Lecture 38 - Amino Acid Metabolism 1
... oxaloacetate, which can be used for glucose synthesis by conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolypyruvate. Under normal conditions, amino acid degradation accounts for ~1015% of the metabolic fuel for animals, more so for animals with high protein diets or during starvation when muscle protein is ...
... oxaloacetate, which can be used for glucose synthesis by conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolypyruvate. Under normal conditions, amino acid degradation accounts for ~1015% of the metabolic fuel for animals, more so for animals with high protein diets or during starvation when muscle protein is ...
The Role of Amino Acids
... chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. Proteins not only catalyze all (or most) of the reactions in living cells, they control virtually all cellular process. In addition, proteins contain within their amino acid sequences the necessary i ...
... chemical properties of the amino acids of proteins determine the biological activity of the protein. Proteins not only catalyze all (or most) of the reactions in living cells, they control virtually all cellular process. In addition, proteins contain within their amino acid sequences the necessary i ...
Sugar Amino Acids - The Krasavin research group
... A recognized strategy in drug discovery for generating new bioactive molecules takes into account the vast array of natural products and fundamental building blocks used by nature, like amino acids, sugars and nucleosides, to produce new chemical entities with multifunctional groups anchored on a si ...
... A recognized strategy in drug discovery for generating new bioactive molecules takes into account the vast array of natural products and fundamental building blocks used by nature, like amino acids, sugars and nucleosides, to produce new chemical entities with multifunctional groups anchored on a si ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... 3-Hydroxybutyrate is oxidized to produce acetoacetate as well as NADH for use in oxidative phosphorylation. ...
... 3-Hydroxybutyrate is oxidized to produce acetoacetate as well as NADH for use in oxidative phosphorylation. ...
Cyclooxygenase mechanisms Lawrence J Marnett
... Activation is completely inhibited by addition of high concentrations of glutathione peroxidase and glutathione, which reduces fatty acid hydroperoxides [33–35]. Once the Tyr385 radical is generated, each enzyme molecule catalyzes several hundred cycles of arachidonic acid oxygenation. Although the ...
... Activation is completely inhibited by addition of high concentrations of glutathione peroxidase and glutathione, which reduces fatty acid hydroperoxides [33–35]. Once the Tyr385 radical is generated, each enzyme molecule catalyzes several hundred cycles of arachidonic acid oxygenation. Although the ...
22: Peptides, Proteins, and α
... When peptide chains are too long for accurate determination of their full sequence by a method such as Edman degradation, we can cleave them into smaller peptides using specific peptide cleavage reactions. We determine the sequences of these smaller peptides and use them to reconstruct the original ...
... When peptide chains are too long for accurate determination of their full sequence by a method such as Edman degradation, we can cleave them into smaller peptides using specific peptide cleavage reactions. We determine the sequences of these smaller peptides and use them to reconstruct the original ...
The effecTs of benzoic acid and proTein level on urine ph and
... urease present in faeces. The most important factors that affect the process are the urea concentration in urine and the pH and temperature of the slurry (Sommer and Husted, 1995). Other factors affecting the production of NH3 is a kind of floor covering system for manure removal, climatic condition ...
... urease present in faeces. The most important factors that affect the process are the urea concentration in urine and the pH and temperature of the slurry (Sommer and Husted, 1995). Other factors affecting the production of NH3 is a kind of floor covering system for manure removal, climatic condition ...
heartsprotein.adv.pdf
... acids appear will determine the 3 dimensional shape of the protein. Interactions between the different R groups will cause the protein to assume and maintain a specific structure. When proteins fold, different amino acids that are distant from each other in the long chain of amino acids, may be near ...
... acids appear will determine the 3 dimensional shape of the protein. Interactions between the different R groups will cause the protein to assume and maintain a specific structure. When proteins fold, different amino acids that are distant from each other in the long chain of amino acids, may be near ...
