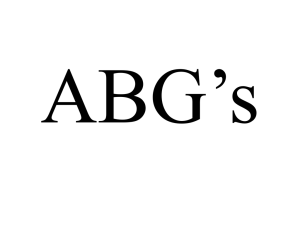NEED TO KNOW 2014 - ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... Mitosis is important because? When cells are damaged or destroyed mitosis is the process that replaces the cells with new ones that are identical to the old ones When an organism grows, mitosis is the process that makes new cells ...
... Mitosis is important because? When cells are damaged or destroyed mitosis is the process that replaces the cells with new ones that are identical to the old ones When an organism grows, mitosis is the process that makes new cells ...
BIOCHEMISTRY (CHEM 360)
... Why do you think the cysteine side chain is involved here instead of the serine side chain (as in protease enzymes) to form an acyl intermediate? The cysteine side chain forms a thio-ester, instead of a normal ester with serine. Thio-esters are more reactive and thus more susceptible to nucleophilic ...
... Why do you think the cysteine side chain is involved here instead of the serine side chain (as in protease enzymes) to form an acyl intermediate? The cysteine side chain forms a thio-ester, instead of a normal ester with serine. Thio-esters are more reactive and thus more susceptible to nucleophilic ...
glucose
... •GLUT 2 is more highly expressed in the periportal cells of the liver, also a characteristic of the gluconeogenic enzymes. •This type of regulation would support the argument that up-regulation of GLUT 2 was more critical in glucose export from the liver to maintain glucose homeostasis than in impor ...
... •GLUT 2 is more highly expressed in the periportal cells of the liver, also a characteristic of the gluconeogenic enzymes. •This type of regulation would support the argument that up-regulation of GLUT 2 was more critical in glucose export from the liver to maintain glucose homeostasis than in impor ...
ANPS 020 Black 03-16
... ISLET BETA CELL INSULIN PRODUCTION Synthesized as 21 amino acid chain 3 disulfide bonds Intervening connecting peptide (also called C-peptide) is removed by dibasic RR/KR cleavage INSULIN REPCEPTOR SIGNALING Insulin binds to tyrosine receptors kinases in target cells Different signaling pathways fro ...
... ISLET BETA CELL INSULIN PRODUCTION Synthesized as 21 amino acid chain 3 disulfide bonds Intervening connecting peptide (also called C-peptide) is removed by dibasic RR/KR cleavage INSULIN REPCEPTOR SIGNALING Insulin binds to tyrosine receptors kinases in target cells Different signaling pathways fro ...
Uncoupling Proteins Cellular Metabolism Cellular Metabolism
... Lactate Oxidation 3. Deamination ...
... Lactate Oxidation 3. Deamination ...
Dysglycemia refers to any disorders in serum (blood) glucose
... is important for the formation of hormones. High cholesterol and the body’s inability to manage it properly negatively impacts hormone balance, as we will see. When the insulin is not managed properly, males and females both have difficulty binding or synthesizing proper hormones and eliminating exc ...
... is important for the formation of hormones. High cholesterol and the body’s inability to manage it properly negatively impacts hormone balance, as we will see. When the insulin is not managed properly, males and females both have difficulty binding or synthesizing proper hormones and eliminating exc ...
MACROMOLECULES - Savitha Sastry
... Monosaccharide to Disaccharide A Glucose monomer and a fructose monomer can be joined using a GLYCOSIDIC LINKAGE to form SUCROSE (know to identify this link) SUCROSE is a DISACCHARIDE SUCROSE ...
... Monosaccharide to Disaccharide A Glucose monomer and a fructose monomer can be joined using a GLYCOSIDIC LINKAGE to form SUCROSE (know to identify this link) SUCROSE is a DISACCHARIDE SUCROSE ...
Harvesting Energy: Glycolysis and Cellular Respiration
... – Fructose bisphosphate is split into two threecarbon molecules of glyceraldehyde 3phosphate (G3P) – In a series of reactions, each G3P molecule is converted into a pyruvate, generating two ATPs per conversion, for a total of four ATPs – Because two ATPs were used to activate the glucose molecule th ...
... – Fructose bisphosphate is split into two threecarbon molecules of glyceraldehyde 3phosphate (G3P) – In a series of reactions, each G3P molecule is converted into a pyruvate, generating two ATPs per conversion, for a total of four ATPs – Because two ATPs were used to activate the glucose molecule th ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... 4. What are the names of both 3 carbon molecules that result when glucose is broken down? a) Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate, 1,3 – biphosphate b) Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate, dihydroxy – acetone phosphate c) Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate, fructose – 1 ,6 biphosphate d) Dihydroxy – acetone phosph ...
... 4. What are the names of both 3 carbon molecules that result when glucose is broken down? a) Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate, 1,3 – biphosphate b) Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate, dihydroxy – acetone phosphate c) Glyceraldehyde – 3 – phosphate, fructose – 1 ,6 biphosphate d) Dihydroxy – acetone phosph ...
Document
... Humans and bacteria that make yogurt produce another product through fermenataion, namely _______. ...
... Humans and bacteria that make yogurt produce another product through fermenataion, namely _______. ...
Cellular Respiration
... The last reaction in the citric acid cycle produces a product that is a substrate for the first reaction of the citric acid cycle. ...
