Ch23_PT MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... 2) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The same enzymes are used in the digestion of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. B) The major physical processes in digestion are mixing, softening, and grinding of food. C) The major chemical reaction in digestion is en ...
... 2) All of the following statements concerning digestion are correct except A) The same enzymes are used in the digestion of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. B) The major physical processes in digestion are mixing, softening, and grinding of food. C) The major chemical reaction in digestion is en ...
6 Energy
... back to work for the gumball glycolysis machine and the Kreb’s machine. Muscles are the only human cells that can do this. When no oxygen is present (such as in muscles during sprinting), the NADH molecules that were generated from glycolysis and the TCA cycle cannot use the electron transport cha ...
... back to work for the gumball glycolysis machine and the Kreb’s machine. Muscles are the only human cells that can do this. When no oxygen is present (such as in muscles during sprinting), the NADH molecules that were generated from glycolysis and the TCA cycle cannot use the electron transport cha ...
Transcriptome analysis of Sacha Inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L
... to form malonyl-CoA; (b) repeated condensation of malonyl-CoA with a growing ACP-bound acyl chain by FA synthase complex, consecutively adding two carbon units to form 16:0-ACP; and (c) elongation and desaturation of 16:0-ACP to form 18:0-ACP and 18:1-ACP, respectively [13]. Desaturation of 18:0-ACP ...
... to form malonyl-CoA; (b) repeated condensation of malonyl-CoA with a growing ACP-bound acyl chain by FA synthase complex, consecutively adding two carbon units to form 16:0-ACP; and (c) elongation and desaturation of 16:0-ACP to form 18:0-ACP and 18:1-ACP, respectively [13]. Desaturation of 18:0-ACP ...
Isoleucine Synthesis by Clostridium sporogenes from
... The amino acid requirements for growth of Clostridium sporogenes and Clostridium botulinum type A were examined several years ago (Campbell & Frank, 1956; Kindler & Mager, 1956; Mager et al., 1954). These bacteria were found to be indistinguishable in nutritional requirements, and have since been sh ...
... The amino acid requirements for growth of Clostridium sporogenes and Clostridium botulinum type A were examined several years ago (Campbell & Frank, 1956; Kindler & Mager, 1956; Mager et al., 1954). These bacteria were found to be indistinguishable in nutritional requirements, and have since been sh ...
08_Cellular respiration ppt
... Electrons are removed from substrates and received by oxygen, which combines with H+ to become water. ...
... Electrons are removed from substrates and received by oxygen, which combines with H+ to become water. ...
Chapter 5 - Hale AP Biology
... unsaturated fats to saturated fats by adding hydrogen • Hydrogenating vegetable oils also creates unsaturated fats with trans double bonds • These trans fats may contribute more than saturated fats to cardiovascular disease Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cum ...
... unsaturated fats to saturated fats by adding hydrogen • Hydrogenating vegetable oils also creates unsaturated fats with trans double bonds • These trans fats may contribute more than saturated fats to cardiovascular disease Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cum ...
Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis Expectations
... • A liver biopsy of a four‐year old boy indicated that the F‐1,6‐Bpase enzyme activity was 20% normal. The patient’s blood glucose levels were normal at the beginning of a fast, but then decreased suddenly. Pyruvate and alanine concentrations were also elevated, as was the glyceraldehyde/DHAP ...
... • A liver biopsy of a four‐year old boy indicated that the F‐1,6‐Bpase enzyme activity was 20% normal. The patient’s blood glucose levels were normal at the beginning of a fast, but then decreased suddenly. Pyruvate and alanine concentrations were also elevated, as was the glyceraldehyde/DHAP ...
Cellular Respiration
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
ppt
... An effect of insulin on insulin-sensitive cells Transport of Glc into cells is dependent on insulin effect (GLUT-4) in the following tissues: skeletal and heart muscle and adipose tissue ...
... An effect of insulin on insulin-sensitive cells Transport of Glc into cells is dependent on insulin effect (GLUT-4) in the following tissues: skeletal and heart muscle and adipose tissue ...