Inhibition of Serine Amidohydrolases by Complexes of Vanadate
... that are believed to be structural analogs of the transition state of the normal acyl transfer reactions catalyzed by these enzymes (3–5). Phosphonylation of the -lactamase active site by 1 is much faster than spontaneous phosphonate hydrolysis and therefore the -lactamase active site must have si ...
... that are believed to be structural analogs of the transition state of the normal acyl transfer reactions catalyzed by these enzymes (3–5). Phosphonylation of the -lactamase active site by 1 is much faster than spontaneous phosphonate hydrolysis and therefore the -lactamase active site must have si ...
The Effect of Detergents on Amino Acid Liberation by
... The total amino acids liberated into the medium by detergent-grown batch cultures of FT-9 and the parent strain were measured at intervals over several weeks (Fig. 2). Only traces of ninhydrin-positive material were detected in control cultures of the parent strain and this was slightly increased in ...
... The total amino acids liberated into the medium by detergent-grown batch cultures of FT-9 and the parent strain were measured at intervals over several weeks (Fig. 2). Only traces of ninhydrin-positive material were detected in control cultures of the parent strain and this was slightly increased in ...
Molecular Recognition and Membrane Transport with Mixed
... 1:2 borate complexes with both ligands being host or guest compounds. However, as proved by this report, there are a number of applications where this complication should not be disabling. Here, we demonstrate the utility of this new recognition strategy by inducing selective glycoside transport thr ...
... 1:2 borate complexes with both ligands being host or guest compounds. However, as proved by this report, there are a number of applications where this complication should not be disabling. Here, we demonstrate the utility of this new recognition strategy by inducing selective glycoside transport thr ...
PLP-dependent Enzymes: a Powerful Tool for - Beilstein
... Alternatively, the active site lysine reacts with the aminoacrylate intermediate inactivating the enzyme (step 3b in Fig. 6). As an example, l-serine O-sulphate [21] and 3-chloro-lalanine [22] are both rapidly converted to pyruvate, ammonia and SO42- or Cl- respectively. The ability of Asp-AT to cat ...
... Alternatively, the active site lysine reacts with the aminoacrylate intermediate inactivating the enzyme (step 3b in Fig. 6). As an example, l-serine O-sulphate [21] and 3-chloro-lalanine [22] are both rapidly converted to pyruvate, ammonia and SO42- or Cl- respectively. The ability of Asp-AT to cat ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm, not in the mitochondria. Because NADH cannot cross the mitochondrial membrane, one ATP is hydrolyzed to transport the electrons from NADH to FAD. The resulting FADH2 produces only 2 ATP for each NADH produced in glycolysis. ...
... Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm, not in the mitochondria. Because NADH cannot cross the mitochondrial membrane, one ATP is hydrolyzed to transport the electrons from NADH to FAD. The resulting FADH2 produces only 2 ATP for each NADH produced in glycolysis. ...
Lecture_5_Control_of_glycolysis
... direction until the next irreversible step, the hydrolysis of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. The enzyme catalyzing this reaction is fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase, an allosteric enzyme. ...
... direction until the next irreversible step, the hydrolysis of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. The enzyme catalyzing this reaction is fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase, an allosteric enzyme. ...
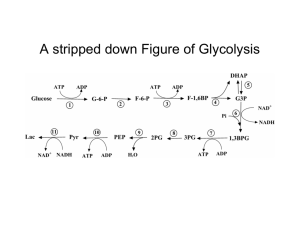
Lecture 3 - Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis 1 2 3 4
... Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol plus CO2. Under aerobic conditions, gluco ...
... Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol plus CO2. Under aerobic conditions, gluco ...
广西医科大学理论课教案(1)
... 2.To be familiar with the activation energy and free energy change in a reaction system, and why enzymes can increase the rate of reaction catalyzed by enzyme, active site of enzymes, substrate specificity of enzyme as well as enzyme classification 3.To have an appreciation of the chemical equilibri ...
