DNA Replication and DNA Repair Study Guide Focus on the
... i. Beginning point of replication ii. Prokaryotes (bacteria)- 1 origin of replication iii. Eukaryotes- 1 to 2000 origins of replication per chromosome b. Direction- two forks proceed in opposite directions c. Forks i. Replication sites ii. Proceed in one direction (one for each direction) iii. Repli ...
... i. Beginning point of replication ii. Prokaryotes (bacteria)- 1 origin of replication iii. Eukaryotes- 1 to 2000 origins of replication per chromosome b. Direction- two forks proceed in opposite directions c. Forks i. Replication sites ii. Proceed in one direction (one for each direction) iii. Repli ...
E. coli - Madeira City Schools
... I. Replicating the ends of DNA strand 1. If ends are not replicated, DNA strand gets shorter and shorter 2. Prokaryotes = circular DNA, no problem 3. Eukaryotes = have telomeres at the ends of their DNA a. do not contain genes b. consist of multiple repetitions of one short nucleotide sequence ---> ...
... I. Replicating the ends of DNA strand 1. If ends are not replicated, DNA strand gets shorter and shorter 2. Prokaryotes = circular DNA, no problem 3. Eukaryotes = have telomeres at the ends of their DNA a. do not contain genes b. consist of multiple repetitions of one short nucleotide sequence ---> ...
and Post-assessment multiple choice questions
... A. Taq polymerase is heat stable and can therefore withstand the high temperature steps required of PCR that most other enzymes cannot tolerate. B. Taq polymerase is more efficient than other polymerases. C. Taq polymerase is pressure stable and can therefore withstand the high pressure steps requi ...
... A. Taq polymerase is heat stable and can therefore withstand the high temperature steps required of PCR that most other enzymes cannot tolerate. B. Taq polymerase is more efficient than other polymerases. C. Taq polymerase is pressure stable and can therefore withstand the high pressure steps requi ...
Document
... •Mutation refers to a change in a base-pair (e.g. G-C bp to A-T bp is a mutation) •Problems arise when DNA damage is converted to mutation ...
... •Mutation refers to a change in a base-pair (e.g. G-C bp to A-T bp is a mutation) •Problems arise when DNA damage is converted to mutation ...
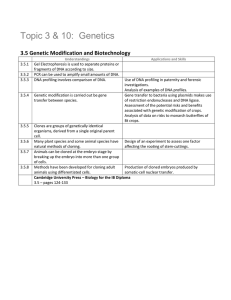
3.5 Genetic Modification and Biotechnology
... Many plant species and some animal species have Design of an experiment to assess one factor natural methods of cloning. affecting the rooting of stem-cuttings. Animals can be cloned at the embryo stage by breaking up the embryo into more than one group of cells. Methods have been developed for clon ...
... Many plant species and some animal species have Design of an experiment to assess one factor natural methods of cloning. affecting the rooting of stem-cuttings. Animals can be cloned at the embryo stage by breaking up the embryo into more than one group of cells. Methods have been developed for clon ...
DNA polymerase
... Helicase: unwinds DNA helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs – usually at the weaker A-T bonds. RNA Primase: produces short pieces of RNA – like primers – that are recognized by DNA polymerase to start replication. DNA polymerase: recruits nucleotides and copies DNA strand in complement ...
... Helicase: unwinds DNA helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between base pairs – usually at the weaker A-T bonds. RNA Primase: produces short pieces of RNA – like primers – that are recognized by DNA polymerase to start replication. DNA polymerase: recruits nucleotides and copies DNA strand in complement ...
Genetics Study Guide Answers
... at the 5' end of the template. B) Okazaki fragments prevent elongation in the 3' to 5' direction. C) the polarity of the DNA molecule prevents addition of nucleotides at the 3' end. D) replication must progress toward the replication fork. E) DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the free 3' en ...
... at the 5' end of the template. B) Okazaki fragments prevent elongation in the 3' to 5' direction. C) the polarity of the DNA molecule prevents addition of nucleotides at the 3' end. D) replication must progress toward the replication fork. E) DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the free 3' en ...
DNA NOTES
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
Mutations Can Change the Meaning of Genes
... sequence of DNA Types of Mutations: Base substitutions: replacement of one nucleotide w/ another. May or may not affect protein Base deletions & Base insertions: May be more harmful b/c all subsequent codons will be altered ...
