![Covalently Bonded Platinum(II) Complexes of [alpha]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022412983_1-66c66ee18551a43164a79702fd995f95-300x300.png)
Covalently Bonded Platinum(II) Complexes of [alpha]
... are direct consequences of the steric and electronic environment around the observed nuclei, and different values are therefore usually obtained, depending on the R group attached to the organometallic site. Thus, peptide functionalization with these complexes provides a biomarker not only for bioch ...
... are direct consequences of the steric and electronic environment around the observed nuclei, and different values are therefore usually obtained, depending on the R group attached to the organometallic site. Thus, peptide functionalization with these complexes provides a biomarker not only for bioch ...
Increasing Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Flux as a Treatment
... decreased and pyruvate oxidation is impaired (16,17), resulting in a lack of metabolic flexibility in substrate selection, contributing to the overuse of fatty acids. Therefore, it follows that the restoration of PDH activity may re-establish a normal fuel balance, thereby restoring cardiac function. ...
... decreased and pyruvate oxidation is impaired (16,17), resulting in a lack of metabolic flexibility in substrate selection, contributing to the overuse of fatty acids. Therefore, it follows that the restoration of PDH activity may re-establish a normal fuel balance, thereby restoring cardiac function. ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... passing through channels in ATP synthase • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... passing through channels in ATP synthase • ATP synthase uses the exergonic flow of H+ to drive phosphorylation of ATP • This is an example of chemiosmosis, the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Principles of Metabolic Regulation
... stress of prolonged flight. The sprinting rabbit relies on breakdown of stored (liver) glycogen and anaerobic glycolysis for short-term production of ATP for muscle activity. The regulation of these two means of ATP production is very different. Under aerobic conditions (see answer to Problem 9), gl ...
... stress of prolonged flight. The sprinting rabbit relies on breakdown of stored (liver) glycogen and anaerobic glycolysis for short-term production of ATP for muscle activity. The regulation of these two means of ATP production is very different. Under aerobic conditions (see answer to Problem 9), gl ...
Mitochondrial Fatty Acid ß-Oxidation in the Human Eye and
... and developmental cataract. Treatment of LCHAD deficiency with a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet (7) seems to markedly improve the prognosis and may even slow progression of the pigmentary retinopathy. LCHAD is one of the three enzyme activities of the mitochondrial trifunctional protein (MTP) local ...
... and developmental cataract. Treatment of LCHAD deficiency with a low-fat, high-carbohydrate diet (7) seems to markedly improve the prognosis and may even slow progression of the pigmentary retinopathy. LCHAD is one of the three enzyme activities of the mitochondrial trifunctional protein (MTP) local ...
Adaptation to hypoxia alters energy metabolism in rat - AJP
... and aspartate-to glutamate concentration ratios in both ventricles of hypoxic rats than in corresponding tissues from controls, indicative of a decreased flux through the malateaspartate shuttle under conditions of O2 limitation. Myocardial glutamine levels were lower in hypoxic rats, and glutamine- ...
... and aspartate-to glutamate concentration ratios in both ventricles of hypoxic rats than in corresponding tissues from controls, indicative of a decreased flux through the malateaspartate shuttle under conditions of O2 limitation. Myocardial glutamine levels were lower in hypoxic rats, and glutamine- ...
Regulation of metabolism by dietary carbohydrates in two lines of
... acids, relatively low number of insulin receptors, lack of inhibition of endogenous glucose production and poor hepatic lipogenesis from glucose were proved to be true (Mommsen and Plisetskaya, 1991; Hemre and Kahrs, 1997; Navarro et al., 1999; Panserat et al., 2000b; Enes et al., 2009); reduced per ...
... acids, relatively low number of insulin receptors, lack of inhibition of endogenous glucose production and poor hepatic lipogenesis from glucose were proved to be true (Mommsen and Plisetskaya, 1991; Hemre and Kahrs, 1997; Navarro et al., 1999; Panserat et al., 2000b; Enes et al., 2009); reduced per ...
