The Emerging Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Insulin
... Despite the positive effects of BCAAs on metabolism, the strong association of BCAA levels with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome suggests that increased levels of BCAAs may cause insulin resistance and T2DM, although this remains a speculation for now. The mechanism underlying that correlat ...
... Despite the positive effects of BCAAs on metabolism, the strong association of BCAA levels with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome suggests that increased levels of BCAAs may cause insulin resistance and T2DM, although this remains a speculation for now. The mechanism underlying that correlat ...
Functional Anatomy of the Liver
... Glycogenolysis in muscle produces lactic acid as major product In Fed State: Liver serves as a reserve for glucose (Insulin Glucagon ) Used to synthesize glycogen Liver captures glucose from portal blood broken down to pyruvate Oxidized to H20 and CO2 (TCA Cycle) aerobic phase ...
... Glycogenolysis in muscle produces lactic acid as major product In Fed State: Liver serves as a reserve for glucose (Insulin Glucagon ) Used to synthesize glycogen Liver captures glucose from portal blood broken down to pyruvate Oxidized to H20 and CO2 (TCA Cycle) aerobic phase ...
MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
... • Ionic interactions between an enzyme-bound metal and a substrate help orient the substrate for reaction or stabilize charged reaction transition states. • Metals also mediate oxidation-reduction reactions by reversible changes in the metal ion’s oxidation state. • For example – in hemoglobin Fe in ...
... • Ionic interactions between an enzyme-bound metal and a substrate help orient the substrate for reaction or stabilize charged reaction transition states. • Metals also mediate oxidation-reduction reactions by reversible changes in the metal ion’s oxidation state. • For example – in hemoglobin Fe in ...
Cellular Respiration
... Begins by the addition of a two-carbon acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule (oxaloacetate), forming a six-carbon molecule (citric acid) NADH, FADH2 capture energy rich electrons ATP formed by substrate-level phosphorylation Turns twice for one glucose molecule. Produces 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 ...
... Begins by the addition of a two-carbon acetyl group to a four-carbon molecule (oxaloacetate), forming a six-carbon molecule (citric acid) NADH, FADH2 capture energy rich electrons ATP formed by substrate-level phosphorylation Turns twice for one glucose molecule. Produces 4 CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH and 2 ...
Acid-Base Equilibria - Riverside Local Schools
... example, a portion of Chapter 4 focused on their reactions. But what makes a substance behave as an acid or as a base? In this chapter we reexamine acids and bases, taking a closer look at how they are identified and characterized. In doing so, we will consider their behavior not only in terms of th ...
... example, a portion of Chapter 4 focused on their reactions. But what makes a substance behave as an acid or as a base? In this chapter we reexamine acids and bases, taking a closer look at how they are identified and characterized. In doing so, we will consider their behavior not only in terms of th ...
Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis
... molecule of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate with the formation of two ATP molecules anaerobic ...
... molecule of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate with the formation of two ATP molecules anaerobic ...
Free aromatic amino acids in egg yolk show antioxidant properties
... Eggs are considered as one of nature’s perfect foods that have been consumed for centuries all over the world. Although they contain all the necessary nutrients for a new life, consumption of eggs in many developed countries has declined due to the public perception on its high content of cholestero ...
... Eggs are considered as one of nature’s perfect foods that have been consumed for centuries all over the world. Although they contain all the necessary nutrients for a new life, consumption of eggs in many developed countries has declined due to the public perception on its high content of cholestero ...
A novel zinc-dependent D-serine dehydratase
... Several D-amino acids have been discovered in eukaryotes, including mammals, and they are reported to have various physiological functions. For example, D-aspartate has been found in the mammalian central nervous system and endocrine tissues and has been suggested to be involved in the regulation of ...
... Several D-amino acids have been discovered in eukaryotes, including mammals, and they are reported to have various physiological functions. For example, D-aspartate has been found in the mammalian central nervous system and endocrine tissues and has been suggested to be involved in the regulation of ...
L-Serine, D- and L-proline and alanine as respiratory substrates of
... 1995). These results suggested that glucose is not a preferred energy substrate of H. pylori. Candidates for the substrates of energy metabolism in this organism are thought to be organic acids such as pyruvate, D-lactate and succinate. Chang et al. (1995) reported that lower concentrations (25 mM) ...
