Chapter 7 How Cells Release Chemical energy
... Second stage of aerobic respiration results in Six CO2, two ATP, eight NADH, and two FADH2 for every two pyruvates Adding the yield from glycolysis, the total is – Twelve reduced coenzymes and four ATP for each glucose molecule Coenzymes deliver electrons and hydrogen to the third stage of reaction ...
... Second stage of aerobic respiration results in Six CO2, two ATP, eight NADH, and two FADH2 for every two pyruvates Adding the yield from glycolysis, the total is – Twelve reduced coenzymes and four ATP for each glucose molecule Coenzymes deliver electrons and hydrogen to the third stage of reaction ...
Metabolism of acyl‐lipids in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
... understanding of acyl-lipid metabolism in model microalgal species (Merchant et al., 2012; Liu and Benning, 2013). Historically, the green model microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has not been the focus of many studies on fatty acid metabolism because it does not synthesize VLC-PUFAs and was consid ...
... understanding of acyl-lipid metabolism in model microalgal species (Merchant et al., 2012; Liu and Benning, 2013). Historically, the green model microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii has not been the focus of many studies on fatty acid metabolism because it does not synthesize VLC-PUFAs and was consid ...
Pancreas
... Activation of acetyl CoA carboxylase. Stimulates production of free fatty acids from acetyl CoA. Activation of lipoprotein lipase (increases breakdown of triacylglycerol in the circulation). Fatty acids are then taken up by adipocytes, and triacylglycerol is made and stored in the ...
... Activation of acetyl CoA carboxylase. Stimulates production of free fatty acids from acetyl CoA. Activation of lipoprotein lipase (increases breakdown of triacylglycerol in the circulation). Fatty acids are then taken up by adipocytes, and triacylglycerol is made and stored in the ...
Galguard Trident - In
... • Trichlosan is reported to be an endocrine disruptor (thyroid function) and is reported to impair cardiac and skeletal muscles. There seems to be a special concern for children who are at higher risk of allergies and the immune systems (Toxicological Sciences, 2009, 107 (1): 56-64, Reproductive Tox ...
... • Trichlosan is reported to be an endocrine disruptor (thyroid function) and is reported to impair cardiac and skeletal muscles. There seems to be a special concern for children who are at higher risk of allergies and the immune systems (Toxicological Sciences, 2009, 107 (1): 56-64, Reproductive Tox ...
25 WORDS: ALANINE Alanine, C3H7NO2, is one of the 20 amino
... 25 WORDS: ALANINE Alanine, C3H7NO2, is one of the 20 amino acids that make up essential proteins in our bodies. It is manufactured in our bodies, so it is called a nonessential amino acid. Alanine (abbreviated as Ala or A) is a crystalline amino acid that is a constituent of many proteins. It can be ...
... 25 WORDS: ALANINE Alanine, C3H7NO2, is one of the 20 amino acids that make up essential proteins in our bodies. It is manufactured in our bodies, so it is called a nonessential amino acid. Alanine (abbreviated as Ala or A) is a crystalline amino acid that is a constituent of many proteins. It can be ...
New Functions for Parts of the Krebs Cycle in Procyclic
... optimal utilization of the carbon sources available in the environment. One of the major mechanisms by which cells adapt is by regulation of gene expression. Analysis of genomic expression has revealed that, in many organisms, multiple genes are differentially transcribed in response to varying gluc ...
... optimal utilization of the carbon sources available in the environment. One of the major mechanisms by which cells adapt is by regulation of gene expression. Analysis of genomic expression has revealed that, in many organisms, multiple genes are differentially transcribed in response to varying gluc ...
VITAMINS
... • Iron and hemoglobin metaboilsm: Ascorbic acid enhances iron absorption by keeping it in the ferrous form. This is due to reducing property of Vitamin C. it help in the formation of ferritin (storage form of iron) and metaboilzation of iron from ferritin. Vitamin C is useful in the reconversion of ...
... • Iron and hemoglobin metaboilsm: Ascorbic acid enhances iron absorption by keeping it in the ferrous form. This is due to reducing property of Vitamin C. it help in the formation of ferritin (storage form of iron) and metaboilzation of iron from ferritin. Vitamin C is useful in the reconversion of ...
Presentation 2013-201307040352
... response to pressure overload–induced hypertrophy, these metabolic shifts are thought to be protective. ...
