Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... + charged - charged Hydroxylated Other ...
... + charged - charged Hydroxylated Other ...
Evaluation of Genotypic variation using SDS-PAGE
... agronomically superior genotypes of chickpea seeds. In this study, total 4 cultivars of chickpea obtained from Sehore M.P. have been studied for their analysis of seed storage protein profiles to examine their relationship by SDS-PAGE technique. The Proteomic assay comprised a total of 64 reliably s ...
... agronomically superior genotypes of chickpea seeds. In this study, total 4 cultivars of chickpea obtained from Sehore M.P. have been studied for their analysis of seed storage protein profiles to examine their relationship by SDS-PAGE technique. The Proteomic assay comprised a total of 64 reliably s ...
Guide 1406 Ch, 1-5
... The difference between weight and mass What are protons, electrons, neutron atomic # Atomic wt Types of bonds, covalent, ionic, hydrogen What are the properties of water and how does water creep up a tube? What if the difference between Acid and base, What is polar molecule? Give example, Polarity, ...
... The difference between weight and mass What are protons, electrons, neutron atomic # Atomic wt Types of bonds, covalent, ionic, hydrogen What are the properties of water and how does water creep up a tube? What if the difference between Acid and base, What is polar molecule? Give example, Polarity, ...
File
... proteasome, a tunnel-like multiprotein structure – As the protein moves through the tunnel, it is straightened and dismantled – Proteasomes also destroy properly-folded proteins that are in excess or no longer needed ...
... proteasome, a tunnel-like multiprotein structure – As the protein moves through the tunnel, it is straightened and dismantled – Proteasomes also destroy properly-folded proteins that are in excess or no longer needed ...
sc-PDB: an annotated database of druggable binding sites from the
... [1] Kellenberger, E., Muller, P., Schalon, C., Bret, G., Foata, N. and Rognan, D. (2006). sc-PDB: an Annotated Database of Druggable Binding Sites from the Protein Data Bank J. chem. Inf. Model. 46, 717-727. [2] Surgand, J.-S.; Rodrigo, J.; Kellenberger, E. and Rognan, D. (2006). A chemogenomic anal ...
... [1] Kellenberger, E., Muller, P., Schalon, C., Bret, G., Foata, N. and Rognan, D. (2006). sc-PDB: an Annotated Database of Druggable Binding Sites from the Protein Data Bank J. chem. Inf. Model. 46, 717-727. [2] Surgand, J.-S.; Rodrigo, J.; Kellenberger, E. and Rognan, D. (2006). A chemogenomic anal ...
chapter3_Sections 4
... place by hydrogen bonds between different parts of the molecule. The same patterns of secondary structure occur in many different proteins. ...
... place by hydrogen bonds between different parts of the molecule. The same patterns of secondary structure occur in many different proteins. ...
Polymer: Macromolecule
... are 3-D polypeptides that can perform a specific function within the cell. Three to four levels of folding are often observed within protein molecules … ...
... are 3-D polypeptides that can perform a specific function within the cell. Three to four levels of folding are often observed within protein molecules … ...
FARM ANIMAL NUTRITION
... meals, molasses and dried milk products • They are high in energy, low in fiber and highly digestible (80% to 90%) ...
... meals, molasses and dried milk products • They are high in energy, low in fiber and highly digestible (80% to 90%) ...
Slide 1 - Denton ISD
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
Hortmon and Udenfriend (I969 Anal. ... Fisher, C. R. Anilinonophthalene rulfonote ...
... lhhe storage conditions for the reagents ore quite important. Both the stock solutions and the diluted stains were greatly inoctivotcd by exparure to light for o few days. Storage in amber bottles with refrigeration prevented any de+ec+oble deterioration over o period of several weeks. By combining ...
... lhhe storage conditions for the reagents ore quite important. Both the stock solutions and the diluted stains were greatly inoctivotcd by exparure to light for o few days. Storage in amber bottles with refrigeration prevented any de+ec+oble deterioration over o period of several weeks. By combining ...
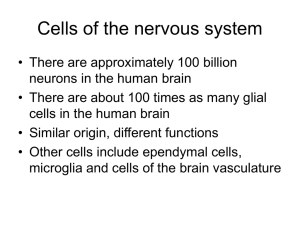
Chapter 2 slides
... • There are approximately 100 billion neurons in the human brain • There are about 100 times as many glial cells in the human brain • Similar origin, different functions • Other cells include ependymal cells, microglia and cells of the brain vasculature ...
... • There are approximately 100 billion neurons in the human brain • There are about 100 times as many glial cells in the human brain • Similar origin, different functions • Other cells include ependymal cells, microglia and cells of the brain vasculature ...
