Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
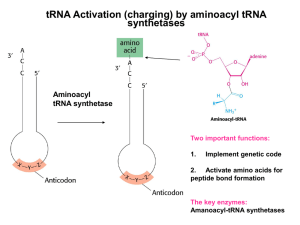
... charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correct tRNAs via by interacting with specific regions of tR ...
... charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correct tRNAs via by interacting with specific regions of tR ...
CHAPTER 1 SAMPLE TEST
... b. two small molecules chemically combine to form a large one c. a base reacts with an acid to form water and a salt d. electrons are transferred from one substance to another e. a large molecule is broken into two smaller molecules During photosynthesis, water molecules are split according to the f ...
... b. two small molecules chemically combine to form a large one c. a base reacts with an acid to form water and a salt d. electrons are transferred from one substance to another e. a large molecule is broken into two smaller molecules During photosynthesis, water molecules are split according to the f ...
Ketone body metabolism and cardiovascular disease - AJP
... pathway for -oxidation-derived acetyl-CoA generated in excess of the liver’s energetic needs (Fig. 2). Acetyl-CoA subsumes several roles integral to hepatic intermediary metabolism beyond ATP generation via terminal oxidation. AcetylCoA allosterically activates 1) pyruvate carboxylase, thereby acti ...
... pathway for -oxidation-derived acetyl-CoA generated in excess of the liver’s energetic needs (Fig. 2). Acetyl-CoA subsumes several roles integral to hepatic intermediary metabolism beyond ATP generation via terminal oxidation. AcetylCoA allosterically activates 1) pyruvate carboxylase, thereby acti ...
BIOCHEMISTRY Which of the following single
... A. fructose 1,6 bisphosphate B. ATP C. Citrate D. fructose 2,6 bisphosphate ...
... A. fructose 1,6 bisphosphate B. ATP C. Citrate D. fructose 2,6 bisphosphate ...
Blueberry Intake Alters Skeletal Muscle and Adipose
... phenotypes such as obesity, systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia. A recent epidemiological study indicated that blueberry intake reduced cardiovascular mortality in humans, but the possible genetic mechanisms of this effect are unknown. Blueberries are a rich source of antho ...
... phenotypes such as obesity, systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia. A recent epidemiological study indicated that blueberry intake reduced cardiovascular mortality in humans, but the possible genetic mechanisms of this effect are unknown. Blueberries are a rich source of antho ...
Anatomy of a Cell :
... not break down cellular components willy-nilly because the cytoplasmic pH is close to neutral and the enzymes do not work well. Once thought to be exclusive to animal cells, lysosomes have now been described in all cells from all eukaryotic kingdoms. ...
... not break down cellular components willy-nilly because the cytoplasmic pH is close to neutral and the enzymes do not work well. Once thought to be exclusive to animal cells, lysosomes have now been described in all cells from all eukaryotic kingdoms. ...
Lactobacillus sanfrancisco a key sourdough lactic acid bacterium: a
... phosphogluconate pathway; (8) phosphoketolase; (9–14) enzymes of the Embden–Meyerhof glycolytic pathway; (15) phosphotransacetylase; (16) alcohol dehydrogenase; (17) acetate kinase; (18) mannitol dehydrogenase; (19) malolactic enzyme; (20) citrate lyase; (21) oxaloacetate-decarboxylase; (22) lactate ...
... phosphogluconate pathway; (8) phosphoketolase; (9–14) enzymes of the Embden–Meyerhof glycolytic pathway; (15) phosphotransacetylase; (16) alcohol dehydrogenase; (17) acetate kinase; (18) mannitol dehydrogenase; (19) malolactic enzyme; (20) citrate lyase; (21) oxaloacetate-decarboxylase; (22) lactate ...
Mistranslation and its control by tRNA synthetases
... frequency of roughly 1/200 [15]. Isoleucine can only be recognized by hydrophobic interactions and valine, which lacks one methylene group compared with Ile, can fit into the same binding pocket on the enzyme. Likewise, valyl-tRNA synthetase (ValRS) misactivates threonine, which is virtually isoster ...
