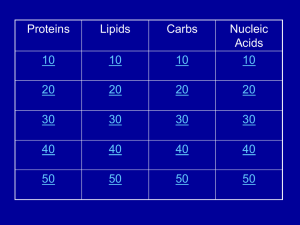
Daily Trivia - James B. Conant High School
... How does information from the DNA get to the cytoplasm? How does the zipper get unzipped in DNA replication? What does the work in getting the amino acids to the worker? ...
... How does information from the DNA get to the cytoplasm? How does the zipper get unzipped in DNA replication? What does the work in getting the amino acids to the worker? ...
Transcription Practice Questions
... (7) Where do eukaryotes store their DNA? ______________________________________________. (8) The following statements are about Transcription. Put a Check next to the statements which are TRUE! ________ One molecule of messenger RNA is produced. ________ The mRNA produced is complimentary to one of ...
... (7) Where do eukaryotes store their DNA? ______________________________________________. (8) The following statements are about Transcription. Put a Check next to the statements which are TRUE! ________ One molecule of messenger RNA is produced. ________ The mRNA produced is complimentary to one of ...
Biology Name: Jacob Smith DNA: Interactive Simulation I: DNA
... Click: “DNA replication” (upper left) and then click “Unzip” Read the script and answer the questions below. 1. In a real cell, what does the DNA molecule do before it unzips? The DNA unwinds from spools made of protein. ...
... Click: “DNA replication” (upper left) and then click “Unzip” Read the script and answer the questions below. 1. In a real cell, what does the DNA molecule do before it unzips? The DNA unwinds from spools made of protein. ...
DNA and RNA DNA: Important scientist: Frederick Griffith: Oswald
... phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base there are 4 of them: two known as purines (which have 2 rings in their structures) called: _____________________________ and __________________________________. Two others called pyrimidines (which have 1 ring in their structure) called _______________________ ...
... phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base there are 4 of them: two known as purines (which have 2 rings in their structures) called: _____________________________ and __________________________________. Two others called pyrimidines (which have 1 ring in their structure) called _______________________ ...
DNA: The Genetic Material
... – Matches existing DNA bases with complementary nucleotides and links them – All have several common features • Add new bases to 3′ end of existing strands • Synthesize in 5′-to-3′ direction • Require a primer of RNA ...
... – Matches existing DNA bases with complementary nucleotides and links them – All have several common features • Add new bases to 3′ end of existing strands • Synthesize in 5′-to-3′ direction • Require a primer of RNA ...
Study Guide Ch
... into ________________________. c. As DNA strand unwinds and unzips the enzyme __________________________________________________ ...
... into ________________________. c. As DNA strand unwinds and unzips the enzyme __________________________________________________ ...
DNA
... bonds. Keep the top hydrogen bond attached. Open the sides of the DNA and make a diagram. ...
... bonds. Keep the top hydrogen bond attached. Open the sides of the DNA and make a diagram. ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... * Technique used to separate samples of DNA, RNA, and protein according to charge and/or size ...
... * Technique used to separate samples of DNA, RNA, and protein according to charge and/or size ...
NAME DNA, RNA, and PROTEINS - BGHS-GRAVES-2011
... 5. Which type(s) of RNA is/are involved in protein synthesis? _______________________________ 6. Where in the cell does transcription take place?_______________________________________ 7. Where in the cell does translation take place?______________________________________ 8. DNA wraps around histone ...
... 5. Which type(s) of RNA is/are involved in protein synthesis? _______________________________ 6. Where in the cell does transcription take place?_______________________________________ 7. Where in the cell does translation take place?______________________________________ 8. DNA wraps around histone ...
CH8 Study Guide
... 8. What is the structural difference between purines and pyrimidines? 9. What type of bond is found in between base pairs to hold the 2 strands together? 10. Chargaff studied the amounts of bases present in different organisms… a. In each type of organism studied, which bases were found in equal amo ...
... 8. What is the structural difference between purines and pyrimidines? 9. What type of bond is found in between base pairs to hold the 2 strands together? 10. Chargaff studied the amounts of bases present in different organisms… a. In each type of organism studied, which bases were found in equal amo ...