... 1995). These results suggested that glucose is not a preferred energy substrate of H. pylori. Candidates for the substrates of energy metabolism in this organism are thought to be organic acids such as pyruvate, D-lactate and succinate. Chang et al. (1995) reported that lower concentrations (25 mM) ...
Dr. V. Main Powerpoint
... • The electron transport chain is in the cristae of the mitochondrion • Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chai ...
... • The electron transport chain is in the cristae of the mitochondrion • Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes • The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons • Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chai ...
Acetic acid - Colorado State University
... = 1 – 9兲, ACOOH+ 共VUV ionization兲 without IR radiation present, and A+ with both IR and VUV radiation present. The intense feature ACOOH+ arises from the cleavage of 共A兲2 at the -CC bond to generate ACOOH+ + CH3 following ionization. The vibrational spectrum of monomeric acetic acid 共2500– 7500 cm− ...
... = 1 – 9兲, ACOOH+ 共VUV ionization兲 without IR radiation present, and A+ with both IR and VUV radiation present. The intense feature ACOOH+ arises from the cleavage of 共A兲2 at the -CC bond to generate ACOOH+ + CH3 following ionization. The vibrational spectrum of monomeric acetic acid 共2500– 7500 cm− ...
The Plasma Membrane - Beck-Shop
... branched fatty acids may be in iso configuration with the methyl group at the second carbon from the end or anteiso configuration with the methyl group on the third carbon from the end. It is unclear why prokaryotes have this great diversity of fatty acids and why certain fatty acids are used by a giv ...
... branched fatty acids may be in iso configuration with the methyl group at the second carbon from the end or anteiso configuration with the methyl group on the third carbon from the end. It is unclear why prokaryotes have this great diversity of fatty acids and why certain fatty acids are used by a giv ...
Directed mutagenesis of the Trypanosoma cruzi trans
... features previously found in influenza neuraminidase and several bacterial sialidases (Vimr, 1994). In particular, the trypanosome proteins contain all the amino acid residues (or classes) which have been described to interact with sialic acid in the substrate binding pockets of Salmonella typhimuri ...
... features previously found in influenza neuraminidase and several bacterial sialidases (Vimr, 1994). In particular, the trypanosome proteins contain all the amino acid residues (or classes) which have been described to interact with sialic acid in the substrate binding pockets of Salmonella typhimuri ...
ADP
... *Yield one molecule of FADH2, three molecules of NADH+H+, two molecules of CO2, one molecule of GTP. ...
... *Yield one molecule of FADH2, three molecules of NADH+H+, two molecules of CO2, one molecule of GTP. ...
Chapter 19: Acids and Bases
... You now know that HCl and HF are acids because they can donate a hydrogen ion in an acid-base reaction. From their chemical formulas, you can see that each acid can donate only one hydrogen ion per molecule. An acid that can donate only one hydrogen ion is called a monoprotic acid. Other monoprotic ...
... You now know that HCl and HF are acids because they can donate a hydrogen ion in an acid-base reaction. From their chemical formulas, you can see that each acid can donate only one hydrogen ion per molecule. An acid that can donate only one hydrogen ion is called a monoprotic acid. Other monoprotic ...
Additional file 1
... dephosphlylating phosphatidic acid Carboxylation of Acetyl CoA to Malonyl CoA Condensation of a malonyl-ACP with an acyl acceptor catalyzes the addition of molecular oxygen to polyunsaturated fatty acids to produce an ...
... dephosphlylating phosphatidic acid Carboxylation of Acetyl CoA to Malonyl CoA Condensation of a malonyl-ACP with an acyl acceptor catalyzes the addition of molecular oxygen to polyunsaturated fatty acids to produce an ...
슬라이드 1
... • Dynamic buffer of lactate in which its concentration remains relatively constant both in the tissues and in the blood stream • Lactate can be used by tissues whenever required for oxidation but also for anabolic purposes • Lactate is converted to pyruvate, which is a precursor for acetyl-CoA, whic ...
... • Dynamic buffer of lactate in which its concentration remains relatively constant both in the tissues and in the blood stream • Lactate can be used by tissues whenever required for oxidation but also for anabolic purposes • Lactate is converted to pyruvate, which is a precursor for acetyl-CoA, whic ...
representation and display of non-standard peptides using semi
... • Worse, once beyond the commonly encountered amino acids, biochemists disagree on the meaning of 3-letter codes… 247th ACS National Meeting, Dallas, TX, Wednesday 19th March 2014 ...