... frequency of roughly 1/200 [15]. Isoleucine can only be recognized by hydrophobic interactions and valine, which lacks one methylene group compared with Ile, can fit into the same binding pocket on the enzyme. Likewise, valyl-tRNA synthetase (ValRS) misactivates threonine, which is virtually isoster ...
On the Uniqueness of the Standard Genetic Code
... to 30 direction of the codon [1]. Each of the 64 codons specifies one of the 20 amino acids or else serves as a punctuation mark signaling the end of a message. Crick proposed the wobble hypothesis [10,11], which accounts for the degeneracy of the SGC: the third position in each codon is said to wob ...
... to 30 direction of the codon [1]. Each of the 64 codons specifies one of the 20 amino acids or else serves as a punctuation mark signaling the end of a message. Crick proposed the wobble hypothesis [10,11], which accounts for the degeneracy of the SGC: the third position in each codon is said to wob ...
Metabolomics based gene function annotation in Escherichia coli
... 3-Ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III catalyzes the first carbon-carbon bondforming reaction (Claisen condensation) of type II fatty acid synthesis systems in bacteria and plant plastids. In E. coli, KASIII is encoded by the fabH gene. FabH deletion mutants were originally thought to be letha ...
... 3-Ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase III catalyzes the first carbon-carbon bondforming reaction (Claisen condensation) of type II fatty acid synthesis systems in bacteria and plant plastids. In E. coli, KASIII is encoded by the fabH gene. FabH deletion mutants were originally thought to be letha ...
The Incorporation of Glycerol and Lysine into the Lipid Fraction of
... of incorporation is increased by the presence of glucose and amino acids. The presence ofamino acids increases incorporation into the fraction containing 0-amino acid esters of phosphatidylglycerol. 2. Glycerol, incorporated into washed cells by incubation with glycerol, glucose and amino acids, is ...
... of incorporation is increased by the presence of glucose and amino acids. The presence ofamino acids increases incorporation into the fraction containing 0-amino acid esters of phosphatidylglycerol. 2. Glycerol, incorporated into washed cells by incubation with glycerol, glucose and amino acids, is ...
Determination of the Amino Acid Content of Peptides by AAA
... in amino acid recovery.3, 4 Furthermore, some amino acid derivatives are unstable.5 Postcolumn derivatization using ninhydrin cannot be performed in samples containing high levels of ammonia because they form insoluble complexes that can plug the instrument’s flow paths.3 Urea, polyacrylamide, and a ...
... in amino acid recovery.3, 4 Furthermore, some amino acid derivatives are unstable.5 Postcolumn derivatization using ninhydrin cannot be performed in samples containing high levels of ammonia because they form insoluble complexes that can plug the instrument’s flow paths.3 Urea, polyacrylamide, and a ...
Porphyrin Metabolism & Porphyrias
... Cytochrome P450s (CYPs) are actually a superfamily of related, heme-containing monooxygenase enzymes that participate in abroad variety of reactions. This system performs different functions in two separate locations in cells. ...
... Cytochrome P450s (CYPs) are actually a superfamily of related, heme-containing monooxygenase enzymes that participate in abroad variety of reactions. This system performs different functions in two separate locations in cells. ...
as a PDF
... fall far short of those observed. Moreover, if any incorporation of activity into carbon dioxide occurred by mechanisms other than recycling, even less recycling could have taken place. It therefore appears impossible that the radioactivity of carboxyls 2 and 3 is due solely to recycling. A similar ...
... fall far short of those observed. Moreover, if any incorporation of activity into carbon dioxide occurred by mechanisms other than recycling, even less recycling could have taken place. It therefore appears impossible that the radioactivity of carboxyls 2 and 3 is due solely to recycling. A similar ...
Manipulating redox and ATP balancing for improved production of
... et al., 2002a). An additional mutation in the ptsG restores fermentative growth on glucose in complex media. This strain produces succinate, acetate and ethanol in a molar ratio of 1:0.5:0.5. It is thought that pyruvate dehydrogenase complex maintains a low level of activity under laboratory anaerob ...
... et al., 2002a). An additional mutation in the ptsG restores fermentative growth on glucose in complex media. This strain produces succinate, acetate and ethanol in a molar ratio of 1:0.5:0.5. It is thought that pyruvate dehydrogenase complex maintains a low level of activity under laboratory anaerob ...
