Chapter 5: Lipids and Nucleic Acids
... The double bond causes a “kink” in the fatty acid chain which prevents the chains from packing close enough together to form a solid b) What is meant by “hydrogenated” vegetable oils? Why is this process done? H’s are added to the unsat. veg. oil; turn the liquid into a solid at room temp. (Ex. Pean ...
... The double bond causes a “kink” in the fatty acid chain which prevents the chains from packing close enough together to form a solid b) What is meant by “hydrogenated” vegetable oils? Why is this process done? H’s are added to the unsat. veg. oil; turn the liquid into a solid at room temp. (Ex. Pean ...
الشريحة 1
... The set of two primers, usually in the range between 15 and 30 nucleotides, are chemically synthesized to correspond to the two ends of the gene or DNA to be amplified. The primer concentrations are always in excess of the DNA target. The nucleotide primer sequences for the DNA amplification reactio ...
... The set of two primers, usually in the range between 15 and 30 nucleotides, are chemically synthesized to correspond to the two ends of the gene or DNA to be amplified. The primer concentrations are always in excess of the DNA target. The nucleotide primer sequences for the DNA amplification reactio ...
EXAM 4.doc
... (1) genotype of the mother _______________________(REMEMBER: sex-linked!!) (1) genotype of the father ________________________(REMEMBER: sex-linked!!) (2) type of gametes produced by the mother and ratio (or percentage) gamete type __________________ percentage of this type of gamete produced ______ ...
... (1) genotype of the mother _______________________(REMEMBER: sex-linked!!) (1) genotype of the father ________________________(REMEMBER: sex-linked!!) (2) type of gametes produced by the mother and ratio (or percentage) gamete type __________________ percentage of this type of gamete produced ______ ...
Genetics = science of heredity - Suffolk County Community College
... SCCC BIO244 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes ...
... SCCC BIO244 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes ...
Recall that the nucleus is a small spherical, dense body in a cell
... building blocks for an organism, proteins make up your skin, your hair, parts of individual cells. How you look is largely determined by the proteins that are made. The proteins that are made are determined by the sequence of DNA in the nucleus. Chromosomes are composed of genes, which is a segment ...
... building blocks for an organism, proteins make up your skin, your hair, parts of individual cells. How you look is largely determined by the proteins that are made. The proteins that are made are determined by the sequence of DNA in the nucleus. Chromosomes are composed of genes, which is a segment ...
BIOCHEMISTRY 461 Dr. Bourque Chapter 28 Study Questions Fall
... The primer for DNA synthesis is an RNA molecule formed by the enzyme ____________ . The DNA strand that is replicated continuously is known as the ________________ strand. DNA polymerase III is approximately _____________ times faster than DNA polymerase I. During DNA replication, the RNA primer pie ...
... The primer for DNA synthesis is an RNA molecule formed by the enzyme ____________ . The DNA strand that is replicated continuously is known as the ________________ strand. DNA polymerase III is approximately _____________ times faster than DNA polymerase I. During DNA replication, the RNA primer pie ...
Identify the goal of DNA replication Explain the role of DNA in
... Explain the role of chromosomes in inheritance ...
... Explain the role of chromosomes in inheritance ...
Central Dogma: Molecular GeneKcs
... You should be able to: Describe the flow of informa2on in a cell from DNA to protein Recognize excep2ons to the central dogma Compare and contrast the structure & func2on of RNA & DNA Predict ...
... You should be able to: Describe the flow of informa2on in a cell from DNA to protein Recognize excep2ons to the central dogma Compare and contrast the structure & func2on of RNA & DNA Predict ...
Name Period _____ Date
... 2) RNA is a nucleic acid the same as DNA except a) RNA sugar is _______________ not Deoxyribose (RNA has _____________) b) RNA uses _____________ instead of Thymine so uracil pairs with ________ U - A c) RNA is a ______________ strand, DNA is a double strand (helix) 3) There are 3 types of RNA _____ ...
... 2) RNA is a nucleic acid the same as DNA except a) RNA sugar is _______________ not Deoxyribose (RNA has _____________) b) RNA uses _____________ instead of Thymine so uracil pairs with ________ U - A c) RNA is a ______________ strand, DNA is a double strand (helix) 3) There are 3 types of RNA _____ ...
DNA and the Genetic Code
... Nirenberg’s mRNA sequence: UUUUUUUUUUUUUUUU Sample mRNA sequence: AUGGCCUUAGGUACUAAAU Questions he couldn’t answer with this experiment are: How long are codons (“words”)? Are they the same length? Do the codons overlap? Are codons consecutive bases? Every other? Is there “punctuation” between codon ...
... Nirenberg’s mRNA sequence: UUUUUUUUUUUUUUUU Sample mRNA sequence: AUGGCCUUAGGUACUAAAU Questions he couldn’t answer with this experiment are: How long are codons (“words”)? Are they the same length? Do the codons overlap? Are codons consecutive bases? Every other? Is there “punctuation” between codon ...
1. A 6-frame translation map of a segment of DNA is shown, with
... strand) so, the RNA transcripts will be smallest at the right (where transcription has just begun) and longest at the left (where it is about to end). For ORF C/D (Watson strand is coding) the situation reversed. Note that the RNA lengths shown aren't quite accurate -- what we are looking for is rel ...
... strand) so, the RNA transcripts will be smallest at the right (where transcription has just begun) and longest at the left (where it is about to end). For ORF C/D (Watson strand is coding) the situation reversed. Note that the RNA lengths shown aren't quite accurate -- what we are looking for is rel ...
Grading rubric DNA Project Unit
... 1. DNA Questions Requirements: complete sentences, word processed, correct 2. Project DNA chart Requirements: shows 6 codons for DNA and RNA, 6 amino acids, 6 traits 3. DNA transcribed into RNA Requirements: all DNA translated correctly into RNA 6 traits should be visible 4. Colored picture of the p ...
... 1. DNA Questions Requirements: complete sentences, word processed, correct 2. Project DNA chart Requirements: shows 6 codons for DNA and RNA, 6 amino acids, 6 traits 3. DNA transcribed into RNA Requirements: all DNA translated correctly into RNA 6 traits should be visible 4. Colored picture of the p ...
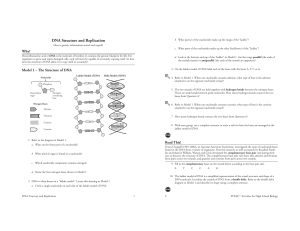
18 DNA Structure and Replication-S
... 12. Locate the DNA helicase on Model 2. a. What type of biological molecule is DNA helicase? b. What is the role of DNA helicase in the replication of DNA? 13. What rule is used to join the free nucleotides to the exposed bases of the DNA? 14. This type of replication is called semi-conservative rep ...
... 12. Locate the DNA helicase on Model 2. a. What type of biological molecule is DNA helicase? b. What is the role of DNA helicase in the replication of DNA? 13. What rule is used to join the free nucleotides to the exposed bases of the DNA? 14. This type of replication is called semi-conservative rep ...
Replisome
The replisome is a complex molecular machine that carries out replication of DNA. The replisome first unwinds double stranded DNA into two single strands. For each of the resulting single strands, a new complementary sequence of DNA is synthesized. The net result is formation of two new double stranded DNA sequences that are exact copies of the original double stranded DNA sequence.In terms of structure, the replisome is composed of two replicative polymerase complexes, one of which synthesizes the leading strand, while the other synthesizes the lagging strand. The replisome is composed of a number of proteins including helicase, RFC, PCNA, gyrase/topoisomerase, SSB/RPA, primase, DNA polymerase I, RNAse H, and ligase.