DNA to Eye Color? Just How does it Happen?
... •A 3 base code in DNA or mRNA is called a codon. Each codon translates to a particular amino acid. •20 amino acids make up all proteins for life •Since codons are 3 bases, there are 64 different codon sequences -Some amino acids have two or more codons. ...
... •A 3 base code in DNA or mRNA is called a codon. Each codon translates to a particular amino acid. •20 amino acids make up all proteins for life •Since codons are 3 bases, there are 64 different codon sequences -Some amino acids have two or more codons. ...
Answer Sheet
... 2. What are the 6 types of nutrients? Carbs, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water. 3. What are two types of carbs? Sugar, starch 4. What is the difference between a simple carb and a complex carb? The body uses simple sugar called glucose. Complex carbs are called starches. The body has to b ...
... 2. What are the 6 types of nutrients? Carbs, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water. 3. What are two types of carbs? Sugar, starch 4. What is the difference between a simple carb and a complex carb? The body uses simple sugar called glucose. Complex carbs are called starches. The body has to b ...
Bio1A Unit 1-2 Biological Molecules Notes File
... •Primary Structure (1°) = Denatured – Sequence (List in order) of amino acids in order •Secondary Structure (2°) – Done by Hydrogen bonding between side chains – specific shapes ...
... •Primary Structure (1°) = Denatured – Sequence (List in order) of amino acids in order •Secondary Structure (2°) – Done by Hydrogen bonding between side chains – specific shapes ...
Ch.2_Organic_Compounds ppt
... Chemical Reactions • chemical reaction: a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 ...
... Chemical Reactions • chemical reaction: a process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 ...
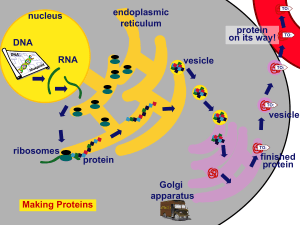
Protein Synthesis
... The ribosome is made of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). All cells need proteins, DNA, and ribosomes. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes have ribosomes. ...
... The ribosome is made of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). All cells need proteins, DNA, and ribosomes. Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes have ribosomes. ...
A European Infrastructure of Ligand Binding
... characterised binders, required to detect all the relevant human proteins in tissues and fluids in health and disease. As the size of the human proteome is at least an order of magnitude greater than the ~ 21.000 protein coding genes known to date, and as for many applications several binde ...
... characterised binders, required to detect all the relevant human proteins in tissues and fluids in health and disease. As the size of the human proteome is at least an order of magnitude greater than the ~ 21.000 protein coding genes known to date, and as for many applications several binde ...
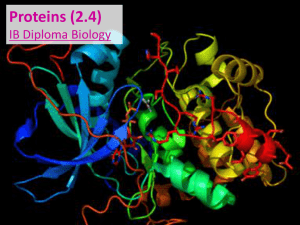
2_4 Slides
... But before they are functional, they must fold into specific structures based on the order / structure of their amino acid sequence. Remember, different amino acids have different chemical properties (i.e. polar / hydrophilic, non-polar / hydrophobic, +/charged, sulfur-containing, carbon rings, etc. ...
... But before they are functional, they must fold into specific structures based on the order / structure of their amino acid sequence. Remember, different amino acids have different chemical properties (i.e. polar / hydrophilic, non-polar / hydrophobic, +/charged, sulfur-containing, carbon rings, etc. ...
... Almost all vital substances which our body requires are converted from various amino acids into peptides or protein. Amino acids are the elementary building blocks of life. They are transported via the blood to the parts of the body where they are transformed and incorporated into the body’s own pro ...
Ms. Robyn Klemptner
... Antibody-based affinity capture Chemical derivatization Metal ion-based affinity capture Thus, more sensitive and reliable method required = DENDRIMERS! Novel proteome investigation in plants since dendrimerbased enrichment techniques have yet to be applied to plant studies. (Meimoun et al., 2 ...
... Antibody-based affinity capture Chemical derivatization Metal ion-based affinity capture Thus, more sensitive and reliable method required = DENDRIMERS! Novel proteome investigation in plants since dendrimerbased enrichment techniques have yet to be applied to plant studies. (Meimoun et al., 2 ...
1345107329.
... - Proteins which contain all the essential amino-acids in the proportions required by the human body have a high biological value i.e. most of their protein is available for growth and repair. - Proteins that are deficient in one or more of the essential amino-acids are proteins of low biological va ...
... - Proteins which contain all the essential amino-acids in the proportions required by the human body have a high biological value i.e. most of their protein is available for growth and repair. - Proteins that are deficient in one or more of the essential amino-acids are proteins of low biological va ...
Molecular Biophysics Unit
... Molecular Biophysics Unit was founded by Prof. G.N. Ramachandran in the year 1971. Presently it has 8 Professors, 2 Associate Professors, 1 Assistant Professor, 1 Technical Officer Gr. III and 10 supporting staff. It has 60 Ph.D. Students including 11 Integrated Ph.D. students, 40 Postdoctoral fello ...