... response to pressure overload–induced hypertrophy, these metabolic shifts are thought to be protective. ...
interaction analysis of aspirin with selective amino acids
... µg/mL. A single poisonous dose of aspirin in adults is not recognized with confidence but death may be anticipated at a dose ≥ 30 g. The blood salicylate levels are measured to determine the severity of aspirin intoxication (12, 13). Thus, it is very important to determine the agents which interact ...
... µg/mL. A single poisonous dose of aspirin in adults is not recognized with confidence but death may be anticipated at a dose ≥ 30 g. The blood salicylate levels are measured to determine the severity of aspirin intoxication (12, 13). Thus, it is very important to determine the agents which interact ...
A minimal growth medium for the basidiomycete Pleurotus sapidus
... supplementation; H0 - H5 equates to 0–5 g L-1 yeast extract, cf. Table 1 for detailed medium composition. Right: Visual comparison of P. sapidus grown for 4 days in standard nutrition medium with 3 g L-1 (SNL-H3-G15, top) and 0 g L-1 (SNL-H0-G15, bottom) yeast extract. ...
... supplementation; H0 - H5 equates to 0–5 g L-1 yeast extract, cf. Table 1 for detailed medium composition. Right: Visual comparison of P. sapidus grown for 4 days in standard nutrition medium with 3 g L-1 (SNL-H3-G15, top) and 0 g L-1 (SNL-H0-G15, bottom) yeast extract. ...
Carbon dioxide fixation.
... as well as serving as the starting material for fuel, fiber, animal feed, oil, and other compounds used by people. Collectively, the biochemical processes by which CO2 is assimilated into organic molecules are known as the photosynthetic dark reactions, not because they must occur in darkness but be ...
... as well as serving as the starting material for fuel, fiber, animal feed, oil, and other compounds used by people. Collectively, the biochemical processes by which CO2 is assimilated into organic molecules are known as the photosynthetic dark reactions, not because they must occur in darkness but be ...
Phosphate stabilizing compositions
... surprising because polyaspartic acid alone does not have any significant phosphate stabilizing effect. The mixtures stabilize phosphates more than was expected in view of the phosphate inhibition activity of the individual components. Although carboxylic polymers alone provide some phosphate stabili ...
... surprising because polyaspartic acid alone does not have any significant phosphate stabilizing effect. The mixtures stabilize phosphates more than was expected in view of the phosphate inhibition activity of the individual components. Although carboxylic polymers alone provide some phosphate stabili ...
A speculation on the origin of protein synthesis
... bound to the messenger RNA so strongly and could perhaps come off and go on again before receiving the polypeptide chain since this would only slow the process rather than make a gross error in it. A tRNA with no amino acid attached should bind rather weakly, if at all, so that it will not interfere ...
... bound to the messenger RNA so strongly and could perhaps come off and go on again before receiving the polypeptide chain since this would only slow the process rather than make a gross error in it. A tRNA with no amino acid attached should bind rather weakly, if at all, so that it will not interfere ...
Amino acid sequence of PR-39
... a fairly stoichiometric cleavage of the peptide was trypsin, but only at a high enzyme/substrate ratio (2 - 3 :5 ) . The tryptic fragments were separated on reverse-phase HPLC and the material corresponding to four peaks (T2, T3, T5, and T6; Fig. 4) were analyzed for amino acid composition and seque ...
... a fairly stoichiometric cleavage of the peptide was trypsin, but only at a high enzyme/substrate ratio (2 - 3 :5 ) . The tryptic fragments were separated on reverse-phase HPLC and the material corresponding to four peaks (T2, T3, T5, and T6; Fig. 4) were analyzed for amino acid composition and seque ...
The Invention of Proteomic Code and mRNA
... as the chief proponent of the Big Bang theory in cosmology. He proposed a Diamond Code [4-6] where DNA acted directly as a template for assembling amino acids into proteins. Various combinations of bases along one of the grooves in the double helix could form distinctively shaped cavities into which ...
... as the chief proponent of the Big Bang theory in cosmology. He proposed a Diamond Code [4-6] where DNA acted directly as a template for assembling amino acids into proteins. Various combinations of bases along one of the grooves in the double helix could form distinctively shaped cavities into which ...