Biochemical Screening of Pyrimidine
... source may be the most sensitive component of the system. Agents which act upon one or more steps in the oxidative cycle could appear to be inhibitors of reactions in which they actually have no effect. However, in this study oxidative phosphorylation was deliberately chosen as an energy source beca ...
... source may be the most sensitive component of the system. Agents which act upon one or more steps in the oxidative cycle could appear to be inhibitors of reactions in which they actually have no effect. However, in this study oxidative phosphorylation was deliberately chosen as an energy source beca ...
Amino Acids
... • Side chains vary: size, shape, charge, reactivity, H-bond capacity • Five aa groups, based on R grp ...
... • Side chains vary: size, shape, charge, reactivity, H-bond capacity • Five aa groups, based on R grp ...
amino-acids - ChemConnections
... Peptides are formed by condensation of the -COOH group of one amino acid and the NH group of another amino acid. The acid forming the peptide bond is named first. Example: if a dipeptide is formed from alanine and glycine so that the COOH group of glycine reacts with the NH group of alanine, then th ...
... Peptides are formed by condensation of the -COOH group of one amino acid and the NH group of another amino acid. The acid forming the peptide bond is named first. Example: if a dipeptide is formed from alanine and glycine so that the COOH group of glycine reacts with the NH group of alanine, then th ...
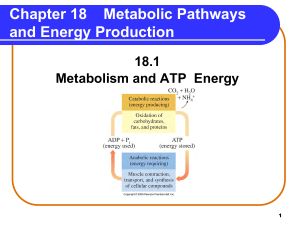
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... A. 4 produced during anaerobic conditions B. 3 reaction series that converts glucose to pyruvate C. 1 metabolic reactions that break down large molecules to smaller molecules + energy D. 2 substances that remove or add H atoms in oxidation and reduction reactions ...
... A. 4 produced during anaerobic conditions B. 3 reaction series that converts glucose to pyruvate C. 1 metabolic reactions that break down large molecules to smaller molecules + energy D. 2 substances that remove or add H atoms in oxidation and reduction reactions ...
Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Phosphatase Deficiency
... (30). fructose-1.6-diphosphatase by the method of Pontremoli (24). phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase by the method of Roobol and P O S T M O R T E M INVESTIGATION Alleyne (25). and pyruvate carboxylase by the method of Crabtree The activities of glucose-6-phosphatase. phosphoenolpyruvnte et a/. (12) ...
... (30). fructose-1.6-diphosphatase by the method of Pontremoli (24). phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase by the method of Roobol and P O S T M O R T E M INVESTIGATION Alleyne (25). and pyruvate carboxylase by the method of Crabtree The activities of glucose-6-phosphatase. phosphoenolpyruvnte et a/. (12) ...
(PSD) July 2015 PBAC Meeting
... submission claimed that such products are shown to provide at least equivalent efficacy to amino acid products in terms of controlling plasma phenylalanine concentrations. While there are no studies done in patients with tyrosinaemia, the ...
... submission claimed that such products are shown to provide at least equivalent efficacy to amino acid products in terms of controlling plasma phenylalanine concentrations. While there are no studies done in patients with tyrosinaemia, the ...
Key area 2 * Cellular respiration
... • Describe the citric acid cycle. • Understand that respiration is a series of enzyme mediated reactions • Explain the importance of the products of the citric acid cycle ...
... • Describe the citric acid cycle. • Understand that respiration is a series of enzyme mediated reactions • Explain the importance of the products of the citric acid cycle ...
Supplement I
... experiment. Measurements of compartment-specific metabolites indicate high exchange between cytosol and plastid and that pools are in near-equilibrium. Data are taken from the [U-13C6]-glucose labeling experiment. (a) GCMS fragments from compartmentspecific metabolites have very similar profiles eve ...
... experiment. Measurements of compartment-specific metabolites indicate high exchange between cytosol and plastid and that pools are in near-equilibrium. Data are taken from the [U-13C6]-glucose labeling experiment. (a) GCMS fragments from compartmentspecific metabolites have very similar profiles eve ...
