is the largest dimension of this motif? (c) Although β-hairpin structures are often unstable in solution, incorporation of D-ProXaa sequences h ...
Document
... were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mutation at a promoter may disrupt the binding of RNA Polymerase. So where once a protein SHOULD have been produced, now NO protein is produced… d.) in the exon-intron boundary? See “b” YES! Disruption of consens ...
... were mutated, could that possibly result inproduction of a non-functional protein? YES! Mutation at a promoter may disrupt the binding of RNA Polymerase. So where once a protein SHOULD have been produced, now NO protein is produced… d.) in the exon-intron boundary? See “b” YES! Disruption of consens ...
Making Proteins
... Making proteins from mRNA 1. Ribosomes attach to the “start” codon of mRNA (AUG), signaling the beginning of the protein chain 2. mRNA codons are matched to corresponding tRNA anticodons and appropriate amino acids are strung together. 3. Dehydration synthesis occurs between the amino acids, and the ...
... Making proteins from mRNA 1. Ribosomes attach to the “start” codon of mRNA (AUG), signaling the beginning of the protein chain 2. mRNA codons are matched to corresponding tRNA anticodons and appropriate amino acids are strung together. 3. Dehydration synthesis occurs between the amino acids, and the ...
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins Essential Cell Biology
... itself to form a __________________ a. A hydrogen bond forms between every __________________ amino acid whit the C=O of one bonding to the N-H of the other b. The __________________ makes a complete turn every 3.6 amino acids c. Sometimes two or three α-helices wrap around each other to form a stru ...
... itself to form a __________________ a. A hydrogen bond forms between every __________________ amino acid whit the C=O of one bonding to the N-H of the other b. The __________________ makes a complete turn every 3.6 amino acids c. Sometimes two or three α-helices wrap around each other to form a stru ...
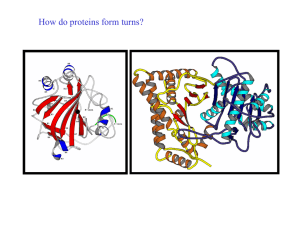
How do proteins form turns? - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... reasons. The calcium ion is octahedrally coordinated by carboxyl side chains, main chain groups and bound solvent ...
... reasons. The calcium ion is octahedrally coordinated by carboxyl side chains, main chain groups and bound solvent ...
Proteins
... given time is largely determined by how much of which proteins are present (“expressed”) at that time. ...
... given time is largely determined by how much of which proteins are present (“expressed”) at that time. ...
Organic Compounds
... Unsaturated Fatty Acids Liquids at room temperature Carbons have double bonds, therefore they are not saturated with Hydrogen atoms Examples: - Olive Oil - Corn Oil ...
... Unsaturated Fatty Acids Liquids at room temperature Carbons have double bonds, therefore they are not saturated with Hydrogen atoms Examples: - Olive Oil - Corn Oil ...
Protein Misfolding and Degenerative Diseases
... increases. Why is this? As incredible as it might sound, these diseases are caused not by bacteria or viruses but rather by something conceptually quite simple: incorrect protein folding. Introductory biology courses teach us that proteins are essential for the organism because they participate in v ...
... increases. Why is this? As incredible as it might sound, these diseases are caused not by bacteria or viruses but rather by something conceptually quite simple: incorrect protein folding. Introductory biology courses teach us that proteins are essential for the organism because they participate in v ...
Sections 5.3-5.5 - BridgesToLiteracy.com
... To Sum It All Up!! Lipids have little or no affinity for water Key types of lips are fats, phospholipids and steroids 3 fatty acids + glycerol = triacylglycerol Carbon skeleton – hydrogen atoms = unsaturated fatty acid A fat’s main purpose is to store energy Many hormones are steroids. ...
... To Sum It All Up!! Lipids have little or no affinity for water Key types of lips are fats, phospholipids and steroids 3 fatty acids + glycerol = triacylglycerol Carbon skeleton – hydrogen atoms = unsaturated fatty acid A fat’s main purpose is to store energy Many hormones are steroids. ...
