Style D 36 by 54 - Bourns College of Engineering
... Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids site-specifically into proteins provides a way to manipulate the structures of proteins, monitor protein function and create proteins with novel properties. In previous studies, by creating orthogonal tRNA- synthetase pairs with specificity to unnatural ...
... Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids site-specifically into proteins provides a way to manipulate the structures of proteins, monitor protein function and create proteins with novel properties. In previous studies, by creating orthogonal tRNA- synthetase pairs with specificity to unnatural ...
CHAPTER TWO
... fluids and tissues. Surface modification must also be achieved without toxic by-products that could be harmful to the patient or degrade the function of the item being coated.19 ...
... fluids and tissues. Surface modification must also be achieved without toxic by-products that could be harmful to the patient or degrade the function of the item being coated.19 ...
CHM 112
... while a triglyceride with the same molar mass is highly insoluble. Explain why. Lipids have large, non-polar hydrocarbon sections which are not attracted to water. Carbohydrates have multiple hydroxyl groups that form hydrogen bonds easily with water so the interactions, and thus the solubility, are ...
... while a triglyceride with the same molar mass is highly insoluble. Explain why. Lipids have large, non-polar hydrocarbon sections which are not attracted to water. Carbohydrates have multiple hydroxyl groups that form hydrogen bonds easily with water so the interactions, and thus the solubility, are ...
Macromolecules
... Proteins consist of one or more polymers called polypeptides, which are made by linking amino acids together with peptide linkages. Peptide linkages are formed through condensation reactions. All proteins are made from the same 20 amino acids. Different amino acids have different chemical pr ...
... Proteins consist of one or more polymers called polypeptides, which are made by linking amino acids together with peptide linkages. Peptide linkages are formed through condensation reactions. All proteins are made from the same 20 amino acids. Different amino acids have different chemical pr ...
Proteins & Nucleic Acids - St. Mary Catholic Secondary School
... within the chain and R-group interactions with the environment. Tertiary structure is also aided by prosthetic groups that are inorganic compounds that act as a central point for bonding within the protein. ...
... within the chain and R-group interactions with the environment. Tertiary structure is also aided by prosthetic groups that are inorganic compounds that act as a central point for bonding within the protein. ...
cell membranes gs
... forming the selectively permeable boundary between the cell and its environment. It is made up of a double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins. ...
... forming the selectively permeable boundary between the cell and its environment. It is made up of a double layer of phospholipids with embedded proteins. ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
Control of Gene Expression
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
Abstract
... The E2 component of the Bacillus stearothermophilus pyruvate dehydrogenase complex can potentially be used as a scaffold to create a targeted drug delivery system. It is capable of assembling into a 60-mer unit dodecahedron with icosahedral symmetry, even with the addition of peptides on the surface ...
... The E2 component of the Bacillus stearothermophilus pyruvate dehydrogenase complex can potentially be used as a scaffold to create a targeted drug delivery system. It is capable of assembling into a 60-mer unit dodecahedron with icosahedral symmetry, even with the addition of peptides on the surface ...
Recombinant Human Olfactory Marker Protein ab140735 Product datasheet 1 Image
... ab140735 was purified using conventional chromatography techniques. ...
... ab140735 was purified using conventional chromatography techniques. ...
Book Reviews - Cancer Research
... tains the high standard of quality established by its predecessors. In the foreword it is mentioned that it was anticipated that there would be some duplication of the sixth ...
... tains the high standard of quality established by its predecessors. In the foreword it is mentioned that it was anticipated that there would be some duplication of the sixth ...
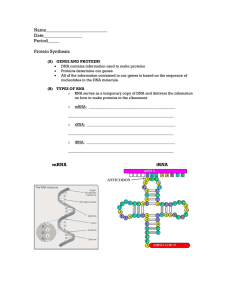
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
... RNA Polymerase knows where to bind on the DNA due to spots on the DNA called promoters, which act as start point signals for transcription. ...
