Ministry of Health of Ukraine
... The right principal (main) bronchus is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the left and is about 2.5 cm long. Before entering the hilum of the right lung, the principal bronchus gives off the superior lobar bronchus. On entering the hilum it divides into a middle and an inferior lobar bronchus. T ...
... The right principal (main) bronchus is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the left and is about 2.5 cm long. Before entering the hilum of the right lung, the principal bronchus gives off the superior lobar bronchus. On entering the hilum it divides into a middle and an inferior lobar bronchus. T ...
Introduction to Human Anatomy& Physiology
... • Eventually I go to the restroom Excretion • Someday I may reproduce Reproduction ...
... • Eventually I go to the restroom Excretion • Someday I may reproduce Reproduction ...
POWERPOINT VERSION ()
... Integrates and coordinates body functions Includes all glands that secrete chemical messengers, also called hormones Hormones alter the metabolism of target cells Examples of organs of the ES are the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes, pineal gland, and ...
... Integrates and coordinates body functions Includes all glands that secrete chemical messengers, also called hormones Hormones alter the metabolism of target cells Examples of organs of the ES are the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes, pineal gland, and ...
Human Excretory System The human excretory system functions to
... The human excretory system functions to remove waste from the human body. This system consists of specialized structures and capillary networks that assist in the excretory process. The human excretory system includes the kidney and its functional unit, the nephron. The excretory activity of the kid ...
... The human excretory system functions to remove waste from the human body. This system consists of specialized structures and capillary networks that assist in the excretory process. The human excretory system includes the kidney and its functional unit, the nephron. The excretory activity of the kid ...
Sheep Brain Dissection - Milton
... 1. Use a knife or long-bladed scalpel to cut the specimen along a midsagittal plane. Use the longitudinal fissure as a cutting guide. 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callo ...
... 1. Use a knife or long-bladed scalpel to cut the specimen along a midsagittal plane. Use the longitudinal fissure as a cutting guide. 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callo ...
divides the body or an organ into front
... • The cranial cavity is formed by the cranial bones and contains the brain. • The vertebral (spinal) canal is formed by the bones of the vertebral column and contains the spinal cord. • Three layers of protective tissue, called meninges, line the dorsal body cavity. ...
... • The cranial cavity is formed by the cranial bones and contains the brain. • The vertebral (spinal) canal is formed by the bones of the vertebral column and contains the spinal cord. • Three layers of protective tissue, called meninges, line the dorsal body cavity. ...
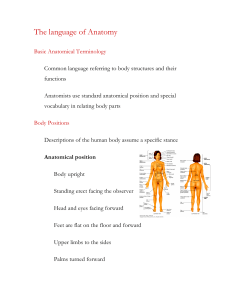
The language of Anatomy
... Divides the body or an organ into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions Transverse plane Divides the body or an organ into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions Also called cross-sectional or horizontal plane ...
... Divides the body or an organ into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions Transverse plane Divides the body or an organ into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions Also called cross-sectional or horizontal plane ...
Atlas A General Orientation to Human Anatomy
... • Appendicular region = upper and lower limbs – upper limb = brachium(arm), antebrachium(forearm), carpus(wrist), manus(hand) and digits(fingers) – lower limb = thigh, crus(leg), tarsus(ankle), pes(foot) and digits(toes) ...
... • Appendicular region = upper and lower limbs – upper limb = brachium(arm), antebrachium(forearm), carpus(wrist), manus(hand) and digits(fingers) – lower limb = thigh, crus(leg), tarsus(ankle), pes(foot) and digits(toes) ...
File - andrus medical anatomy and physiology
... 1. Which term is used to show an one organ is in front of the other? a. superior b. anterior c. posterior d. inferior 2. How many body systems are there? a. 9 b. 10 c. 11 d. 12 3. This separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity a. umbilicus b. navel c. diaphragm d. mediastinum 4. T ...
... 1. Which term is used to show an one organ is in front of the other? a. superior b. anterior c. posterior d. inferior 2. How many body systems are there? a. 9 b. 10 c. 11 d. 12 3. This separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity a. umbilicus b. navel c. diaphragm d. mediastinum 4. T ...
Chapter 19 - 21.doc
... What causes the lubb - dupp sounds of the heart? Intrinsic vs. extrinsic regulation of the heart What is the Effects PH, blood pressure, body temperature and extra cellular ion concentration on heart Effects of Aging on the Heart Chapter 21 The Systemic and the pulmonary vessels Describe the Arterie ...
... What causes the lubb - dupp sounds of the heart? Intrinsic vs. extrinsic regulation of the heart What is the Effects PH, blood pressure, body temperature and extra cellular ion concentration on heart Effects of Aging on the Heart Chapter 21 The Systemic and the pulmonary vessels Describe the Arterie ...
Surface Anatomy
... but _10_ to the shoulder. The abdominopelvic cavity is _11_ to the thoracic cavity and _12_ to the spinal cavity. In humans, the dorsal surface can also be called the _13_ surface; however, in quadruped animals, the dorsal surface is the _14_ surface. If an incision cuts the heart into right and lef ...
... but _10_ to the shoulder. The abdominopelvic cavity is _11_ to the thoracic cavity and _12_ to the spinal cavity. In humans, the dorsal surface can also be called the _13_ surface; however, in quadruped animals, the dorsal surface is the _14_ surface. If an incision cuts the heart into right and lef ...
the human body: an orientation
... the (2) body surface, and the top of the head is the most (3) part of the body. The ears are (4) to the shoulders and (5) to the nose. The heart is (6) to the spine and (7) to the lungs. The elbow is (8 ) to the fingers but (9) to the shoulder. In humans, the dorsal surface can also be called the ( ...