Amino Acids [PDF:247KB]
... food name, etc. of food listed to be consistent with the Food Composition Tables 2015, and new assignment of index numbers to foods. Additionally, from the viewpoint of ensuring convenience for the users with the increased number of foods listed, the component values calculated from the ratio of raw ...
... food name, etc. of food listed to be consistent with the Food Composition Tables 2015, and new assignment of index numbers to foods. Additionally, from the viewpoint of ensuring convenience for the users with the increased number of foods listed, the component values calculated from the ratio of raw ...
Redacted for Privacy
... Becker, Dr. Sonia Anderson, Dr. Daniel Arp and Dr. Thomas Savage. Dr. Savage, in particular, for guiding me through several editions of this work. His patience and standards are to be commended. I wish to thank both Dr. Becker and Dr. Anderson for introducing me into the study of proteins; and to Dr ...
... Becker, Dr. Sonia Anderson, Dr. Daniel Arp and Dr. Thomas Savage. Dr. Savage, in particular, for guiding me through several editions of this work. His patience and standards are to be commended. I wish to thank both Dr. Becker and Dr. Anderson for introducing me into the study of proteins; and to Dr ...
2 H
... • The citric acid cycle, also called the Krebs cycle, takes place within the mitochondrial matrix • The cycle oxidizes organic fuel derived from pyruvate, generating one ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 per turn ...
... • The citric acid cycle, also called the Krebs cycle, takes place within the mitochondrial matrix • The cycle oxidizes organic fuel derived from pyruvate, generating one ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 per turn ...
video slide
... • The citric acid cycle, also called the Krebs cycle, takes place within the mitochondrial matrix • The cycle oxidizes organic fuel derived from pyruvate, generating one ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 per turn ...
... • The citric acid cycle, also called the Krebs cycle, takes place within the mitochondrial matrix • The cycle oxidizes organic fuel derived from pyruvate, generating one ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 per turn ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e
... 56) When an organism such as a yeast lives by fermentation, it converts the pyruvate from glycolysis into a different compound, such as alcohol. Why doesn't it secrete the pyruvate directly? A) The conversion yields one ATP per pyruvate molecule. B) The conversion yields one NADH per pyruvate molecu ...
... 56) When an organism such as a yeast lives by fermentation, it converts the pyruvate from glycolysis into a different compound, such as alcohol. Why doesn't it secrete the pyruvate directly? A) The conversion yields one ATP per pyruvate molecule. B) The conversion yields one NADH per pyruvate molecu ...
Biology: Concepts and Connections, 6e (Campbell)
... 56) When an organism such as a yeast lives by fermentation, it converts the pyruvate from glycolysis into a different compound, such as alcohol. Why doesn't it secrete the pyruvate directly? A) The conversion yields one ATP per pyruvate molecule. B) The conversion yields one NADH per pyruvate molecu ...
... 56) When an organism such as a yeast lives by fermentation, it converts the pyruvate from glycolysis into a different compound, such as alcohol. Why doesn't it secrete the pyruvate directly? A) The conversion yields one ATP per pyruvate molecule. B) The conversion yields one NADH per pyruvate molecu ...
A Quaternion-Based Definition of Protein
... The Jmol Molecular Visualization Project • As the current principal developer and project manager of the Jmol molecular visualization project, I get requests periodically for new visualization ideas. ...
... The Jmol Molecular Visualization Project • As the current principal developer and project manager of the Jmol molecular visualization project, I get requests periodically for new visualization ideas. ...
Answers to Problems in Text - pdf
... than that of the atom from which it is derived. For anions, the nuclear charge is unchanged, but an added electron introduces new repulsions and the electron cloud swells because of the increased electron-to-electron repulsions. (b) Fact: The atomic radius of a cation is always smaller than that of ...
... than that of the atom from which it is derived. For anions, the nuclear charge is unchanged, but an added electron introduces new repulsions and the electron cloud swells because of the increased electron-to-electron repulsions. (b) Fact: The atomic radius of a cation is always smaller than that of ...
