File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... Simplified structural formula Rules: do not draw the ring carbons, or any single hydrogens ...
... Simplified structural formula Rules: do not draw the ring carbons, or any single hydrogens ...
Exam 1 Q2 Review Sheet
... why they cause a problem. For example, why would DNP be an excellent weight loss drug? 27. It turns out that you need only very small amounts of vitamin B3 (niacin), which is used to make NAD+. The same goes for riboflavin, the vitamin used in the synthesis of FAD. However, you have incredible numbe ...
... why they cause a problem. For example, why would DNP be an excellent weight loss drug? 27. It turns out that you need only very small amounts of vitamin B3 (niacin), which is used to make NAD+. The same goes for riboflavin, the vitamin used in the synthesis of FAD. However, you have incredible numbe ...
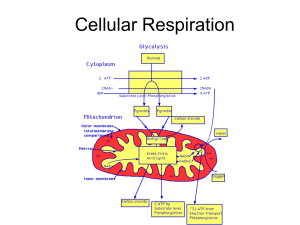
Cellular Respiration
... 3. Electron transport chain: Third step uses the electrons to make a lot of ATP ...
... 3. Electron transport chain: Third step uses the electrons to make a lot of ATP ...
the Overview - The United Mitochondrial Disease
... well as take in, glucose to the cell. Export of glucose is required for gluconeogenesis. This isoform has a very high Km for glucose (17mM). Uptake of glucose through this transporter is not regulated by expression levels as most others are, but through phosphorylation reactions. GLUT 3 is expressed ...
... well as take in, glucose to the cell. Export of glucose is required for gluconeogenesis. This isoform has a very high Km for glucose (17mM). Uptake of glucose through this transporter is not regulated by expression levels as most others are, but through phosphorylation reactions. GLUT 3 is expressed ...
Stable Isotope and Metabolomics Core Facility
... test hypotheses about the metabolic consequences of various changes in gene expression and protein function, in order to guide further integrative systems biology analyses of the underlying mechanisms in diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetic complications. The Core objectives includes ...
... test hypotheses about the metabolic consequences of various changes in gene expression and protein function, in order to guide further integrative systems biology analyses of the underlying mechanisms in diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetic complications. The Core objectives includes ...
design of energy metabolism
... 1. Main pathway in Vertebrates = Glycolysis (catabolism of carbohydrates) a) ATP production by glycolysis begins rapidly after initiation of activity or exposure to hypoxia/anoxia. Begins after stores of phosphagens (ATP, creatine phosphate, arginine phosphate – cephalopods) are depleted. b) Rapid p ...
... 1. Main pathway in Vertebrates = Glycolysis (catabolism of carbohydrates) a) ATP production by glycolysis begins rapidly after initiation of activity or exposure to hypoxia/anoxia. Begins after stores of phosphagens (ATP, creatine phosphate, arginine phosphate – cephalopods) are depleted. b) Rapid p ...
Protein and Carbohydrate Chemistry
... young animals living on mother's milk use the glucose for quick energy and send the galactose to their livers where it will stored for future energy needs as glycogen -- bonded together; sucrose consists of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose bonded together. The bonds that hold the ...
... young animals living on mother's milk use the glucose for quick energy and send the galactose to their livers where it will stored for future energy needs as glycogen -- bonded together; sucrose consists of one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose bonded together. The bonds that hold the ...
Test # 1
... Concerning the biosynthesis of urea by mammalian liver, each of the following statements is correct EXCEPT A. The first nitrogen atom entering the urea cycle does so in the form of carbamoyl phosphate. B. The second nitrogen atom entering the urea cycle is supplied by the amino group of aspartate. C ...
... Concerning the biosynthesis of urea by mammalian liver, each of the following statements is correct EXCEPT A. The first nitrogen atom entering the urea cycle does so in the form of carbamoyl phosphate. B. The second nitrogen atom entering the urea cycle is supplied by the amino group of aspartate. C ...
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... 5. Identify the inputs and outputs and location of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 7. Compare and contrast the structure and function of mitochondria and chloroplasts. ...
... 5. Identify the inputs and outputs and location of glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 7. Compare and contrast the structure and function of mitochondria and chloroplasts. ...
Four Types of Organic Molecules
... Disease characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in ...
... Disease characterized by high levels of blood glucose resulting from defects in ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS & RESPIRATION
... d. thylakoid membrane What product of the light dependent rxn is used in the Calvin Cycle a. oxygen b. carbon dioxide c. NADPH d. chlorophyll What is used in the first step of the Calvin Cycle a. oxygen b. carbon dioxide c. hydrogen d. water How many rounds of the Calvin Cycle are needed to form one ...
... d. thylakoid membrane What product of the light dependent rxn is used in the Calvin Cycle a. oxygen b. carbon dioxide c. NADPH d. chlorophyll What is used in the first step of the Calvin Cycle a. oxygen b. carbon dioxide c. hydrogen d. water How many rounds of the Calvin Cycle are needed to form one ...
24,7 Loctic Fermentotion
... (synthetic) pathway. Like most anabolic pathways, it requires the expenditure of ATP Six molecules of ATP are required to convert two molecules of lactate to one molecule of glucose.However,only two molecules of ATP were gained by converting one molecule of glucose to two molecules of lactate in lac ...
