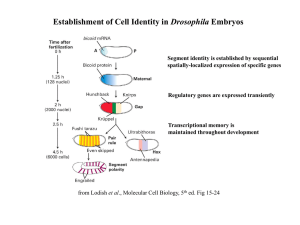
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Polycomb and Trithorax Complexes Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
... Polycomb and Trithorax Complexes Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
No Slide Title
... cDNA clones for two closely related HLH factors, myf5 and myogenin by low stringency hybridization. All three genes are necessary for correct muscle differentiation in vivo, as demonstrated by mouse "knockout" studies. ...
... cDNA clones for two closely related HLH factors, myf5 and myogenin by low stringency hybridization. All three genes are necessary for correct muscle differentiation in vivo, as demonstrated by mouse "knockout" studies. ...
Genetic dissection of trisomy 21 pathology using a
... Genetic dissection of trisomy 21 pathology using a transchromosomic mouse Down Syndrome model. C. Canzonetta, S. Devita, E.M Fisher, V. Tybulewicz, J. Groet and Dean Nizetic Since Down Syndrome (DS) is not an inherited disease, and the DNA sequence of the supernumerary chromosome 21 causing it is pe ...
... Genetic dissection of trisomy 21 pathology using a transchromosomic mouse Down Syndrome model. C. Canzonetta, S. Devita, E.M Fisher, V. Tybulewicz, J. Groet and Dean Nizetic Since Down Syndrome (DS) is not an inherited disease, and the DNA sequence of the supernumerary chromosome 21 causing it is pe ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 6. The 5’ and 3’ ends of mRNA are good target sites for antisense oligonucleotides. 7. Diagnostic probes for pathogens are identified from a genomic library of that pathogen. 8. Trypsinization is used to cleave cell surface proteins from cells in culture. ...
... 6. The 5’ and 3’ ends of mRNA are good target sites for antisense oligonucleotides. 7. Diagnostic probes for pathogens are identified from a genomic library of that pathogen. 8. Trypsinization is used to cleave cell surface proteins from cells in culture. ...
Epigenetics
... This is because not every gene is expressed in each cell. There are many opportunities to turn off and on a certain gene, and to alter its phenotype, such things like… ...
... This is because not every gene is expressed in each cell. There are many opportunities to turn off and on a certain gene, and to alter its phenotype, such things like… ...
National Research Program
... these cells is driven by stem cells in the bone marrow, which continuously reproduce throughout life. If these stem cells are damaged in any way, diseases such as leukaemia may develop. Dr Carmichael is studying the regulation of bone marrow stem cell function, as well as leukaemia development. In p ...
... these cells is driven by stem cells in the bone marrow, which continuously reproduce throughout life. If these stem cells are damaged in any way, diseases such as leukaemia may develop. Dr Carmichael is studying the regulation of bone marrow stem cell function, as well as leukaemia development. In p ...
The Epigenetic Code regulates Chromatin Structure and
... The tissue microenvironment (Inflammation, Hypoxia) can affect histone modifying enzyme activity, and thus regulates the malleable process of progenitor cell differentiation to terminally differentiated ...
... The tissue microenvironment (Inflammation, Hypoxia) can affect histone modifying enzyme activity, and thus regulates the malleable process of progenitor cell differentiation to terminally differentiated ...
Bill Nye: Genes - stephaniemcoggins
... 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? ...
... 4. How long is the DNA string model of science? 5. How many times longer is DNA than it is wide? 6. How does Bill define a Gene? 7. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 8. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? ...
Unit 5 review
... Unit 5 – Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. List the three reasons a cell divides: a. _____________________________________ b. _____________________________________ c. _____________________________________ 2. The longest phase of the cell cycle is _____________________. 3. In G1, they cell ____________ ...
... Unit 5 – Cell Growth and Reproduction 1. List the three reasons a cell divides: a. _____________________________________ b. _____________________________________ c. _____________________________________ 2. The longest phase of the cell cycle is _____________________. 3. In G1, they cell ____________ ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 21 The Genetic Basis Of Development
... in 3.5 days. Its genome has been sequenced. They are also hermaphrodites ...
... in 3.5 days. Its genome has been sequenced. They are also hermaphrodites ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: ______ Unit 4 Vocabulary: (Chapters
... Define the following terms using your book, notes, or internet. Be sure to study and familiarize yourself with each word and be prepared for your weekly vocabulary quizzes. 1. What are chromosomes made of? ...
... Define the following terms using your book, notes, or internet. Be sure to study and familiarize yourself with each word and be prepared for your weekly vocabulary quizzes. 1. What are chromosomes made of? ...
Learning Targets
... 17. Explain 3 reasons why a doctor would want to perform a karyotype. 18. Explain how chromosomes might be removed from an adult, fetus and embryo. 19. Explain how a karyotype is arranged. 20. Determine if a person or embryo is a male or female by evaluating a karyotype. 21. Evaluate a karyotype to ...
... 17. Explain 3 reasons why a doctor would want to perform a karyotype. 18. Explain how chromosomes might be removed from an adult, fetus and embryo. 19. Explain how a karyotype is arranged. 20. Determine if a person or embryo is a male or female by evaluating a karyotype. 21. Evaluate a karyotype to ...
Cellular Reproduction For a cell to reproduce... -parent cell=
... For a cell to reproduce... -parent cell= -daughter cells= To divide, a cell must: 1. Copy its genetic material (make 2 nuclei) 2. Divide everything else into 2 groups. Genetic Material composed of DNA in the form of chromosomes= Prokaryote Reproduction -how bacteria multiply -1 circular DNA Molecule ...
