Introduction to biotechnology - Indiana University School of Informatics
... • Most vertebrate cells stop dividing after a finite number of cell divisions in culture – senescence; • "immortalized" cell line: telemerase • Inactivate the checkpoint mechanisms • Cell lines can often be most easily generated from cancer cells. ...
... • Most vertebrate cells stop dividing after a finite number of cell divisions in culture – senescence; • "immortalized" cell line: telemerase • Inactivate the checkpoint mechanisms • Cell lines can often be most easily generated from cancer cells. ...
Embryonic stem cell Embryonic stem cells Pluripotent: Embryonic
... Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, that is, they are able to differentiate into all derivatives of the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. These include each of the more than 220 cell types in the adult body. Pluripotency distinguishes embryonic stem cells from adult stem ...
... Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, that is, they are able to differentiate into all derivatives of the three primary germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm. These include each of the more than 220 cell types in the adult body. Pluripotency distinguishes embryonic stem cells from adult stem ...
Lesson Overview - Midland Park School
... Frontiers in Stem Cell Research What are some possible benefits and issues associated with stem cell research? Stem cells offer the potential benefit of using undifferentiated cells to repair or replace badly damaged cells and tissues. Human embryonic stem cell research is controversial because the ...
... Frontiers in Stem Cell Research What are some possible benefits and issues associated with stem cell research? Stem cells offer the potential benefit of using undifferentiated cells to repair or replace badly damaged cells and tissues. Human embryonic stem cell research is controversial because the ...
iclicker
... suicide rather than phagocytosis D. ced-1 and ced-2 are different genes affect dead cell engulfment E. None of the above ...
... suicide rather than phagocytosis D. ced-1 and ced-2 are different genes affect dead cell engulfment E. None of the above ...
Chapter 31: Epigenetic Effects Are Inherited
... • The Xic (X inactivation center) is a cis-acting region on the X chromosome that is necessary and sufficient to ensure that only one X chromosome remains active • Xic includes the Xist gene, which codes for an RNA that is found only on inactive X chromosomes • The mechanism that is responsible for ...
... • The Xic (X inactivation center) is a cis-acting region on the X chromosome that is necessary and sufficient to ensure that only one X chromosome remains active • Xic includes the Xist gene, which codes for an RNA that is found only on inactive X chromosomes • The mechanism that is responsible for ...
Study Guide
... Bacteria as tools for Manipulating DNA & Gene regulation a. Know the 3 methods of utilizing bacteria to manipulate DNA. i. Transduction ii. Transformation iii. Conjugation b. What are Plasmids? – How are they utilized? c. Restriction enzymes – How do they work? i. Recombinant DNA & Sticky ends ii. D ...
... Bacteria as tools for Manipulating DNA & Gene regulation a. Know the 3 methods of utilizing bacteria to manipulate DNA. i. Transduction ii. Transformation iii. Conjugation b. What are Plasmids? – How are they utilized? c. Restriction enzymes – How do they work? i. Recombinant DNA & Sticky ends ii. D ...
Max-Planck-Institut für molekulare Biomedizin
... The Robert-Koch Foundation bestows the prize to the renowned stem cell researchers Hans Robert Schöler, Irving Weissman and Shinya Yamanaka Münster – The Robert-Koch Foundation bestows this year’s prize to Schöler, Weissman and Yamanaka for „their outstanding accomplishments in the field of stem cel ...
... The Robert-Koch Foundation bestows the prize to the renowned stem cell researchers Hans Robert Schöler, Irving Weissman and Shinya Yamanaka Münster – The Robert-Koch Foundation bestows this year’s prize to Schöler, Weissman and Yamanaka for „their outstanding accomplishments in the field of stem cel ...
Biotech unit Objectives
... Biotech unit Objectives Chapters 19-21 Flex Day: January 18 Holiday: January 21 Chapter 19 Key Terms Chromatin Nucleosomes DNA methylation Control elements Leucine zipper motif ...
... Biotech unit Objectives Chapters 19-21 Flex Day: January 18 Holiday: January 21 Chapter 19 Key Terms Chromatin Nucleosomes DNA methylation Control elements Leucine zipper motif ...
Ch. 18 - ltcconline.net
... A third type of operon uses activators, which are proteins that turn operons ON by binding to DNA. These proteins make it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter, rather than by blocking RNA polymerase. – positive gene regulation B. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes must alter gene expression dep ...
... A third type of operon uses activators, which are proteins that turn operons ON by binding to DNA. These proteins make it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter, rather than by blocking RNA polymerase. – positive gene regulation B. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes must alter gene expression dep ...
genetics - Lemon Bay High School
... DNA is located in the NUCLEUS of the cell as in Sometimes the DNA is EUKARYOTES NOT located in the NUCLEUS of the cell as in PROKARYOTES ...
... DNA is located in the NUCLEUS of the cell as in Sometimes the DNA is EUKARYOTES NOT located in the NUCLEUS of the cell as in PROKARYOTES ...
1997 – First direct evidence of cancer stem cells
... Human DNA arranged into 46 chromosomes in 23 pairs At the ends of these are telomeres. These shorten whenever a cell divides and this process Is called senescence (cellular ageing) Immortal cells like cancer or stem cells do not age A G C G A A T C T ...