Full Text - Harvard University
... (mmol/mL)/22.5 (10) and insulin resistance defined as the top quartile of HOMA-IR from the entire FHS Offspring cohort free of diabetes at the fifth examination cycle. Although individuals were not selected based on insulin resistance status, the sample was selected based on a high propensity for the ...
... (mmol/mL)/22.5 (10) and insulin resistance defined as the top quartile of HOMA-IR from the entire FHS Offspring cohort free of diabetes at the fifth examination cycle. Although individuals were not selected based on insulin resistance status, the sample was selected based on a high propensity for the ...
Document
... • Energy exists in different forms but is neither created nor destroyed; it simply converts to another form. ...
... • Energy exists in different forms but is neither created nor destroyed; it simply converts to another form. ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
LipidMetabolism
... Desaturase adds a cis-double bond; if the FA already has unsaturations, the new one is added three carbons closer to the carboxyl Elongases condense FA with malonyl CoA; ...
... Desaturase adds a cis-double bond; if the FA already has unsaturations, the new one is added three carbons closer to the carboxyl Elongases condense FA with malonyl CoA; ...
Gluconeogenesis Glycogen metabolism
... The liver is the organ that serves as a supplier of glucose for the whole body (having glycogen as a reservoir of glucose), and the liver therefore responds to changes in the blood glucose level by degrading or synthesizing glycogen, as required. The response is mediated mostly by hormones – by the ...
... The liver is the organ that serves as a supplier of glucose for the whole body (having glycogen as a reservoir of glucose), and the liver therefore responds to changes in the blood glucose level by degrading or synthesizing glycogen, as required. The response is mediated mostly by hormones – by the ...
Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
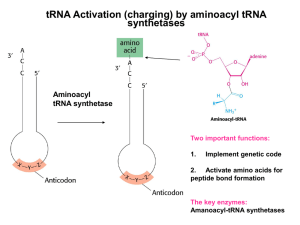
... charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correct tRNAs via by interacting with specific regions of tR ...
... charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correct tRNAs via by interacting with specific regions of tR ...
Lec 16: Nitrogen (ammonia) assimilation
... adenylylated. Once the adenylylation occurs, active site is inactived. This enzyme is 12‐mer (i.e. 12 GlnA polypeptide forms the function enzyme). Similar to cumulative feedback inhibition above, partial adenylylation inhibits the enzyme partially. ...
... adenylylated. Once the adenylylation occurs, active site is inactived. This enzyme is 12‐mer (i.e. 12 GlnA polypeptide forms the function enzyme). Similar to cumulative feedback inhibition above, partial adenylylation inhibits the enzyme partially. ...
Engineering Cytosolic Acetyl-CoA Metabolism in Saccharomyces
... cell factories such that the raw material, typically sugars, can be efficiently converted to the product of interest. Although IMI076 could grow on glucose, it was still inefficient at conversion of pyruvate to cytosolic acetyl-CoA. To increase cytosolic acetyl-CoA supply from pyruvate, pyruvate for ...
... cell factories such that the raw material, typically sugars, can be efficiently converted to the product of interest. Although IMI076 could grow on glucose, it was still inefficient at conversion of pyruvate to cytosolic acetyl-CoA. To increase cytosolic acetyl-CoA supply from pyruvate, pyruvate for ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... biological activity of proteins. Although amino acids can be classified in various ways, one common approach is to classify them according to whether the functional group on the side chain at neutral pH is nonpolar, polar but uncharged, negatively charged, or positively charged. The structures and n ...
... biological activity of proteins. Although amino acids can be classified in various ways, one common approach is to classify them according to whether the functional group on the side chain at neutral pH is nonpolar, polar but uncharged, negatively charged, or positively charged. The structures and n ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.







![Amino Acids [PDF:247KB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002278939_1-1b03d0bc0e7fdaaa14234846bba6ef6c-300x300.png)