... (synthetic) pathway. Like most anabolic pathways, it requires the expenditure of ATP Six molecules of ATP are required to convert two molecules of lactate to one molecule of glucose.However,only two molecules of ATP were gained by converting one molecule of glucose to two molecules of lactate in lac ...
Fructose-1,6 - LSU School of Medicine
... List gluconeogenic precursors List the enzymes and intermediates involved in gluconeogenesis List the irreversible and regulated steps of gluconeogenesis Discuss regulation of gluconeogenesis ...
... List gluconeogenic precursors List the enzymes and intermediates involved in gluconeogenesis List the irreversible and regulated steps of gluconeogenesis Discuss regulation of gluconeogenesis ...
Regulation of Metabolism
... • Some glucose is reused to form glycogen. • Only need about 150 g/day. • Average daily turnover for protein is 150 g/day. • Some protein may be reused for protein synthesis. • Only need 35 g/day. • 9 essential amino acids. • Average daily turnover for fats is 100 g/day. • Little is actually require ...
... • Some glucose is reused to form glycogen. • Only need about 150 g/day. • Average daily turnover for protein is 150 g/day. • Some protein may be reused for protein synthesis. • Only need 35 g/day. • 9 essential amino acids. • Average daily turnover for fats is 100 g/day. • Little is actually require ...
Chapter 24 Metabolism
... • Are an important energy source during periods of starvation when glucose supplies are limited • Liver cells, cardiac muscle cells, skeletal muscle fibers, etc. metabolize free fatty acids • Excess dietary glycerol and fatty acids undergo lipogenesis to form triglycerides for storage • Glucose is e ...
... • Are an important energy source during periods of starvation when glucose supplies are limited • Liver cells, cardiac muscle cells, skeletal muscle fibers, etc. metabolize free fatty acids • Excess dietary glycerol and fatty acids undergo lipogenesis to form triglycerides for storage • Glucose is e ...
Oxidations – loss of electrons
... – Occurs when oxygen is not available – Organic molecule is the final electron acceptor ...
... – Occurs when oxygen is not available – Organic molecule is the final electron acceptor ...
Chapter 25
... molecules used by mitochondria • Does not require oxygen so it is anaerobic • 1 molecule of glucose yields only 2 ATP • Yields very little energy on its own, but it is enough to power your muscles for short periods • Some bacteria are entirely anaerobic and survive by performing only glycolysis • RB ...
... molecules used by mitochondria • Does not require oxygen so it is anaerobic • 1 molecule of glucose yields only 2 ATP • Yields very little energy on its own, but it is enough to power your muscles for short periods • Some bacteria are entirely anaerobic and survive by performing only glycolysis • RB ...
CASE 37
... depending on their relative concentrations, the liver either extracts glucose from the blood (high insulin/glucagon ratio) or produces and adds glucose to the blood (low insulin/glucagon ratio). The responses can be divided into short-term ones such as the changes occurring during a normal daily cyc ...
... depending on their relative concentrations, the liver either extracts glucose from the blood (high insulin/glucagon ratio) or produces and adds glucose to the blood (low insulin/glucagon ratio). The responses can be divided into short-term ones such as the changes occurring during a normal daily cyc ...
Launch Activity
... this is very soluble and toxic, so is not around for long! It is then combined with CO2 using ATP to produce UREA (CO(NH2)2 this occurs in the ornithine cycle. ...
... this is very soluble and toxic, so is not around for long! It is then combined with CO2 using ATP to produce UREA (CO(NH2)2 this occurs in the ornithine cycle. ...
Notes
... the citric acid cycle. As soon as acetyl-CoA is formed, then the acetic acid component (2 carbon compound) can combine with oxaloacetic acid (4 carbon compounds) to make a molecule of citric acid (6 carbon compounds). Co-enzyme A acts only as a transporter of acetic acid. The formation of citric aci ...
... the citric acid cycle. As soon as acetyl-CoA is formed, then the acetic acid component (2 carbon compound) can combine with oxaloacetic acid (4 carbon compounds) to make a molecule of citric acid (6 carbon compounds). Co-enzyme A acts only as a transporter of acetic acid. The formation of citric aci ...
Biomolecules - Good Earth School
... Cyclic form: The five membered ring structure contains 4 – carbon atoms and an oxygen atom and is called the furanose form. Resemblance with (C4H4O) ...
... Cyclic form: The five membered ring structure contains 4 – carbon atoms and an oxygen atom and is called the furanose form. Resemblance with (C4H4O) ...
Energy Systems and Muscle Fibre Types
... Pi + Energy (this energy will be used to bind Pi + ADP, can not be used for cellular work) CP is in limited supply within the muscle, thus this system supplies a large amount of energy but CP levels decline rapidly as it is used up as the system replenishes ATP stores. ATP-CP system only lasts 3-10s ...
... Pi + Energy (this energy will be used to bind Pi + ADP, can not be used for cellular work) CP is in limited supply within the muscle, thus this system supplies a large amount of energy but CP levels decline rapidly as it is used up as the system replenishes ATP stores. ATP-CP system only lasts 3-10s ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.