... • Worse, once beyond the commonly encountered amino acids, biochemists disagree on the meaning of 3-letter codes… 247th ACS National Meeting, Dallas, TX, Wednesday 19th March 2014 ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism
... molecules, two NADH molecules are synthesized during this step. Each 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate is subsequently dephosphorylated (i.e., a phosphate is removed) by phosphoglycerate kinase into 3-phosphoglycerate. Each phosphate released in this reaction can convert one molecule of ADP into one high-ener ...
... molecules, two NADH molecules are synthesized during this step. Each 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate is subsequently dephosphorylated (i.e., a phosphate is removed) by phosphoglycerate kinase into 3-phosphoglycerate. Each phosphate released in this reaction can convert one molecule of ADP into one high-ener ...
FEMS Microbiology Ecology 28:
... proton extrusion associated with ammonium assimilation [12], or by organic acid production [13]. Therefore, P solubilizing microorganisms can be ...
... proton extrusion associated with ammonium assimilation [12], or by organic acid production [13]. Therefore, P solubilizing microorganisms can be ...
Gly - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Glucose is a main metabolic fuel in most organisms. Other sugars convert to glycolytic intermediates. •Fructose metabolism is faster than glucose in blood. •Hexokinase can phosphorylate fructose: Fructose + ATP Fructose 6-P + ADP Km for fructose >> Km for glucose, thus important only if [frucose] ...
... Glucose is a main metabolic fuel in most organisms. Other sugars convert to glycolytic intermediates. •Fructose metabolism is faster than glucose in blood. •Hexokinase can phosphorylate fructose: Fructose + ATP Fructose 6-P + ADP Km for fructose >> Km for glucose, thus important only if [frucose] ...
BIOCHEMISTRY Carbohydrate Metabolism
... • Step 3 – Phosphofructokinase (an allosteric enzyme) is inhibited by high levels of ATP & Citrate & is activated by high levels of ADP. • Step 10 – Pyruvate kinase (an allosteric enzyme) is inhibited by high levels of ATP & Acetyl CoA. ...
... • Step 3 – Phosphofructokinase (an allosteric enzyme) is inhibited by high levels of ATP & Citrate & is activated by high levels of ADP. • Step 10 – Pyruvate kinase (an allosteric enzyme) is inhibited by high levels of ATP & Acetyl CoA. ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... Vitamin D Vitamin D (D3) • is synthesized in skin exposed to sunlight. • regulates the absorption of phosphorus and calcium during bone growth. • deficiency can result in weakened bones. • sources include cod liver oil, egg yolk, and enriched milk. ...
... Vitamin D Vitamin D (D3) • is synthesized in skin exposed to sunlight. • regulates the absorption of phosphorus and calcium during bone growth. • deficiency can result in weakened bones. • sources include cod liver oil, egg yolk, and enriched milk. ...
Gluconeogenesis
... Mn++ is thought to promote Pi transfer by interacting simultaneously with the enolate oxygen atom and an oxygen atom of the terminal phosphate of GTP or ATP. ...
... Mn++ is thought to promote Pi transfer by interacting simultaneously with the enolate oxygen atom and an oxygen atom of the terminal phosphate of GTP or ATP. ...
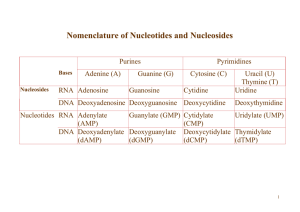
Nomenclature of Nucleotides and Nucleosides
... a. Base. The pyrimidine ring, unlike the purine ring, is not built on a molecule of PRPP. Instead, the pyrimidine ring is formed, and then it reacts with PRPP to form the nucleotide. b. The precursors of the ring are glutamine, aspartate, and CO2. 2. The formation of uridine 5'-monophosphate (uridyl ...
... a. Base. The pyrimidine ring, unlike the purine ring, is not built on a molecule of PRPP. Instead, the pyrimidine ring is formed, and then it reacts with PRPP to form the nucleotide. b. The precursors of the ring are glutamine, aspartate, and CO2. 2. The formation of uridine 5'-monophosphate (uridyl ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.