Protein Synthesis Drawing
... More tRNA molecules transfer correct amino acids to the growing protein chain (by matching the anticodon on tRNA to the codons on mRNA). Remember: One tRNA only carries one kind of A.A. ...
... More tRNA molecules transfer correct amino acids to the growing protein chain (by matching the anticodon on tRNA to the codons on mRNA). Remember: One tRNA only carries one kind of A.A. ...
Structure and Properties of Proteins
... acid), they’re going to interact. When the amino acids are interacting, the proteins would bend. When the proteins bend because of the attractions, it’s going to form the B-pleated sheet (functional group) or alpha helix and it’ll depend on what the amino acids are and how they interact. When they i ...
... acid), they’re going to interact. When the amino acids are interacting, the proteins would bend. When the proteins bend because of the attractions, it’s going to form the B-pleated sheet (functional group) or alpha helix and it’ll depend on what the amino acids are and how they interact. When they i ...
intracellular protein synthesis, post
... production of most antigenic peptides presented to the immune system on MHC-class I molecules. In this process, intracellular proteins are degraded to 8-9 residue fragments, are then transported into the ER, and become associated with class I molecules. 20s and 2 6 s proteasomes degrade proteins pro ...
... production of most antigenic peptides presented to the immune system on MHC-class I molecules. In this process, intracellular proteins are degraded to 8-9 residue fragments, are then transported into the ER, and become associated with class I molecules. 20s and 2 6 s proteasomes degrade proteins pro ...
Announcements - Hiram College
... What does it do? How similar is it to something else? How does it fold? Where does it go in a cell? What does it interact with? How it is regulated? Level of confidence? ...
... What does it do? How similar is it to something else? How does it fold? Where does it go in a cell? What does it interact with? How it is regulated? Level of confidence? ...
Proteins and DNA
... Answer: DNA is the genetic material. It contains the information that describes the proteins that should be made. Like proteins DNA is similar to a string of pearls, but in this case, there are only four kinds of pearls. The letters A, C, G and T represents the four kinds. Their order in the string ...
... Answer: DNA is the genetic material. It contains the information that describes the proteins that should be made. Like proteins DNA is similar to a string of pearls, but in this case, there are only four kinds of pearls. The letters A, C, G and T represents the four kinds. Their order in the string ...
Analytical Sciences, Poster AS-101 Kinetics and identification of non
... by pipets is the low reproducibility due to spreading and therefore the dilution of the sample. To overcome this, we developed a protocol to spray trypsin or matrix solution. This works in a short time and preserves the multiplexing SPRi measurements. As a proof of concept we will show an investigat ...
... by pipets is the low reproducibility due to spreading and therefore the dilution of the sample. To overcome this, we developed a protocol to spray trypsin or matrix solution. This works in a short time and preserves the multiplexing SPRi measurements. As a proof of concept we will show an investigat ...
custom protein production service
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
Complete Protein - Kelloggs Nutrition
... Proteins, along with carbohydrates and fats, make up the bulk of our diet. We tend to think of proteins as body builders, and they are;; they form the structure of things like muscle, hair and connective tissue. They also make up hormones that regulate our system, enzymes that trigger chemical react ...
... Proteins, along with carbohydrates and fats, make up the bulk of our diet. We tend to think of proteins as body builders, and they are;; they form the structure of things like muscle, hair and connective tissue. They also make up hormones that regulate our system, enzymes that trigger chemical react ...
103 Lecture Ch20b
... • Peptide bonds are amide bonds and are resistant to hydrolysis • However, they can be hydrolyzed with enzymes or with strong acid or base and heat • Proteins are hydrolyzed in the stomach with both acid (HCl) and enzymes (such as pepsin) - the amino acids are then absorbed in the intestines and use ...
... • Peptide bonds are amide bonds and are resistant to hydrolysis • However, they can be hydrolyzed with enzymes or with strong acid or base and heat • Proteins are hydrolyzed in the stomach with both acid (HCl) and enzymes (such as pepsin) - the amino acids are then absorbed in the intestines and use ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.