Chapter 6
... The accumulated protons diffuse back into the matrix through ATP synthase. The energy released from the diffusion fuels the formation of ATP. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... The accumulated protons diffuse back into the matrix through ATP synthase. The energy released from the diffusion fuels the formation of ATP. Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
aerobic respiration
... Lactate Fermentation NADH gives e-s and H+ to pyruvate → lactate e.g. bacteria (Lactobacillus spp. and others) in ...
... Lactate Fermentation NADH gives e-s and H+ to pyruvate → lactate e.g. bacteria (Lactobacillus spp. and others) in ...
Ch16b: Peptides
... ‣ Insulin was first identified in 1869. ‣ Insulin was sequenced by Frederick Sanger in 1953 (84 years later). ‣ This was the first protein to have its primary structure determined. ‣ Sanger was awarded the 1958 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work. ‣ The primary structure of two polypeptide chains ...
... ‣ Insulin was first identified in 1869. ‣ Insulin was sequenced by Frederick Sanger in 1953 (84 years later). ‣ This was the first protein to have its primary structure determined. ‣ Sanger was awarded the 1958 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work. ‣ The primary structure of two polypeptide chains ...
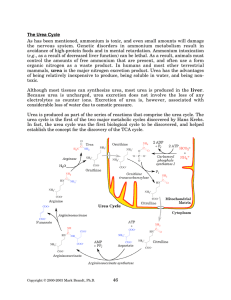
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... the source of the free ammonium via glutamate dehydrogenase. Glutamate also frequently acts as an a-amino donor for the aminotransferase reaction that supplies aspartate with the nitrogen it donates to urea. Glutamate acts as the source of Nacetylglutamate, the stimulator of the urea cycle limiting ...
... the source of the free ammonium via glutamate dehydrogenase. Glutamate also frequently acts as an a-amino donor for the aminotransferase reaction that supplies aspartate with the nitrogen it donates to urea. Glutamate acts as the source of Nacetylglutamate, the stimulator of the urea cycle limiting ...
Proteins are made of chains of amino acids
... Essential amino acids and nutrition • Consider why protein is needed and what amino acids and proteins are used for in the body. Describe the symptoms you would expect a person with protein deficiency to have. • Look at Table 1. Which amino acids does corn lack (not have)? Which amino acids do bean ...
... Essential amino acids and nutrition • Consider why protein is needed and what amino acids and proteins are used for in the body. Describe the symptoms you would expect a person with protein deficiency to have. • Look at Table 1. Which amino acids does corn lack (not have)? Which amino acids do bean ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle
... The Point is to Make ATP! AP Biology ...
... The Point is to Make ATP! AP Biology ...
Characterization of the production regions ofChardonnay - Vitis-vea
... General parameters ofChardonnay varietal wines originating from different regions are shown in Tab . 2 . Results of 21 amino acids are presented as mg amino acid per 100 mg amino nitrogen in order to minimize the variation in the nitrogen fraction arising from climatic conditions or viticultural pra ...
... General parameters ofChardonnay varietal wines originating from different regions are shown in Tab . 2 . Results of 21 amino acids are presented as mg amino acid per 100 mg amino nitrogen in order to minimize the variation in the nitrogen fraction arising from climatic conditions or viticultural pra ...
"Fermentation Pathways". In: Microbial Physiology (Fourth Edition)
... glucose + HSO3 − −−−→ glycerol + acetaldehyde-HSO3 − + CO2 Under these conditions, acetaldehyde is unable to serve as a hydrogen acceptor. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate becomes the preferred hydrogen acceptor, yielding glycerol-3-phosphate, which is then hydrolyzed to glycerol and Pi . The fermentation ...
... glucose + HSO3 − −−−→ glycerol + acetaldehyde-HSO3 − + CO2 Under these conditions, acetaldehyde is unable to serve as a hydrogen acceptor. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate becomes the preferred hydrogen acceptor, yielding glycerol-3-phosphate, which is then hydrolyzed to glycerol and Pi . The fermentation ...
HOW CELLS HARVEST ENERGY
... cell has enuf ATP it acts as allosteric inhibitor and inhibits oxidation of pyruvate High ADP means cell needs more ATP and ADP acts as allosteric activator to activate phosphofructokinase ...
... cell has enuf ATP it acts as allosteric inhibitor and inhibits oxidation of pyruvate High ADP means cell needs more ATP and ADP acts as allosteric activator to activate phosphofructokinase ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.