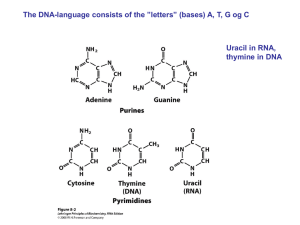
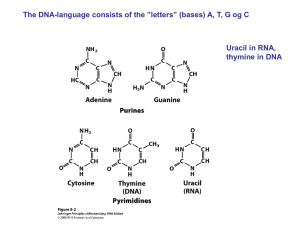
individual paired chromosomes sets of DNA, specifically paired
... sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
... sets of DNA, specifically paired alleles for individual inheritable traits ...
corriganpaperabstract - Workspace
... Nucleotide signalling molecules are important messengers in key pathways that allow cellular responses to changing environments. Canonical secondary signalling molecules act through specific receptor proteins by direct binding to alter their activity. Cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is a ...
... Nucleotide signalling molecules are important messengers in key pathways that allow cellular responses to changing environments. Canonical secondary signalling molecules act through specific receptor proteins by direct binding to alter their activity. Cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is a ...
Slide 1
... Specific chemical properties (charge, hydrophic, hydrophilic) Amino acid chemistries give proteins their primary, secondary, tertiary structure Structure function relationships Biological roles of proteins ...
... Specific chemical properties (charge, hydrophic, hydrophilic) Amino acid chemistries give proteins their primary, secondary, tertiary structure Structure function relationships Biological roles of proteins ...
Chapter 2 Section 3: The Chemistry of Life
... ________; a group of like or different atoms held together by chemical forces. ...
... ________; a group of like or different atoms held together by chemical forces. ...
College 5
... (meaning contacts that also occur in the functional protein). The potential energy drives the system to a conformation where a certain number of native contacts has been established, but the chain is not yet folded. Note that there are many possible pathways. Once this point is reached, the chain fo ...
... (meaning contacts that also occur in the functional protein). The potential energy drives the system to a conformation where a certain number of native contacts has been established, but the chain is not yet folded. Note that there are many possible pathways. Once this point is reached, the chain fo ...
amino acids
... ● results in a “backbone” with a repeating pattern of sugar-phosphatesugar-phosphate... ...
... ● results in a “backbone” with a repeating pattern of sugar-phosphatesugar-phosphate... ...
The Amino Acid Song
... (to the tune of Old McDonald) Tracey Tripp, Nell Ditch, Julie Milam and Frances Jenkins Amino acids are the building blocks of protein And there are 20 of them. Nine of them we call essential Our body cannot make them. They are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threo ...
... (to the tune of Old McDonald) Tracey Tripp, Nell Ditch, Julie Milam and Frances Jenkins Amino acids are the building blocks of protein And there are 20 of them. Nine of them we call essential Our body cannot make them. They are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threo ...
Lesson 4 Protein Synthesis.notebook
... • your DNA contains the instructions on how your cells are to assemble amino acids into proteins • these instructions must first be passed onto a molecule called RNA which will then take the message to a ribosome to produce a certain protein from amino acids ...
... • your DNA contains the instructions on how your cells are to assemble amino acids into proteins • these instructions must first be passed onto a molecule called RNA which will then take the message to a ribosome to produce a certain protein from amino acids ...
Microsoft Word - Organic Macromolecules HOMEWORK (1)x
... As matter and energy flow through different organizational levels of living systems, chemical elements are recombined in different ways to form different products. Research an example where this can be observed in the human body. Cite your resource. ...
... As matter and energy flow through different organizational levels of living systems, chemical elements are recombined in different ways to form different products. Research an example where this can be observed in the human body. Cite your resource. ...
Cellular Chemical Reactions
... What are the four main types of large molecules and what characteristic do they share? What is an important property of lipids? What are some things that proteins do? What are the subunits of nucleic acids called? Use pg 537 to describe how a cell membrane is ...
... What are the four main types of large molecules and what characteristic do they share? What is an important property of lipids? What are some things that proteins do? What are the subunits of nucleic acids called? Use pg 537 to describe how a cell membrane is ...
(DNA) and ribose (RNA)
... Lipids typically have long chains of carbon atoms, but exist in many forms, also linked to polysaccharides (lipopolysacchariders), phosphate (phospholipids) and as triglycerides. They are typically found in cell membranes and as stored fat (do you see it on yourself?). Candle-lights are composed of ...
... Lipids typically have long chains of carbon atoms, but exist in many forms, also linked to polysaccharides (lipopolysacchariders), phosphate (phospholipids) and as triglycerides. They are typically found in cell membranes and as stored fat (do you see it on yourself?). Candle-lights are composed of ...