CHEM 260 | ELEMENTS OF BIOCHEMISTRY L/L
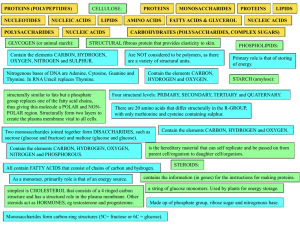
... and Proteins - Enzymes - Carbohydrates - Carbohydrate Metabolism - Protein Metabolism - Lipids and Membranes - Lipid Metabolism - Aerobic Metabolism - Nucleic Acids - Genetic Information ...
... and Proteins - Enzymes - Carbohydrates - Carbohydrate Metabolism - Protein Metabolism - Lipids and Membranes - Lipid Metabolism - Aerobic Metabolism - Nucleic Acids - Genetic Information ...
Document
... Proteins: Composed of a long chain of subunits called AMINO ACIDS. Proteins function as Structural molecules – Hair for example And Proteins function as ENZYMES. Nucleic Acids: Are made up of Nucleotides. The Nucleotides are the ...
... Proteins: Composed of a long chain of subunits called AMINO ACIDS. Proteins function as Structural molecules – Hair for example And Proteins function as ENZYMES. Nucleic Acids: Are made up of Nucleotides. The Nucleotides are the ...
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life
... -tertiary structure – folded shape of the polypeptide chain -quaternary structure – interactions between multiple polypeptide subunits Protein folding is aided by chaperone proteins. ...
... -tertiary structure – folded shape of the polypeptide chain -quaternary structure – interactions between multiple polypeptide subunits Protein folding is aided by chaperone proteins. ...
Nutrition
... (1) Water has an important structural function, it is a component of cytoplasm and body fluids. (2) Water is a good solvent. Many substances in the body can dissolve in water, so it provides a medium for chemical reactions to take place in. (3) Water can easily move through membranes in the body and ...
... (1) Water has an important structural function, it is a component of cytoplasm and body fluids. (2) Water is a good solvent. Many substances in the body can dissolve in water, so it provides a medium for chemical reactions to take place in. (3) Water can easily move through membranes in the body and ...
File
... 1. Color the monosaccharide (glucose) molecules RED. 2. Cut out the molecules and paste them together in appropriate ways so that you have a. one monosaccharide (just glucose) b. two disaccharides (2 simple sugars bonded together) c. one polysaccharide molecule (many sugars bonded together (starch)) ...
... 1. Color the monosaccharide (glucose) molecules RED. 2. Cut out the molecules and paste them together in appropriate ways so that you have a. one monosaccharide (just glucose) b. two disaccharides (2 simple sugars bonded together) c. one polysaccharide molecule (many sugars bonded together (starch)) ...
Document
... • secondary: interactions between backbone atoms; “local” structure; helices: side chains move • tertiary : packing on secondary • quaternary structures: packing on different proteins ...
... • secondary: interactions between backbone atoms; “local” structure; helices: side chains move • tertiary : packing on secondary • quaternary structures: packing on different proteins ...
BIO520 Final Exam 5/07 Jim Lund You may use any books, notes
... 8 (2pt). Aside from its sequence what other information describing a SNP is the most important and useful to know? 9 (2pt). You profile human adrenal tumor samples on a microarray and find that human estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1) is up-regulated in the tumor samples compared to the control samples. You ...
... 8 (2pt). Aside from its sequence what other information describing a SNP is the most important and useful to know? 9 (2pt). You profile human adrenal tumor samples on a microarray and find that human estrogen receptor 1 (ESR1) is up-regulated in the tumor samples compared to the control samples. You ...
Molecules of Life
... vegetable oil. All lipids are hydrophobic. This means that they do not mix with water. If you make salad dressing using oil and water, you can shake it to mix it but the oil and water will quickly separate again. This is because the oil (a lipid) is hydrophobic and does not mix with water. Proteins ...
... vegetable oil. All lipids are hydrophobic. This means that they do not mix with water. If you make salad dressing using oil and water, you can shake it to mix it but the oil and water will quickly separate again. This is because the oil (a lipid) is hydrophobic and does not mix with water. Proteins ...
Protein adsorption

Adsorption (not to be mistaken for absorption) is the accumulation and adhesion of molecules, atoms, ions, or larger particles to a surface, but without surface penetration occurring. The adsorption of larger biomolecules such as proteins is of high physiological relevance, and as such they adsorb with different mechanisms than their molecular or atomic analogs. Some of the major driving forces behind protein adsorption include: surface energy, intermolecular forces, hydrophobicity, and ionic or electrostatic interaction. By knowing how these factors affect protein adsorption, they can then be manipulated by machining, alloying, and other engineering techniques to select for the most optimal performance in biomedical or physiological applications.