File
... When preparing to look at the structures of the body, medical students find if necessary to make a section or cut. When the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary line called plane. A sagittal section is an imaginary plane that travels vertically fro ...
... When preparing to look at the structures of the body, medical students find if necessary to make a section or cut. When the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary line called plane. A sagittal section is an imaginary plane that travels vertically fro ...
Chapter 2 Body Structures
... right angles to the sagittal plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions. b. Horizontal planes i. Transverse plane also known as the horizontal plane divides the body into superior and inferior portions. This division can be at the waist. ...
... right angles to the sagittal plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions. b. Horizontal planes i. Transverse plane also known as the horizontal plane divides the body into superior and inferior portions. This division can be at the waist. ...
1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... and contraction of organs without disrupting the activities of other organs. A. Dorsal Cavity The dorsal cavity is located on the posterior/dorsal surface of the body and surrounds the _________________________________. 1. Spinal (Vertebral) Cavity The spinal cavity is formed by the ___________ of t ...
... and contraction of organs without disrupting the activities of other organs. A. Dorsal Cavity The dorsal cavity is located on the posterior/dorsal surface of the body and surrounds the _________________________________. 1. Spinal (Vertebral) Cavity The spinal cavity is formed by the ___________ of t ...
Unit 1 - Perry Local Schools
... Sagittal – divides body into Left & Right Transverse – divides body into Superior & Inferior Coronal or Frontal – divides body into Anterior & ...
... Sagittal – divides body into Left & Right Transverse – divides body into Superior & Inferior Coronal or Frontal – divides body into Anterior & ...
1.3 PowerPoint
... Posterior side of the body Area that is medial to the shoulder g. Area that is superior to the lungs h. Area that is inferior to the heart ...
... Posterior side of the body Area that is medial to the shoulder g. Area that is superior to the lungs h. Area that is inferior to the heart ...
Unit 1 Anatomy Study Guide KD16
... Body Cavities: Match the organs below with the correct cavity in which it is located: stomach, heart, lungs, back, spine, groin, brain Body Cavities ...
... Body Cavities: Match the organs below with the correct cavity in which it is located: stomach, heart, lungs, back, spine, groin, brain Body Cavities ...
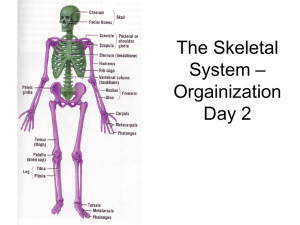
The Skeletal System – Day 2
... • The purpose of the axial skeleton (among other things) is to protect the body's most vital organs ...
... • The purpose of the axial skeleton (among other things) is to protect the body's most vital organs ...
A) Identify the proper anatomical terms for these body regions:
... 6. Is found in both right and left lumbar regions. ____________________ 7. Is found in the epigastric and left hypochondriac region. ____________________ 8. Is found in the right iliac region. ____________________ ...
... 6. Is found in both right and left lumbar regions. ____________________ 7. Is found in the epigastric and left hypochondriac region. ____________________ 8. Is found in the right iliac region. ____________________ ...
Bio Nervous System PPT 2013
... and spinal cord “Coordination/communication center” Receives most impulses and determines “next steps” Sends communication along spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – all the nerve cells not part of the CNS Receives internal and external sensory input Receives and sends impulses to mus ...
... and spinal cord “Coordination/communication center” Receives most impulses and determines “next steps” Sends communication along spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) – all the nerve cells not part of the CNS Receives internal and external sensory input Receives and sends impulses to mus ...
The Language of Anatomy - Holly H. Nash
... 2 body surface; and the top of the head is the most 3 part of the body. The ears are 4 and 5 to the shoulders and 6 to the nose. The heart is 7 to the vertebral column (spine) and 8 to the lungs. The elbow is 9 to the fingers but 10 to the shoulder. The abdominopelvic cavity is 11 to the thoracic ca ...
... 2 body surface; and the top of the head is the most 3 part of the body. The ears are 4 and 5 to the shoulders and 6 to the nose. The heart is 7 to the vertebral column (spine) and 8 to the lungs. The elbow is 9 to the fingers but 10 to the shoulder. The abdominopelvic cavity is 11 to the thoracic ca ...
Organ
... Characteristics of Life Composed of Cells Movement – change in position; motion Responsiveness – reaction to a change Growth/Maturation – increase in size, maturity Reproduction – production of new organisms and new cells ...
... Characteristics of Life Composed of Cells Movement – change in position; motion Responsiveness – reaction to a change Growth/Maturation – increase in size, maturity Reproduction – production of new organisms and new cells ...
Chapter 1
... The abdominopelvic cavity is separated from the superior thoracic cavity by the dome-shaped diaphragm It is composed of two subdivisions – Abdominal cavity – contains the stomach, intestines, ...