(DNA) and ribose (RNA)
... Lipids typically have long chains of carbon atoms, but exist in many forms, also linked to polysaccharides (lipopolysacchariders), phosphate (phospholipids) and as triglycerides. They are typically found in cell membranes and as stored fat (do you see it on yourself?). Candle-lights are composed of ...
... Lipids typically have long chains of carbon atoms, but exist in many forms, also linked to polysaccharides (lipopolysacchariders), phosphate (phospholipids) and as triglycerides. They are typically found in cell membranes and as stored fat (do you see it on yourself?). Candle-lights are composed of ...
Molecules of life
... in many polypeptides ◦ Useful in determining the function of unknown proteins ...
... in many polypeptides ◦ Useful in determining the function of unknown proteins ...
November 19, 2012 3:00 PM Livermore Center 101 Isaac C. Sanchez
... combination of molecular dynamics (MD) and Monte Carlo methods for 6 thermally rearranged (TR) polyimides and their precursors. Diffusion, solubility, and permeation of gases in TR polymers and their precursors were simulated at 308 K, with results that agree with experimental data. A similar method ...
... combination of molecular dynamics (MD) and Monte Carlo methods for 6 thermally rearranged (TR) polyimides and their precursors. Diffusion, solubility, and permeation of gases in TR polymers and their precursors were simulated at 308 K, with results that agree with experimental data. A similar method ...
HonBio Chapter 3 notes
... structures and functions of life Structural proteins provide associations between body parts. Contractile proteins are found within muscle. Defensive proteins include antibodies of the immune system. ...
... structures and functions of life Structural proteins provide associations between body parts. Contractile proteins are found within muscle. Defensive proteins include antibodies of the immune system. ...
Chapter 2 SWBATS Content Standards Cell Biology 1. The
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
Proteins File
... more) or polymer of a-amino-acids, linked together by peptide (amide) bonds. Short chains are called peptides. The free NH3+ end is called the N-terminus, and the free CO2- end the C terminus. The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of amino-acids in the chain. The sequence of -N–C–C- seg ...
... more) or polymer of a-amino-acids, linked together by peptide (amide) bonds. Short chains are called peptides. The free NH3+ end is called the N-terminus, and the free CO2- end the C terminus. The primary structure of a protein is the sequence of amino-acids in the chain. The sequence of -N–C–C- seg ...
FROM TRAIT TO PROTEIN - CLASSROOM
... Part I Proteins are large, complex macromolecules that play critical roles in the body. Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a prot ...
... Part I Proteins are large, complex macromolecules that play critical roles in the body. Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids that can be combined to make a prot ...
Proteins
... it is small enough to fit through the cell membrane… THEN, the cell uses those micromolecules to make macromolecules! ...
... it is small enough to fit through the cell membrane… THEN, the cell uses those micromolecules to make macromolecules! ...
Unit 03 Macromolecule Review
... 5. Describe what happens to a carbohydrate when it is consumed by an organism. Do the same for a lipid, and then again for a protein. 6. How are monosaccharides important to plants? To humans? 7. How is cellulose important to plants? To humans? 8. How is starch important to plants? To humans? 9. Wha ...
... 5. Describe what happens to a carbohydrate when it is consumed by an organism. Do the same for a lipid, and then again for a protein. 6. How are monosaccharides important to plants? To humans? 7. How is cellulose important to plants? To humans? 8. How is starch important to plants? To humans? 9. Wha ...
Making Proteins
... Making proteins from mRNA 1. Ribosomes attach to the “start” codon of mRNA (AUG), signaling the beginning of the protein chain 2. mRNA codons are matched to corresponding tRNA anticodons and appropriate amino acids are strung together. 3. Dehydration synthesis occurs between the amino acids, and the ...
... Making proteins from mRNA 1. Ribosomes attach to the “start” codon of mRNA (AUG), signaling the beginning of the protein chain 2. mRNA codons are matched to corresponding tRNA anticodons and appropriate amino acids are strung together. 3. Dehydration synthesis occurs between the amino acids, and the ...
Name: Ch 6 Take Home Quiz Due: 3/22/13 Multiple
... 14) The type of RNA that carries the amino acid to the ribosome is A) mRNA. B) rRNA. C) tRNA. D) All of these answers are correct. 15) Which of the following is a protein that provides structural support to body tissues? A) antibody B) hemoglobin C) insulin D) collagen 16) The proteins that act as c ...
... 14) The type of RNA that carries the amino acid to the ribosome is A) mRNA. B) rRNA. C) tRNA. D) All of these answers are correct. 15) Which of the following is a protein that provides structural support to body tissues? A) antibody B) hemoglobin C) insulin D) collagen 16) The proteins that act as c ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.