... Human DNA arranged into 46 chromosomes in 23 pairs At the ends of these are telomeres. These shorten whenever a cell divides and this process Is called senescence (cellular ageing) Immortal cells like cancer or stem cells do not age A G C G A A T C T ...
Identification of gene that promotes differentiation of pluripotential
... required for growth and differentiation of pluripotential cells in the mouse embryos. The gene, Vps52, is a mouse homolog of yeast VPS52 that is thought to be involved in the retrograde endocytic trafficking. The research group found that Vps52 promotes differentiation of pluripotential cells includ ...
... required for growth and differentiation of pluripotential cells in the mouse embryos. The gene, Vps52, is a mouse homolog of yeast VPS52 that is thought to be involved in the retrograde endocytic trafficking. The research group found that Vps52 promotes differentiation of pluripotential cells includ ...
Stem Cells: Links to Human Cancer and Aging
... signaling pathway intermediates (9). Global silencing of developmentally important genes that can be selectively activated in response to environmental cues appears to be controlled by a small group of transcription factors (10-12). For example, it has been shown that retrovirus-mediated introductio ...
... signaling pathway intermediates (9). Global silencing of developmentally important genes that can be selectively activated in response to environmental cues appears to be controlled by a small group of transcription factors (10-12). For example, it has been shown that retrovirus-mediated introductio ...
Review (12/13/16)
... • H3K4me2/3 is associated with transcriptional activity. • Methylation of H3K9me2/3 is associated with repression ...
... • H3K4me2/3 is associated with transcriptional activity. • Methylation of H3K9me2/3 is associated with repression ...
1. (10pts) What is a Fate Map? How would you experimentally
... Describe what went right and what went wrong. How would you change the protocol to avoid the same problem? In the first trial they use “ex-vivo” infection of marrow cells from SCIDs children. The retroviral vector carrying the normal gamma C gene inserted “randomly” in the marrow cells. Unfortunatel ...
... Describe what went right and what went wrong. How would you change the protocol to avoid the same problem? In the first trial they use “ex-vivo” infection of marrow cells from SCIDs children. The retroviral vector carrying the normal gamma C gene inserted “randomly” in the marrow cells. Unfortunatel ...
Exercise week 10, with answers File
... 5) In mammalian embryos, Sox2 and the POU domain factor Oct4 are required at the blastocyst stage to specify the pluripotent inner cell mass (ICM) cells that give rise to all cells and tissues of the future body. Forced ...
... 5) In mammalian embryos, Sox2 and the POU domain factor Oct4 are required at the blastocyst stage to specify the pluripotent inner cell mass (ICM) cells that give rise to all cells and tissues of the future body. Forced ...
OPTIMISING GENE TRANSFER INTO EMBRYONIC KIDNEYS AS A
... branching ureteric tree and nephron precursors. Kidneys were exposed to replication defective vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (VSVg) pseudotyped lentiviruses expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) from either a cytomegalovirus (CMV) or a 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) promoter. Kidneys ...
... branching ureteric tree and nephron precursors. Kidneys were exposed to replication defective vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein (VSVg) pseudotyped lentiviruses expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) from either a cytomegalovirus (CMV) or a 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) promoter. Kidneys ...
Two Epigenetic Mechanisms
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
Chapter 31
... Heterochromatin is nucleated at a specific sequence and the inactive structure propagates along the chromatin fiber. Genes within regions of heterochromatin are inactivated. The length of the inactive region varies from cell to cell. o As a result, inactivation of genes in this vicinity causes posit ...
... Heterochromatin is nucleated at a specific sequence and the inactive structure propagates along the chromatin fiber. Genes within regions of heterochromatin are inactivated. The length of the inactive region varies from cell to cell. o As a result, inactivation of genes in this vicinity causes posit ...
Genes and Development Outline
... 1. These cells have many possabilities as to what they will develop into as they develop. B. They are said to be “embryonic” in development. They also have no genes “locked up”; therefore they can make any protein or enzyme. C. Origins of stem cells. (Embryonic vs. Adult) Embryonic are found in deve ...
... 1. These cells have many possabilities as to what they will develop into as they develop. B. They are said to be “embryonic” in development. They also have no genes “locked up”; therefore they can make any protein or enzyme. C. Origins of stem cells. (Embryonic vs. Adult) Embryonic are found in deve ...
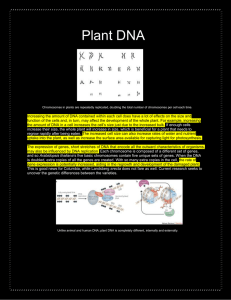
Plant DNA - The uniqueness of DNA
... Chromosomes in plants are repeatedly replicated, doubling the total number of chromosomes per cell each time. ...
... Chromosomes in plants are repeatedly replicated, doubling the total number of chromosomes per cell each time. ...
Teacher PowerPoint - UNC Institute for the Environment
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
Companion PowerPoint slide
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
Biology: Genetic Technology questions
... 13. How much of the human genome codes for proteins? only 1.5% a. What is the nickname for non-coding part and what is its main function? ...
... 13. How much of the human genome codes for proteins? only 1.5% a. What is the nickname for non-coding part and what is its main function? ...