Nutritional Aspects of Inborn Errors of Metabolism
... growth period and the first two years of life, the human brain grows at an impressive rate. This brain growth spurt period (1) is associated with a very high rate of protein synthesis that makes the central nervous system vulnérable to any interférence with protein synthesis. Biochemical insuit at t ...
... growth period and the first two years of life, the human brain grows at an impressive rate. This brain growth spurt period (1) is associated with a very high rate of protein synthesis that makes the central nervous system vulnérable to any interférence with protein synthesis. Biochemical insuit at t ...
IMGT Colliers de Perles: Standardized Sequence
... proteins include more particularly proteins other than IG, TR and MHC that belong to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) and to the MHC superfamily (MhcSF) [1]. The IgSF comprises not only the IG and TR proteins involved in antigen recognition, but also a great number of proteins that are involved ...
... proteins include more particularly proteins other than IG, TR and MHC that belong to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) and to the MHC superfamily (MhcSF) [1]. The IgSF comprises not only the IG and TR proteins involved in antigen recognition, but also a great number of proteins that are involved ...
Mechanism of CS, Cont`d
... • PDH complex is a noncovalent assembly of three different enzymes operating in concert to catalyze successive steps in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA • The active sites of all three enzymes are not far removed from one another, and the product of the first enzyme is passed directly to the ...
... • PDH complex is a noncovalent assembly of three different enzymes operating in concert to catalyze successive steps in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA • The active sites of all three enzymes are not far removed from one another, and the product of the first enzyme is passed directly to the ...
Utilization of dietary glucose in the metabolic syndrome
... water balance because of its osmotic properties [33], and increase the glycation (and consequent loss in function) of a number of proteins, especially those in contact with the bloodstream [34]. Thus, over a certain limit, excess glucose may be lost via urine. However, before these drastic measures ...
... water balance because of its osmotic properties [33], and increase the glycation (and consequent loss in function) of a number of proteins, especially those in contact with the bloodstream [34]. Thus, over a certain limit, excess glucose may be lost via urine. However, before these drastic measures ...
Part 5 Coenzyme-Dependent Enzyme Mechansims
... • PDH complex is a noncovalent assembly of three different enzymes operating in concert to catalyze successive steps in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA • The active sites of all three enzymes are not far removed from one another, and the product of the first enzyme is passed directly to the ...
... • PDH complex is a noncovalent assembly of three different enzymes operating in concert to catalyze successive steps in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA • The active sites of all three enzymes are not far removed from one another, and the product of the first enzyme is passed directly to the ...
Note - EtoosIndia
... Anaerobic respiration was first reported by Kostytchev. Anaerobic respiration may takes place in bacteria, some lower parasitic animals (Ascaris, Taenia) plants, R.BCs. & muscles of human body. When oxygen is not available, then food is incompletely oxidised in to some organic compounds like eth ...
... Anaerobic respiration was first reported by Kostytchev. Anaerobic respiration may takes place in bacteria, some lower parasitic animals (Ascaris, Taenia) plants, R.BCs. & muscles of human body. When oxygen is not available, then food is incompletely oxidised in to some organic compounds like eth ...
Carnitine Overview
... carries a molecule of cytosolic acylcarnitine within the mitochondrion exchanging it with one molecule of free carnitine present in the mitochondrion, that is transported in the cytosol. ...
... carries a molecule of cytosolic acylcarnitine within the mitochondrion exchanging it with one molecule of free carnitine present in the mitochondrion, that is transported in the cytosol. ...
Chapter 1 - Research Explorer
... acyl-CoAs (of various chain lengths) may affect the function of the 2-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, isocitrate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase and citrate synthase to varying degrees (Stumpf et al., 1985; Lai et al., 1991; Lai et al., 1994). However, the inhibition of these enzymes by iso ...
... acyl-CoAs (of various chain lengths) may affect the function of the 2-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, isocitrate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase and citrate synthase to varying degrees (Stumpf et al., 1985; Lai et al., 1991; Lai et al., 1994). However, the inhibition of these enzymes by iso ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.