... the (2) body surface, and the top of the head is the most (3) part of the body. The ears are (4) to the shoulders and (5) to the nose. The heart is (6) to the spine and (7) to the lungs. The elbow is (8 ) to the fingers but (9) to the shoulder. In humans, the dorsal surface can also be called the ( ...
Living-Organisms-PVMS-NEW
... A group of similar cells working together form tissues. Tissues are more complex than cells. Types of tissues are: ...
... A group of similar cells working together form tissues. Tissues are more complex than cells. Types of tissues are: ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 1
... within a cell. Organelles are at a lower level of organization than a cell, but organs are at a higher level. A tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function. 3. D. The nervous and endocrine systems are the most important regulatory systems of the body. The circulatory system transp ...
... within a cell. Organelles are at a lower level of organization than a cell, but organs are at a higher level. A tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function. 3. D. The nervous and endocrine systems are the most important regulatory systems of the body. The circulatory system transp ...
2. Dissection of Pickle or Potato
... Stage Three: (Use your book p. 13-15 to help you with this after the ribcage is sawn through, the abdominopelvic region (F) can be opened like hinged doors (G) to expose the internal organs (H). The contents of the thoracic cavity (I) will also be visible. The second stage of the autopsy includes ca ...
... Stage Three: (Use your book p. 13-15 to help you with this after the ribcage is sawn through, the abdominopelvic region (F) can be opened like hinged doors (G) to expose the internal organs (H). The contents of the thoracic cavity (I) will also be visible. The second stage of the autopsy includes ca ...
Circulatory System Directs blood from the heart to the rest of the
... course of the experiment. All good experiments have at least one control -Variable Factor in the experiment changes. The fewer the variables in an experiment, the better the design. -Theory Hypothesis that is tested repeatedly and never disproved ...
... course of the experiment. All good experiments have at least one control -Variable Factor in the experiment changes. The fewer the variables in an experiment, the better the design. -Theory Hypothesis that is tested repeatedly and never disproved ...
Chapter 1
... Cranial cavity is within the skull and encases the brain Vertebral cavity runs within the vertebral column and encases the spinal cord ...
... Cranial cavity is within the skull and encases the brain Vertebral cavity runs within the vertebral column and encases the spinal cord ...
Sheep Brain Dissection
... 1. Use a knife or long-bladed scalpel to cut the specimen along a midsagittal plane. Use the longitudinal fissure as a cutting guide. 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callo ...
... 1. Use a knife or long-bladed scalpel to cut the specimen along a midsagittal plane. Use the longitudinal fissure as a cutting guide. 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callo ...
Unit 1 Part II Notes
... explorations of the human body. • Herophilus dissected the entire human body & differed from the authority at the time, Aristotle, when he claimed that consciousness was stored in the brain rather than in the heart. • Erasistratus explained the workings of human ...
... explorations of the human body. • Herophilus dissected the entire human body & differed from the authority at the time, Aristotle, when he claimed that consciousness was stored in the brain rather than in the heart. • Erasistratus explained the workings of human ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy& Physiology
... The membrane that lines the cavity in which the lungs are located is called parietal pleura. The space between these two membranes is called the pleural cavity, and it is filled with serous fluid. ...
... The membrane that lines the cavity in which the lungs are located is called parietal pleura. The space between these two membranes is called the pleural cavity, and it is filled with serous fluid. ...
Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology (1st Diploma – option) Unit abstract
... The digestive system: parts of the digestive system and how they are involved in digestion, eg mouth, stomach, small intestine, large intestine; mechanical digestion (teeth, swallowing, peristalsis); chemical digestion (enzymatic breakdown of, eg carbohydrates, fats and proteins); absorption and ass ...
... The digestive system: parts of the digestive system and how they are involved in digestion, eg mouth, stomach, small intestine, large intestine; mechanical digestion (teeth, swallowing, peristalsis); chemical digestion (enzymatic breakdown of, eg carbohydrates, fats and proteins); absorption and ass ...
Chapter 1
... plane, but to the left or right of median • Frontal or Coronal divides body into anterior and ...
... plane, but to the left or right of median • Frontal or Coronal divides body into anterior and ...
Introduction to A and P Outline
... Life is built on successive levels of increasing complexity: • Chemical (or Molecular) • Organ • Cellular • Organ System • Tissue • Organism Overview of Organ Systems The human body is arranged in 11 organ systems: • Integumentary • Endocrine • Digestive • Skeletal • Cardiovascular • Urinary • Muscu ...
... Life is built on successive levels of increasing complexity: • Chemical (or Molecular) • Organ • Cellular • Organ System • Tissue • Organism Overview of Organ Systems The human body is arranged in 11 organ systems: • Integumentary • Endocrine • Digestive • Skeletal • Cardiovascular • Urinary • Muscu ...
anatomy physiology
... These spaces are very important, providing housing and protection for vital organs. The following list identifies the cavities and subcavities of the human body: • Dorsal cavity: Bones of the cranial portion of the skull and vertebral column, toward the dorsal (posterior) side of the body. • Cranial ...
... These spaces are very important, providing housing and protection for vital organs. The following list identifies the cavities and subcavities of the human body: • Dorsal cavity: Bones of the cranial portion of the skull and vertebral column, toward the dorsal (posterior) side of the body. • Cranial ...
Head and neck anatomy

This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.