... sequence of DNA Types of Mutations: Base substitutions: replacement of one nucleotide w/ another. May or may not affect protein Base deletions & Base insertions: May be more harmful b/c all subsequent codons will be altered ...
Replication Worksheet
... o Assuming that helicase is moving in this ⃪ direction, which strand is leading and which is lagging? What if helicase moves this → direction? o What happens on the lagging strand? How is this corrected? o What is the end result of replication and what is each molecule made of (is it old or new?) o ...
... o Assuming that helicase is moving in this ⃪ direction, which strand is leading and which is lagging? What if helicase moves this → direction? o What happens on the lagging strand? How is this corrected? o What is the end result of replication and what is each molecule made of (is it old or new?) o ...
Genes and Heredity Nucleotide Structure A G C T A C DNA
... A DNA molecule is made up of two strands. These strands are antiparallel (they run in opposite directions). The sequence of one strand is complementary to the sequence of the other strand (A pairs with T; G pairs with C). ...
... A DNA molecule is made up of two strands. These strands are antiparallel (they run in opposite directions). The sequence of one strand is complementary to the sequence of the other strand (A pairs with T; G pairs with C). ...
CS 262—Lecture 1 Notes • 4-‐5 HWs, 3 late days • (Optional
... • DNA in nucleus and each cell has copies of DNA o Although we have trillions of cells, an average somatic cell only has 30-‐60 differences from the “pure”, original genome • DNA packed into chromosom ...
... • DNA in nucleus and each cell has copies of DNA o Although we have trillions of cells, an average somatic cell only has 30-‐60 differences from the “pure”, original genome • DNA packed into chromosom ...
Goal 3: Learner will develop an understanding of the continuity of
... 9. After translation, what would the amino acid sequence be for this section of mRNA? (read from right to left) ...
... 9. After translation, what would the amino acid sequence be for this section of mRNA? (read from right to left) ...
Class 2
... Non essential gene and α-complementation already present Large dsDNA region contains adenine methylation which should help limit the mismatch repair of the mutations arising during in vitro synthesis Easy to score large numbers of plaques Single stranded phage are readily sequenced ...
... Non essential gene and α-complementation already present Large dsDNA region contains adenine methylation which should help limit the mismatch repair of the mutations arising during in vitro synthesis Easy to score large numbers of plaques Single stranded phage are readily sequenced ...
Road To Discovery of DNA
... – 2 different sugar groups – Ribose or Deoxyribose – contain repeating subunits he called nucleotides – both DNA/RNA contain 1 of 4 different nitrogen bases. (A, C, G and T or U). ...
... – 2 different sugar groups – Ribose or Deoxyribose – contain repeating subunits he called nucleotides – both DNA/RNA contain 1 of 4 different nitrogen bases. (A, C, G and T or U). ...
Across
... 2. the two sides of DNA held together by weak ____ bonds 5. always pairs with cytosine 6. where protein is assembled from the message on the RNA 7. the shape of DNA, double ____ 9. process of copying DNA 13. composed of a sugar, a base, and a phosphate 14. sections of DNA that code for a trait 15. r ...
... 2. the two sides of DNA held together by weak ____ bonds 5. always pairs with cytosine 6. where protein is assembled from the message on the RNA 7. the shape of DNA, double ____ 9. process of copying DNA 13. composed of a sugar, a base, and a phosphate 14. sections of DNA that code for a trait 15. r ...
Neuraspora crassa
... RNA is transcribed in a 5’ to 3’ direction Only ONE strand of DNA is transcribed at a time ...
... RNA is transcribed in a 5’ to 3’ direction Only ONE strand of DNA is transcribed at a time ...
The Bioinformatics Institute
... Key events prior to the replication process (E. coli): • Binding of DnaA protein at Origin separate (‘melt’) the strands. • DnaC & DnaB bind at Origin. • Then Helicase (DnaB) unwinding of duplex in opposite directions away from Origin. • Unwinding of duplex is an ATP-dependent process. • Single- ...
... Key events prior to the replication process (E. coli): • Binding of DnaA protein at Origin separate (‘melt’) the strands. • DnaC & DnaB bind at Origin. • Then Helicase (DnaB) unwinding of duplex in opposite directions away from Origin. • Unwinding of duplex is an ATP-dependent process. • Single- ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.