Nomenclature for incompletely specified bases in nucleic acid
... Restriction enzymes are highly specific for particular nucleic acid sequences. For many other enzymes the specificity is rather more lax, however, and the symbols are intended to meet in part the need for presenting a schematic summary of the sequence features. For instance, sequences recognized by ...
... Restriction enzymes are highly specific for particular nucleic acid sequences. For many other enzymes the specificity is rather more lax, however, and the symbols are intended to meet in part the need for presenting a schematic summary of the sequence features. For instance, sequences recognized by ...
Glutaric Aciduria Type 11: Evidence for a Defect Related to
... Medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity estimated by direct dehydrogenation of (CO-CIO)acyl-CoA by fibroblast homogenate is shown in Table 4. Normal activity was found in the homogenates of G A I1 fibroblasts. Glutamate dehydrogenase was determined as a reference mitochondria1 enzyme. The norma ...
... Medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity estimated by direct dehydrogenation of (CO-CIO)acyl-CoA by fibroblast homogenate is shown in Table 4. Normal activity was found in the homogenates of G A I1 fibroblasts. Glutamate dehydrogenase was determined as a reference mitochondria1 enzyme. The norma ...
Toward D-peptide biosynthesis: Elongation Factor P
... two consecutive D-amino acids, and hence enables the translation of D-peptides. Life is an anti-entropic phenomenon with two mutually-reinforcing characters: homochirality and stereospecific catalysis. The exclusive presence of L-amino acids in proteins of the living world is a prominent example of ...
... two consecutive D-amino acids, and hence enables the translation of D-peptides. Life is an anti-entropic phenomenon with two mutually-reinforcing characters: homochirality and stereospecific catalysis. The exclusive presence of L-amino acids in proteins of the living world is a prominent example of ...
purine
... • GTP is involved in AMP synthesis and ATP is involved in GMP synthesis (reciprocal control of production) • PRPP is a biosynthetically “central” molecule (why?) – ADP/GDP levels – negative feedback on Ribose Phosphate ...
... • GTP is involved in AMP synthesis and ATP is involved in GMP synthesis (reciprocal control of production) • PRPP is a biosynthetically “central” molecule (why?) – ADP/GDP levels – negative feedback on Ribose Phosphate ...
S4 Text
... Concentration of aa i (not incorporated in protein) Concentration of tRNA charged with aa i Concentration of free tRNA conjugate to aa i Total concentration of tRNA conjugate to aa i Total concentration of ribosome with an A-site for aa i Ribosomes with uncharged tRNA in an A-site for aa i Concentra ...
... Concentration of aa i (not incorporated in protein) Concentration of tRNA charged with aa i Concentration of free tRNA conjugate to aa i Total concentration of tRNA conjugate to aa i Total concentration of ribosome with an A-site for aa i Ribosomes with uncharged tRNA in an A-site for aa i Concentra ...
Aromatic amino acid metabolism
... indole-3- glycerol phosphate, which reacts with serine to form tryptophan. ...
... indole-3- glycerol phosphate, which reacts with serine to form tryptophan. ...
Glycolysis 2
... in the mitochondria to acetyl CoA, and ultimately to CO2 and H2O which are the products of the citrate cycle and electron transport chain. 2. Under anaerobic conditions, such as occurs in muscle cells during strenuous exercise, or in erythrocytes which lack mitochondria, pyruvate is converted to lac ...
... in the mitochondria to acetyl CoA, and ultimately to CO2 and H2O which are the products of the citrate cycle and electron transport chain. 2. Under anaerobic conditions, such as occurs in muscle cells during strenuous exercise, or in erythrocytes which lack mitochondria, pyruvate is converted to lac ...
1- Glycolysis
... The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle: is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical ene ...
... The citric acid cycle – also known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle or the Krebs cycle: is a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats and proteins into carbon dioxide and chemical ene ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.