... 2.To be familiar with the activation energy and free energy change in a reaction system, and why enzymes can increase the rate of reaction catalyzed by enzyme, active site of enzymes, substrate specificity of enzyme as well as enzyme classification 3.To have an appreciation of the chemical equilibri ...
Document
... reduces all four ribonucleotides to their deoxyribo derivitives. A free radical mechanism is involved in the ribonucleotide reductase reaction. There are three classes of ribonucleotide reductase enzymes in nature: Class I: tyrosine radical, uses NDP Class II: adenosylcobalamin. uses NTPs (cyanobact ...
... reduces all four ribonucleotides to their deoxyribo derivitives. A free radical mechanism is involved in the ribonucleotide reductase reaction. There are three classes of ribonucleotide reductase enzymes in nature: Class I: tyrosine radical, uses NDP Class II: adenosylcobalamin. uses NTPs (cyanobact ...
Lecture 3 - Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol plus CO2. Under aerobic conditions, gluco ...
... Pyruvic acid is more oxidized than glucose The energy released from the oxidation is used to create 2 molecules of ATP from 2 ADP and 2 Pi This is an anaerobic process. Under anaerobic conditions the pyruvic acid can be fermented to lactic acid or to ethanol plus CO2. Under aerobic conditions, gluco ...
Figure 17-3 Degradation of glucose via the glycolytic pathway.
... SUMMARY: Pathways from glucose to pyruvate and pyruvate to glucose are regulated by both the level of respiratory fuels and energy charge. Thus, whenever cell has ample ATP and respiratory fuels such as acetylCoA, citrate, or NADH glycolysis is inhibited and gluconeogenesis ...
... SUMMARY: Pathways from glucose to pyruvate and pyruvate to glucose are regulated by both the level of respiratory fuels and energy charge. Thus, whenever cell has ample ATP and respiratory fuels such as acetylCoA, citrate, or NADH glycolysis is inhibited and gluconeogenesis ...
Evolution of Amino Acid Metabolism Inferred through Cladistic
... obtained by organisms able to synthesize this nutrient from an available precursor. Each biosynthetic step was selected according to successive depletions of precursors in the environment. The first enzyme to appear in the biosynthetic pathway was, therefore, the most distal (i.e. downstream) in the ...
... obtained by organisms able to synthesize this nutrient from an available precursor. Each biosynthetic step was selected according to successive depletions of precursors in the environment. The first enzyme to appear in the biosynthetic pathway was, therefore, the most distal (i.e. downstream) in the ...
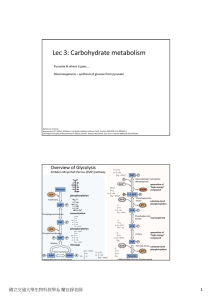
Lec 3: Carbohydrate metabolism
... Lots of heme‐containing mitochondria, used in aerobic metabolism ...
... Lots of heme‐containing mitochondria, used in aerobic metabolism ...
2 ATP - HONORS BIOLOGY
... Occurs in the Matrix of the Mitochondria Everything in the Krebs Cycle happens twice because there are two pyruvates from glycolysis. 1) Pyruvate enters the mitochondria and immediately loses a CO2 and makes a NADH forming acetic acid which binds to an enzyme called Co-enzyme A. CO2 Acetic Acid + Co ...
... Occurs in the Matrix of the Mitochondria Everything in the Krebs Cycle happens twice because there are two pyruvates from glycolysis. 1) Pyruvate enters the mitochondria and immediately loses a CO2 and makes a NADH forming acetic acid which binds to an enzyme called Co-enzyme A. CO2 Acetic Acid + Co ...
Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... 2) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The same enzymes are used in the digestion of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. B) The major physical processes in digestion are mixing, softening, and grinding of food. C) The major chemical reaction in digestion is en ...
... 2) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The same enzymes are used in the digestion of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. B) The major physical processes in digestion are mixing, softening, and grinding of food. C) The major chemical reaction in digestion is en ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.