... For a cell to reproduce... -parent cell= -daughter cells= To divide, a cell must: 1. Copy its genetic material (make 2 nuclei) 2. Divide everything else into 2 groups. Genetic Material composed of DNA in the form of chromosomes= Prokaryote Reproduction -how bacteria multiply -1 circular DNA Molecule ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... – Histone acetylation- acetyl groups are added to amino acids of histone proteins, making the chromatin less tightly packaged, encouraging transcription. ...
... – Histone acetylation- acetyl groups are added to amino acids of histone proteins, making the chromatin less tightly packaged, encouraging transcription. ...
The Basics of Cancer Biology
... • Recent research has shown that to acquire all these biological properties, epithelial cancer cells must lose some of their epithelial characteristics and become more similar to a mesodermal (mesenchymal) cell. This phenomenon is called EMT. It involves changing surface adhesion molecules (from Eca ...
... • Recent research has shown that to acquire all these biological properties, epithelial cancer cells must lose some of their epithelial characteristics and become more similar to a mesodermal (mesenchymal) cell. This phenomenon is called EMT. It involves changing surface adhesion molecules (from Eca ...
Chap 8 Vocab Questions Chap 9 Vocab Questions
... What are the 4 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of mitosis? Be able identify them in pictures. How does the process of cell division differ in prokaryotes and eukaryotes? What is differentiation of stem cells? What would happen to a cell if it were to just split into two without ...
... What are the 4 phases of the cell cycle? What are the 4 phases of mitosis? Be able identify them in pictures. How does the process of cell division differ in prokaryotes and eukaryotes? What is differentiation of stem cells? What would happen to a cell if it were to just split into two without ...
Regarding question 1:
... Regarding question 1: 1. Callus and Meristem contain both undifferentiated embryonic cells that can give rise to a whole organism. Nevertheless there are major differences between them. The Meristem differentiation is part of the normal development and originates from true embryonic cells. The callu ...
... Regarding question 1: 1. Callus and Meristem contain both undifferentiated embryonic cells that can give rise to a whole organism. Nevertheless there are major differences between them. The Meristem differentiation is part of the normal development and originates from true embryonic cells. The callu ...
PDF
... to the germarium’s anteroposterior axis. They also show that somatic escort cells (the glial-like partners of early germ cells) do not adhere to and migrate with GSC daughters as previously proposed, but pass the GSC daughters from one escort cell to the next using dynamic membrane activity. These a ...
... to the germarium’s anteroposterior axis. They also show that somatic escort cells (the glial-like partners of early germ cells) do not adhere to and migrate with GSC daughters as previously proposed, but pass the GSC daughters from one escort cell to the next using dynamic membrane activity. These a ...
Abstract Human fetal liver is the major site of haematopoiesis
... factors which are known to stimulate hepatogenesis. A greater degree of hepatogenesis from flMSC was observed when the medium was supplemented with oncostatin M (OSM), in comparison to culture in a medium supplemented with fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). A hepatocyt ...
... factors which are known to stimulate hepatogenesis. A greater degree of hepatogenesis from flMSC was observed when the medium was supplemented with oncostatin M (OSM), in comparison to culture in a medium supplemented with fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). A hepatocyt ...
Adult stem cells isolated from human intestinal tissue for the first time
... By Tim / 5 April 2013 / ...
... By Tim / 5 April 2013 / ...
What unites these phenomena?
... Dnmt1 and associated proteins scan newly replicated DNA for hemimethylated sites and methylate the CpG’s on the newly synthesized strands ...
... Dnmt1 and associated proteins scan newly replicated DNA for hemimethylated sites and methylate the CpG’s on the newly synthesized strands ...
PDF
... GABAA receptor signalling can control adult neurogenesis in the mouse. Verdon Taylor and co-workers now investigate a role for GABAB receptors in the adult mouse hippocampus (p. 83), finding that deletion or inhibition of GABAB1 promotes proliferation of neural stem cells (NSCs), whereas GABAB-recep ...
... GABAA receptor signalling can control adult neurogenesis in the mouse. Verdon Taylor and co-workers now investigate a role for GABAB receptors in the adult mouse hippocampus (p. 83), finding that deletion or inhibition of GABAB1 promotes proliferation of neural stem cells (NSCs), whereas GABAB-recep ...
PDF
... GABAA receptor signalling can control adult neurogenesis in the mouse. Verdon Taylor and co-workers now investigate a role for GABAB receptors in the adult mouse hippocampus (p. 83), finding that deletion or inhibition of GABAB1 promotes proliferation of neural stem cells (NSCs), whereas GABAB-recep ...
... GABAA receptor signalling can control adult neurogenesis in the mouse. Verdon Taylor and co-workers now investigate a role for GABAB receptors in the adult mouse hippocampus (p. 83), finding that deletion or inhibition of GABAB1 promotes proliferation of neural stem cells (NSCs), whereas GABAB-recep ...
PDF
... GABAA receptor signalling can control adult neurogenesis in the mouse. Verdon Taylor and co-workers now investigate a role for GABAB receptors in the adult mouse hippocampus (p. 83), finding that deletion or inhibition of GABAB1 promotes proliferation of neural stem cells (NSCs), whereas GABAB-recep ...
... GABAA receptor signalling can control adult neurogenesis in the mouse. Verdon Taylor and co-workers now investigate a role for GABAB receptors in the adult mouse hippocampus (p. 83), finding that deletion or inhibition of GABAB1 promotes proliferation of neural stem cells (NSCs), whereas GABAB-recep ...