... The abdominopelvic cavity is separated from the superior thoracic cavity by the dome-shaped diaphragm It is composed of two subdivisions – Abdominal cavity – contains the stomach, intestines, ...
Body Organization/Planes
... Anterior (or ventral) Towards the front of the body (in front of). The sternum lies anterior to the heart. Posterior (or dorsal) Towards the back of the body (behind). The heart lies posterior the sternum. Superior (or cranial) Above (on top of). The heart lies superior to the diaphragm. Inferior (o ...
... Anterior (or ventral) Towards the front of the body (in front of). The sternum lies anterior to the heart. Posterior (or dorsal) Towards the back of the body (behind). The heart lies posterior the sternum. Superior (or cranial) Above (on top of). The heart lies superior to the diaphragm. Inferior (o ...
The Human Body (Organism) (Chapter 1) Imp. Definition: Anatomy
... There are several smaller body cavities. Most of these are in the head and most open to the body exterior: 1. Oral and digestive cavities. The oral cavity, commonly called the mouth, contains the teeth and tongue. This cavity is part of and continuous with the cavity of the digestive organs. 2. Nasa ...
... There are several smaller body cavities. Most of these are in the head and most open to the body exterior: 1. Oral and digestive cavities. The oral cavity, commonly called the mouth, contains the teeth and tongue. This cavity is part of and continuous with the cavity of the digestive organs. 2. Nasa ...
1 The Human Body (Organism) (Chapter 1) Imp. Definition: Anatomy
... There are several smaller body cavities. Most of these are in the head and most open to the body exterior: 1. Oral and digestive cavities. The oral cavity, commonly called the mouth, contains the teeth and tongue. This cavity is part of and continuous with the cavity of the digestive organs. 2. Nasa ...
... There are several smaller body cavities. Most of these are in the head and most open to the body exterior: 1. Oral and digestive cavities. The oral cavity, commonly called the mouth, contains the teeth and tongue. This cavity is part of and continuous with the cavity of the digestive organs. 2. Nasa ...
Organs - Napa Valley College
... is a group of tissues that perform a specific function or group of functions. ...
... is a group of tissues that perform a specific function or group of functions. ...
skeletal system
... abbreviated C1. This vertebra supports the skull. Its appearance is different from the other spinal vertebrae. The atlas is a ring of bone made up of two lateral masses joined at the front and back by the anterior arch and the posterior arch. Axis (C2) The Axis is the second cervical vertebra or C2. ...
... abbreviated C1. This vertebra supports the skull. Its appearance is different from the other spinal vertebrae. The atlas is a ring of bone made up of two lateral masses joined at the front and back by the anterior arch and the posterior arch. Axis (C2) The Axis is the second cervical vertebra or C2. ...
The Human Body in Health and Design
... ►The “ventral” cavity contains many of the organs that maintain homeostasis. ►It is divided into three parts: ►thoracic cavity – (chest cavity) – protects the heart and lungs. ►The diaphragm separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ...
... ►The “ventral” cavity contains many of the organs that maintain homeostasis. ►It is divided into three parts: ►thoracic cavity – (chest cavity) – protects the heart and lungs. ►The diaphragm separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. ...
Fall Guide Part I Answers
... the lungs are lateral to the heart. Negative feedback systems operate in such a way that the initial stimulus is shutoff or reduced Which orientation and directional terms have the same meaning in humans: anterior and ventral Your body thermostat is located in a part of the brain called the hypothal ...
... the lungs are lateral to the heart. Negative feedback systems operate in such a way that the initial stimulus is shutoff or reduced Which orientation and directional terms have the same meaning in humans: anterior and ventral Your body thermostat is located in a part of the brain called the hypothal ...
Ch. 1 Introduction to the human body (pp. 3-10)
... Composed of many systems, which depend on one another to perform. Survival and reproduction are the goals of the body’s internal activities. ...
... Composed of many systems, which depend on one another to perform. Survival and reproduction are the goals of the body’s internal activities. ...
Chapter 1: The Human Body An Orientation
... • The body is in an erect or standing posture w/ the arms at the sides & palms turned forward - head & feet also turned forward • Humans are bilaterally symmetrical - ...
... • The body is in an erect or standing posture w/ the arms at the sides & palms turned forward - head & feet also turned forward • Humans are bilaterally symmetrical - ...
Subluxation: A Scientific Reality - ChiropracticWorks Collinsville, IL
... poetry and other functions usually associated with the brain.” 4 Robert Ornstein, PhD & David Sobel, M.D. The Healing Brain ...
... poetry and other functions usually associated with the brain.” 4 Robert Ornstein, PhD & David Sobel, M.D. The Healing Brain ...
Head and neck anatomy

This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.