02 DNA and RNA and protein synthesis
... When two are there, one will attach its amino acid to the amino acid of the other one, creating a chain of amino acids. Once this happens, that tRNA leaves and the one with the chain moves to its place. ...
... When two are there, one will attach its amino acid to the amino acid of the other one, creating a chain of amino acids. Once this happens, that tRNA leaves and the one with the chain moves to its place. ...
Lecture 1
... (codons) forming the genetic code specify the particular amino acids that make up an ( bases individual protein. This process, called translation, is accomplished by ribosomes (cellular components composed of proteins and another class of RNA) that read the genetic code from the mRNA, and transfer R ...
... (codons) forming the genetic code specify the particular amino acids that make up an ( bases individual protein. This process, called translation, is accomplished by ribosomes (cellular components composed of proteins and another class of RNA) that read the genetic code from the mRNA, and transfer R ...
Chapt. 3-Proteins - University of New England
... • Example: enzyme binding sites, substrate binding sites ...
... • Example: enzyme binding sites, substrate binding sites ...
Biological Molecules
... • Blood clotting involves many different proteins • Keratin is the protein that gives strength to hair, skin and nails ...
... • Blood clotting involves many different proteins • Keratin is the protein that gives strength to hair, skin and nails ...
O 95: Metal Substrates: Adsorption of Atoms and Inorganic Molecules
... observed that a second layer initially forms an amorphous structure when grown on the crystalline monolayer. To facilitate the growth of ice in a bulk-like hexagonal arrangement, the first wetting layer needs to rearrange into a purely hexagonal structure commensurate with the surface. Ammonia (NH3) ...
... observed that a second layer initially forms an amorphous structure when grown on the crystalline monolayer. To facilitate the growth of ice in a bulk-like hexagonal arrangement, the first wetting layer needs to rearrange into a purely hexagonal structure commensurate with the surface. Ammonia (NH3) ...
Document
... Specific Expectations: SBI4U Introduction Proteins have specific uses inside cells to support biochemical reactions important for cell structures and metabolic processes. Cells maintain a balanced internal environment that allows these proteins to retain the structure important to whatever action it ...
... Specific Expectations: SBI4U Introduction Proteins have specific uses inside cells to support biochemical reactions important for cell structures and metabolic processes. Cells maintain a balanced internal environment that allows these proteins to retain the structure important to whatever action it ...
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter #2
... 1) Synthesis when two or more atoms or reactants bond to form a new, more complex structure. Synthesis requires energy and is important to the growth of body parts. 2) Decomposition the opposite of ...
... 1) Synthesis when two or more atoms or reactants bond to form a new, more complex structure. Synthesis requires energy and is important to the growth of body parts. 2) Decomposition the opposite of ...
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter #2
... 1) Synthesis when two or more atoms or reactants bond to form a new, more complex structure. Synthesis requires energy and is important to the growth of body parts. 2) Decomposition the opposite of ...
... 1) Synthesis when two or more atoms or reactants bond to form a new, more complex structure. Synthesis requires energy and is important to the growth of body parts. 2) Decomposition the opposite of ...
A genetically programmable protein module as
... Divya Sivaraman, Payal Biswas, and Wilfred Chen Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Riverside, CA, 92521 ...
... Divya Sivaraman, Payal Biswas, and Wilfred Chen Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Riverside, CA, 92521 ...
Protein adsorption

Adsorption (not to be mistaken for absorption) is the accumulation and adhesion of molecules, atoms, ions, or larger particles to a surface, but without surface penetration occurring. The adsorption of larger biomolecules such as proteins is of high physiological relevance, and as such they adsorb with different mechanisms than their molecular or atomic analogs. Some of the major driving forces behind protein adsorption include: surface energy, intermolecular forces, hydrophobicity, and ionic or electrostatic interaction. By knowing how these factors affect protein adsorption, they can then be manipulated by machining, alloying, and other engineering techniques to select for the most optimal performance in biomedical or physiological applications.