... The last reaction in the citric acid cycle produces a product that is a substrate for the first reaction of the citric acid cycle. ...
biologically important molecules
... INSULIN hormone causes glucose to enter LIVER and MUSCLE where it is condensed into GLYCOGEN for storage. GLUCAGON hormone causes GLYCOGEN to be hydrolyzed back into individual glucose monomers and released into the bloodstream where it is transported to cells and used for energy. ...
... INSULIN hormone causes glucose to enter LIVER and MUSCLE where it is condensed into GLYCOGEN for storage. GLUCAGON hormone causes GLYCOGEN to be hydrolyzed back into individual glucose monomers and released into the bloodstream where it is transported to cells and used for energy. ...
File
... there is a lot of lactic acid in the culture fluid. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the poor condition of the cells? a. There is too much glucose in the culture fluid b. There is not enough glucose in the culture fluid c. There is too much oxygen in the culture fluid d. The ...
... there is a lot of lactic acid in the culture fluid. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the poor condition of the cells? a. There is too much glucose in the culture fluid b. There is not enough glucose in the culture fluid c. There is too much oxygen in the culture fluid d. The ...
Chapter Two Crossword Puzzle 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
... 7. ________ is a storage polysaccharide composed of glucose monomers and found in plants 11. Fats are lipids made from ________ and fatty acids. 13. _______ is a polysaccharide used by insects and crustaceans to build an exoskeleton. 14. A fat contains one glycerol linked to________fatty acids. 15. ...
... 7. ________ is a storage polysaccharide composed of glucose monomers and found in plants 11. Fats are lipids made from ________ and fatty acids. 13. _______ is a polysaccharide used by insects and crustaceans to build an exoskeleton. 14. A fat contains one glycerol linked to________fatty acids. 15. ...
Respiration Notes (chapter 8)
... Several Types of Fermentation: -Prokaryotic (Bacteria) fermentation -Sulfer Bacteria (Coal Mines) -Iron Bacteria (TITANIC Rusticles) -Decomposing Bacteria -indicated by a black color & aromatic methane smell. -found in: ...
... Several Types of Fermentation: -Prokaryotic (Bacteria) fermentation -Sulfer Bacteria (Coal Mines) -Iron Bacteria (TITANIC Rusticles) -Decomposing Bacteria -indicated by a black color & aromatic methane smell. -found in: ...
Blood Glucose Concentration
... 1. Remove glucose from blood [primary and unique effect of insulin] ...
... 1. Remove glucose from blood [primary and unique effect of insulin] ...
DB QS
... Gluconeogenesis is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms.[2] In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis takes place mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. Diabetic ketoacidosis arises because of a lack of insulin in the b ...
... Gluconeogenesis is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms.[2] In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis takes place mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. Diabetic ketoacidosis arises because of a lack of insulin in the b ...
ABG’s
... • Need oxygen to live • Need to get rid of CO2 a waste product • Enzymes need pH 7.35 to 7.45 for optimal working ...
... • Need oxygen to live • Need to get rid of CO2 a waste product • Enzymes need pH 7.35 to 7.45 for optimal working ...
LECTURE #1 STUDY GUIDE
... Anaerobic Energy from Glucose: Glycolysis (Glucose Splitting) Glycolysis occurs in what part of the cell? ...
... Anaerobic Energy from Glucose: Glycolysis (Glucose Splitting) Glycolysis occurs in what part of the cell? ...
Instructor: Brendan Leezer
... Example = sucrose (table sugar) formed by combining glucose and fructose Polysaccharides = The largest carbohydrate molecules. They are polymers composed of many monosaccharide subunits. Examples = starch, glycogen, and cellulose Starch consists of highly branched chains of glucose units. o It is ...
... Example = sucrose (table sugar) formed by combining glucose and fructose Polysaccharides = The largest carbohydrate molecules. They are polymers composed of many monosaccharide subunits. Examples = starch, glycogen, and cellulose Starch consists of highly branched chains of glucose units. o It is ...
Metabolism 2010edit
... A Metabolic economy • Basic principles of supply & demand regulate metabolic economy – balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced – these molecules become feedback regulators • they control enzymes at strategic points in glycolysis & Krebs cycle – levels of AMP, ADP, ATP » regul ...
... A Metabolic economy • Basic principles of supply & demand regulate metabolic economy – balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced – these molecules become feedback regulators • they control enzymes at strategic points in glycolysis & Krebs cycle – levels of AMP, ADP, ATP » regul ...
Human Body Systems
... • Occurs when there’s NOT enough O2 to complete the aerobic phase. • Fermentation turns pyruvic acid into lactic acid. • Later lactic acid can be converted back to pyruvic acid when O2 is present. ...
... • Occurs when there’s NOT enough O2 to complete the aerobic phase. • Fermentation turns pyruvic acid into lactic acid. • Later lactic acid can be converted back to pyruvic acid when O2 is present. ...
9.6 Respiration 4 (Control and other metabolites)
... A Metabolic economy • Basic principles of supply & demand regulate metabolic economy – balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced – these molecules become feedback regulators • they control enzymes at strategic points in glycolysis & Krebs cycle – levels of AMP, ADP, ATP » regul ...
... A Metabolic economy • Basic principles of supply & demand regulate metabolic economy – balance the supply of raw materials with the products produced – these molecules become feedback regulators • they control enzymes at strategic points in glycolysis & Krebs cycle – levels of AMP, ADP, ATP » regul ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.