... Molecular Biophysics Unit was founded by Prof. G.N. Ramachandran in the year 1971. Presently it has 8 Professors, 2 Associate Professors, 1 Assistant Professor, 1 Technical Officer Gr. III and 10 supporting staff. It has 60 Ph.D. Students including 11 Integrated Ph.D. students, 40 Postdoctoral fello ...
alborz-final
... tissues cannot be used in the above approach. Furthermore, use of isotopes for temporal analysis limits the number of time points that are possible. MS is highly statistical and often done in conjunction with another protein separation technique because presence of peaks in the MS spectra must often ...
... tissues cannot be used in the above approach. Furthermore, use of isotopes for temporal analysis limits the number of time points that are possible. MS is highly statistical and often done in conjunction with another protein separation technique because presence of peaks in the MS spectra must often ...
CAÑIHUA (Chenopodium pallidicaule) Origin Highlands
... (pre-Incan culture). Nutrients/Main compounds High content of protein. Essential amino acids (lysine, isoleucine and tryptophan). Source of vitamin Bcomplex and essential minerals: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, copper, phosphorus and manganese. Properties It works as a regulator of intestinal act ...
... (pre-Incan culture). Nutrients/Main compounds High content of protein. Essential amino acids (lysine, isoleucine and tryptophan). Source of vitamin Bcomplex and essential minerals: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, copper, phosphorus and manganese. Properties It works as a regulator of intestinal act ...
THIN FILM STRUCTURES
... In addition, these approaches do not provide much support for efficiently querying subsequences, a process that is essential for tracking localized database matches. In this manuscript, we first propose a query-based alignment method for biological sequences that first maps sequences to time-domain ...
... In addition, these approaches do not provide much support for efficiently querying subsequences, a process that is essential for tracking localized database matches. In this manuscript, we first propose a query-based alignment method for biological sequences that first maps sequences to time-domain ...
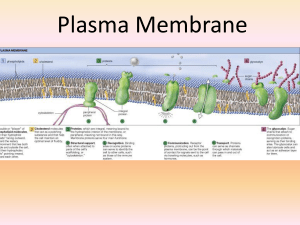
Plasma membrane
... - Isotonic: no net movement of water across the membrane (normal). - Hypertonic : the cell loses water to its environment (crenation). - Hypotonic : the cell gains water from its environment (lysis). ...
... - Isotonic: no net movement of water across the membrane (normal). - Hypertonic : the cell loses water to its environment (crenation). - Hypotonic : the cell gains water from its environment (lysis). ...
Anatomy & Physiology
... extended and thread-like. Water insoluble, have secondary structure Ex) collagen, keratin, elastin Globular proteins (functional proteins) are spherical and compact. Water soluble with tertiary structure. Ex) enzymes and antibodies ...
... extended and thread-like. Water insoluble, have secondary structure Ex) collagen, keratin, elastin Globular proteins (functional proteins) are spherical and compact. Water soluble with tertiary structure. Ex) enzymes and antibodies ...
Chapter 7 - Madeira City Schools
... A “pump” that is powered by ATP builds up a concentration gradient that is then used by another carrier protein to transport something else. The energy for the second transport is from the flow of the first substance down its concentration gradient. ...
... A “pump” that is powered by ATP builds up a concentration gradient that is then used by another carrier protein to transport something else. The energy for the second transport is from the flow of the first substance down its concentration gradient. ...
Gene Expression
... All levels of transcription and translation are involved: 1. DNA sequence will encode for specific regulation – promoters, exons/introns, etc 2. RNAs – will affect which genes complete the process to become proteins 3. Proteins – function as enzymes and machinery to activate or silence specific gene ...
... All levels of transcription and translation are involved: 1. DNA sequence will encode for specific regulation – promoters, exons/introns, etc 2. RNAs – will affect which genes complete the process to become proteins 3. Proteins – function as enzymes and machinery to activate or silence specific gene ...
Gene Expression
... All levels of transcription and translation are involved: 1. DNA sequence will encode for specific regulation – promoters, exons/introns, etc 2. RNAs – will affect which genes complete the process to become proteins 3. Proteins – function as enzymes and machinery to activate or silence specific gene ...
... All levels of transcription and translation are involved: 1. DNA sequence will encode for specific regulation – promoters, exons/introns, etc 2. RNAs – will affect which genes complete the process to become proteins 3. Proteins – function as enzymes and machinery to activate or silence specific gene ...
Plasma Membrane
... A. They can act as a channel, allowing the transport of ions across the membrane. B. They often require ATP to actively transport materials across the membrane against a concentration gradient. C. They may be receptor proteins that bind specific molecules from the surrounding solution, which trigger ...
... A. They can act as a channel, allowing the transport of ions across the membrane. B. They often require ATP to actively transport materials across the membrane against a concentration gradient. C. They may be receptor proteins that bind specific molecules from the surrounding solution, which trigger ...
Protein adsorption

Adsorption (not to be mistaken for absorption) is the accumulation and adhesion of molecules, atoms, ions, or larger particles to a surface, but without surface penetration occurring. The adsorption of larger biomolecules such as proteins is of high physiological relevance, and as such they adsorb with different mechanisms than their molecular or atomic analogs. Some of the major driving forces behind protein adsorption include: surface energy, intermolecular forces, hydrophobicity, and ionic or electrostatic interaction. By knowing how these factors affect protein adsorption, they can then be manipulated by machining, alloying, and other engineering techniques to select for the most optimal performance in biomedical or physiological applications.