Review–Protein Synthesis 15
... 23. If one nitrogen base is changed to another. How will it affect the amino acids? What if it codes for the same amino acid? ...
... 23. If one nitrogen base is changed to another. How will it affect the amino acids? What if it codes for the same amino acid? ...
File
... genetic crosses. b. determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses. c. determine which species should be used in genetic crosses. d. decide which organisms are best to use in genetic crosses. ...
... genetic crosses. b. determine the actual outcomes of genetic crosses. c. determine which species should be used in genetic crosses. d. decide which organisms are best to use in genetic crosses. ...
DNA Structure - Colorado State University
... still generally have the same proteins, but make them very differently (such as English vs. German). Generally, the more closely related two species (or organisms) are, the more similar their DNA and protein sequences are to each other. The greater the time since the two species shared a common ance ...
... still generally have the same proteins, but make them very differently (such as English vs. German). Generally, the more closely related two species (or organisms) are, the more similar their DNA and protein sequences are to each other. The greater the time since the two species shared a common ance ...
DNA - TeacherWeb
... Is it DNA? In 1928, Griffith found out that the information carried in the cell could be transferred to another cell. He called this transfer “transformation”. He did not yet know about DNA and the prevailing thought of the time was that protein was the more likely culprit. ...
... Is it DNA? In 1928, Griffith found out that the information carried in the cell could be transferred to another cell. He called this transfer “transformation”. He did not yet know about DNA and the prevailing thought of the time was that protein was the more likely culprit. ...
Chapter 12 DNA and RNA ANSWER KEY
... acids used in the construction of proteins. 8. Answers may vary. Having a sequence of DNA that could be edited into several different mRNA molecules makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different proteins specifically used in different tissues. This allows a cell to carry less gene ...
... acids used in the construction of proteins. 8. Answers may vary. Having a sequence of DNA that could be edited into several different mRNA molecules makes it possible for a single gene to produce several different proteins specifically used in different tissues. This allows a cell to carry less gene ...
DNA is the genetic material DNA structure
... • Insertion or deletion of 3/6/9 etc. nucleotides will insert or delete one/two/three amino acids but other amino acids will remain the same ...
... • Insertion or deletion of 3/6/9 etc. nucleotides will insert or delete one/two/three amino acids but other amino acids will remain the same ...
The protein that assesses distances
... Institute for Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden when they started their work for this research. “It is indeed a ‘sensory’ issue, but let’s not forget we are dealing with protein complexes, which don’t have organs of sense”, explains Florescu. ...
... Institute for Physics of Complex Systems in Dresden when they started their work for this research. “It is indeed a ‘sensory’ issue, but let’s not forget we are dealing with protein complexes, which don’t have organs of sense”, explains Florescu. ...
Ch 14- 17 Unit Test - Akron Central Schools
... • During meiosis, a defect occurs in a cell that results in the failure of microtubules, spindle fibers, to bind at the kinetochores, a protein structure on chromatids where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart. Which of the following is the most likely res ...
... • During meiosis, a defect occurs in a cell that results in the failure of microtubules, spindle fibers, to bind at the kinetochores, a protein structure on chromatids where the spindle fibers attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart. Which of the following is the most likely res ...
Nucleic Acids and DNA Replication
... • Pyrimidines (1 ring) • Cytosine, C • Thymine, T (only in DNA) • Uracil, U (only in RNA) ...
... • Pyrimidines (1 ring) • Cytosine, C • Thymine, T (only in DNA) • Uracil, U (only in RNA) ...
DNA notes
... bind to each other in a complimentary and antiparallel fashion, you should be able to work out many problems in molecular biol. and this will save you confusion and lots of memorization!! DNA structure slide, CAP DNA, lac DNA ...
... bind to each other in a complimentary and antiparallel fashion, you should be able to work out many problems in molecular biol. and this will save you confusion and lots of memorization!! DNA structure slide, CAP DNA, lac DNA ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.